Large-Size Envelope Encryption and Decryption
Envelope encryption is a high-performance encryption and decryption solution for massive data. A one-time DEK, which is randomly generated locally, is used to encrypt and decrypt massive data in seconds. The DEK is immediately encrypted by the CMK and stored on the disk. You can call the KMS API to decrypt the DEK ciphertext into plaintext and store the plaintext in the memory. The encryption and decryption performance is close to that of the local AES. The key is securely managed in the KMS.
Encryption Solutions
|
Item |
Sensitive Information Encryption |
Envelope Encryption |
|---|---|---|
|
Key |
CMK |
CMK and DEK |
|
Performance |
Symmetric encryption, remote calling |
Remote symmetric encryption for small-size data and local symmetric encryption for large-size data |
|
Scenario |
Keys, certificates, and small-size data, which are applicable to scenarios where the calling frequency is low. |
Large-size data, which is applicable to scenarios where high performance is required. |
|
Cloud API calling |
Cloud APIs are called each time encryption or decryption is performed. |
An API is called once after the process is started to decrypt the DEK ciphertext. |
Encryption and Decryption Principles
- Large-size data encryption
Figure 1 Encrypting a local file
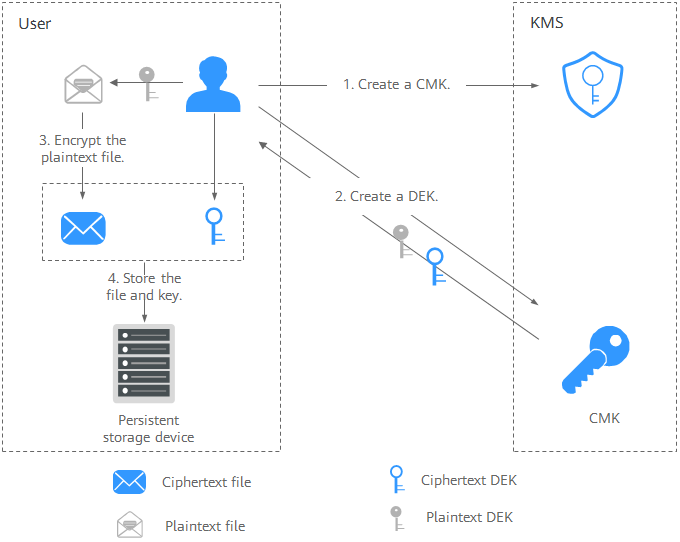
The process is as follows:
- Create a CMK on KMS.
- Call the create-datakey API of KMS to create a DEK. Then you get a plaintext DEK and a ciphertext DEK. The ciphertext DEK is generated when you use a CMK to encrypt the plaintext DEK.
- Use the plaintext DEK to encrypt the file. A ciphertext file is generated.
- Save the ciphertext DEK and the ciphertext file together in a persistent storage device or a storage service.
- Large-size data decryption
Figure 2 Decrypting a local file
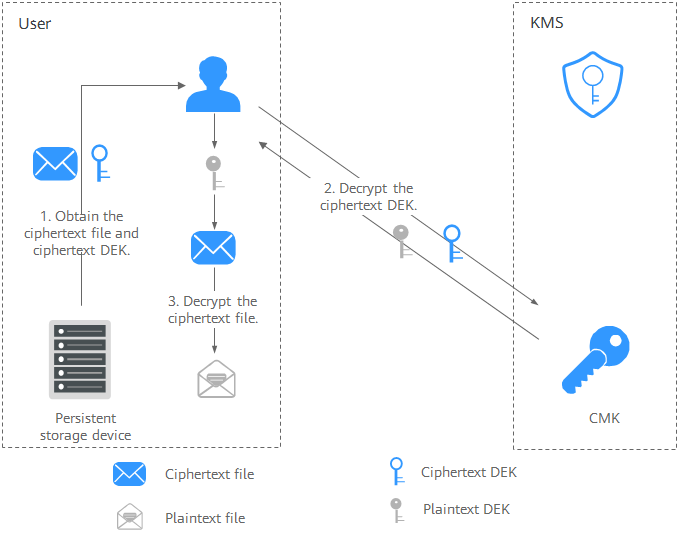 The process is as follows:
The process is as follows:- Obtain the ciphertext DEK and file from the persistent storage device or the storage service.
- Call the decrypt-datakey API of KMS and use the corresponding CMK (the one used for encrypting the DEK) to decrypt the ciphertext DEK. Then you get the plaintext DEK.
If the CMK is deleted, the decryption fails. Therefore, properly keep your CMKs.
- Use the plaintext DEK to decrypt the ciphertext file.
APIs Related to Envelope Encryption
You can use the APIs listed in the following table to encrypt and decrypt data.
|
API |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Create a DEK. |
|
|
Encrypt a DEK with the specified master key. |
|
|
Decrypt a DEK with the specified master key. |
Procedure
- Create a CMK on the management console. For details, see Creating a Custom Key.
- Prepare basic authentication information.
- ACCESS_KEY: Access key of the Huawei account
- SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: Secret access key of the Huawei account
- PROJECT_ID: project ID of a Huawei Cloud site. For details, see Obtaining Account, IAM User, Group, Project, Region, and Agency Information.
- KMS_ENDPOINT: endpoint for accessing KMS. For details, see Endpoints.
