Binding and Unbinding Load Balancers for a DWS Cluster
Overview
If the private IP address or EIP of a CN is used to connect to a cluster, the failure of this CN will lead to cluster connection failure. If a private domain name is used for connection, the DNS service randomly selects a private IP address or EIP for each client. This cannot balance loads or avoid single-CN failures. ELB is used to solve these problems.
An ELB distributes access traffic to multiple ECSs for traffic control based on forwarding policies. It improves the fault tolerance capability of application programs. For details, see the Elastic Load Balance User Guide.
With ELB health checks, CN requests of a cluster can be quickly forwarded to normal CNs. If a CN is faulty, the workload can be immediately shifted to a healthy node, minimizing cluster access faults.
- This feature is supported only in cluster version 8.1.1.200 or later.
- To ensure load balancing and high availability and prevent service interruption, ensure created clusters are to an ELB.
- ELB does not support cross-database access.
Constraints and Limitations
- To bind a load balancer to a DWS cluster, ensure that the load balancer is in the same region, VPC, and enterprise project as the cluster.
- Only dedicated load balancers can be bound to DWS.

Load balancing is not supported in regions where the dedicated load balancer is not available. You can check whether dedicated load balancers are supported on the ELB console.
- The ELB to be associated must use TCP and has a private IP address.
- When creating an ELB instance, determine its specifications based on your service access traffic. You are advised to select the maximum specifications. On the DWS console, you can bind to a load balancer but cannot change its specifications.
- You only need to create a load balancer if you want to use ELB. DWS automatically creates the ELB listeners and backend server groups required.
- When creating a load balancer, ensure that the listeners do not use the same port as the database. Otherwise, ELB cannot be associated.
- When you bind a load balancer to a cluster, the ROUND_ROBIN policy is set by default. In addition, the health check interval is set to 10 seconds, the timeout duration is set to 50 seconds, and the number of maximum retries is set to 3. Exercise caution when you modify these ELB parameters.
- When you unbind a load balancer from a cluster, related cluster information is cleared on DWS but the load balancer is not deleted.
- If you need to access the ELB cluster using a public IP address or domain name, bind an EIP or domain name on the ELB management console.
- If the cluster is an IPv4 cluster, only IPv4 ELBs can be bound. If the cluster is an IPv6 dual-stack cluster, only IPv6 dual-stack ELBs can be bound.
Associating ELB
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters. All clusters are displayed by default.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The Cluster Information page is displayed.
- On the Basic Information page that is displayed, click Associate ELB and select the ELB name. If no load balancer exists, create one on the ELB management console. Then refresh the DWS page and associate ELB with the cluster.
- After the request is delivered, go back to the Clusters page. Task information Associating ELB of the cluster is displayed. The process takes some time.
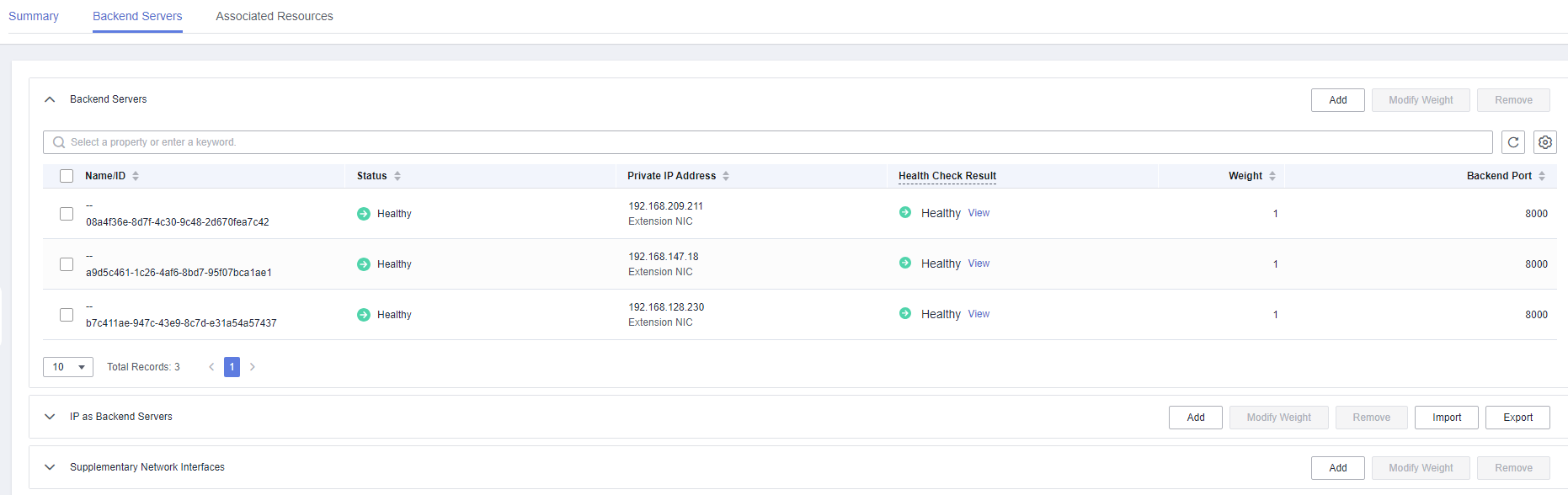
- Log in to the ELB management console, choose Elastic Load Balance > Load Balancers, click the name of the bound load balancer, switch to the Backend Server Groups tab, and check whether the cluster CNs are associated with the load balancer.
- In the Basic Information area of the Cluster Information page, check the ELB Address, which is used for connecting to the cluster.
Disassociating ELB
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters. All clusters are displayed by default.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The Cluster Information page is displayed.
- On the Basic Information page that is displayed, click Disassociate ELB.
- After the request is delivered, go back to the Clusters page. Task information Dissociating ELB of the cluster is displayed. The process takes some time.
- Log in to the ELB management console, click the name of the dissociated ELB, switch to the Backend Server Groups tab, and check whether the cluster CNs are deleted.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