- There will be security risks if the AK/SK used for authentication is directly written into code. Encrypt the AK/SK in the configuration file or environment variables for storage.
- In this example, the AK/SK stored in the environment variables are used for identity authentication. Configure the environment variables HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK and HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK in the local environment first.
- Encrypt and decrypt local files.
Go code example
package main import ( "crypto/aes" "crypto/cipher" "crypto/sha256" "encoding/hex" "io" "io/ioutil" "log" "math/rand" "os" "time" "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/core/auth/basic" "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/core/config" "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/core/region" kms "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/services/kms/v2" kmsModel "github.com/huaweicloud/huaweicloud-sdk-go-v3/services/kms/v2/model" ) const ( AadData = "Demo for aad" ) // There will be security risks if the AK/SK used for authentication is directly written into code. Encrypt the AK/SK in the configuration file or environment variables for storage. // In this example, the AK and SK are stored in environment variables. Before running this example, set environment variables HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK and HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK. var ak = os.Getenv("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK") var sk = os.Getenv("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK") var iamEndpoint = "https://<IAM_ENDPOINT>" var endpoint = "<ENDPOINT>" var regionID = "<REGION_ID>" func main() { // CMK ID keyId := "xxxxxxxx-xxx-xxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx3" // 1. Prepare the authentication information. auth := basic.NewCredentialsBuilder(). WithAk(ak). WithSk(sk). WithIamEndpointOverride(iamEndpoint). Build() httpConfig := config.DefaultHttpConfig() httpConfig.WithIgnoreSSLVerification(true) // 2. Initialize the SDK and import the authentication information and KMS device information. client := kms.NewKmsClient( kms.KmsClientBuilder(). WithRegion(region.NewRegion(regionID, endpoint)). WithHttpConfig(httpConfig). WithCredential(auth). Build()) // 3. Create a DEK. aesDataKeyLength := "256" createDataKeyRequest := kmsModel.CreateDatakeyRequest{ Body: &kmsModel.CreateDatakeyRequestBody{KeyId: keyId, DatakeyLength: &aesDataKeyLength}, } createDataKeyResponse, err := client.CreateDatakey(&createDataKeyRequest) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Create data key occur error.") } // Read the file to be encrypted and store it after GCM encryption. readData, err := FileReader("FirstPlainFile.jpg") if err != nil { log.Fatal("Read file occur error.") return } nonce := GenRandomBytes(12) cryptData, err := GcmCrypt(readData, *createDataKeyResponse.PlainText, nonce, 0) err = FileWriter(cryptData, "SecondEncryptFile.jpg") if err != nil { log.Fatal("Write encrypt file occur error.") return } // 4. Decrypt the DEK. decryptDataKeyRequest := kmsModel.DecryptDatakeyRequest{ Body: &kmsModel.DecryptDatakeyRequestBody{KeyId: keyId, CipherText: *createDataKeyResponse.CipherText, DatakeyCipherLength: "32"}, } decryptDataKeyResponse, err := client.DecryptDatakey(&decryptDataKeyRequest) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Decrypt data key occur error.") } // 5. Read the encrypted file, and use the decrypted DEK for GCM decryption and storage. readData, err = FileReader("SecondEncryptFile.jpg") if err != nil { log.Fatal("Read file occur error.") return } decryptData, err := GcmCrypt(readData, *decryptDataKeyResponse.DataKey, nonce, 1) err = FileWriter(decryptData, "ThirdDecryptFile.jpg") if err != nil { log.Fatal("Write encrypt file occur error.") return } // 6. For example, check whether the digest of the source file is the same as that of the encrypted and decrypted file. log.Printf("result is %t", FileSha256("FirstPlainFile.jpg") == FileSha256("ThirdDecryptFile.jpg")) } // GcmCrypt AES-GCM encryption and decryption data stream // data: file to be encrypted or decrypted // plainKey: plaintext key // nonce: initialized vector // mode: 0 indicates encryption and 1 indicates decryption. func GcmCrypt(data []byte, plainKey string, nonce []byte, mode int) ([]byte, error) { plainKeyByte, err := hex.DecodeString(plainKey) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Invalid aes key.") return nil, err } block, err := aes.NewCipher(plainKeyByte) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Invalid init aes.") return nil, err } gcm, err := cipher.NewGCM(block) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Invalid init gcm.") return nil, err } if mode == 0 { return gcm.Seal(nil, nonce, data, []byte(AadData)), nil } else { return gcm.Open(nil, nonce, data, []byte(AadData)) } } func FileReader(path string) ([]byte, error) { file, err := ioutil.ReadFile(path) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Read file failed.") return nil, err } return file, nil } func FileWriter(data []byte, path string) error { err := ioutil.WriteFile(path, data, 0600) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Write file failed.") return err } return nil } func GenRandomBytes(size int) (randomBytes []byte) { rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano()) randomBytes = make([]byte, size) _, err := rand.Read(randomBytes) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Read data failed.") return } return randomBytes } func FileSha256(filePath string) string { file, err := os.Open(filePath) if err != nil { return "" } defer file.Close() hash := sha256.New() _, err = io.Copy(hash, file) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Sha256 file data failed.") return "" } return hex.EncodeToString(hash.Sum(nil)) }
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





