Halaman ini belum tersedia dalam bahasa lokal Anda. Kami berusaha keras untuk menambahkan lebih banyak versi bahasa. Terima kasih atas dukungan Anda.
- What's New
- Function Overview
- Product Bulletin
- Technology Poster
- Service Overview
- Billing
- Getting Started
-
User Guide
- Using IAM to Grant Access to HSS
- Accessing HSS
- Checking the Dashboard
- Asset Management
- Risk Management
- Server Protection
-
Container Protection
-
Container Firewalls
- Container Firewall Overview
- Configuring a Network Defense Policy (for a Cluster Using the Container Tunnel Network Model)
- Configuring a Network Defense Policy (for a Cluster Using the VPC Tunnel Network Model)
- Configuring a Network Defense Policy (for a Cluster Using the Cloud Native Network 2.0 Model)
- Container Cluster Protection
-
Container Firewalls
- Detection and Response
- Security Operations
- Installation and Configuration on Servers
- Installation and Configuration on Containers
- Account Management
- Plug-in Settings
- Authorization
- Monitoring and Auditing
- Enterprise Project Management
-
Best Practices
- HSS Best Practices You May Need
-
Suggestions on How to Fix Official Disclosed Vulnerabilities Provided by HSS
- Git Credential Disclosure Vulnerability (CVE-2020-5260)
- SaltStack Remote Command Execution Vulnerabilities (CVE-2020-11651 and CVE-2020-11652)
- OpenSSL High-risk Vulnerability (CVE-2020-1967)
- Adobe Font Manager Library Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2020-1020/CVE-2020-0938)
- Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability (CVE-2020-1027)
- Windows CryptoAPI Spoofing Vulnerability (CVE-2020-0601)
- Third-Party Servers Accessing HSS Through a Direct Connect and Proxy Servers
- Connecting Third-Party Servers to HSS Through Direct Connect and VPC Endpoint
- Installing the HSS Agent Using CBH
- Using HSS to Improve Server Login Security
- Using HSS and CBR to Defend Against Ransomware
- Using HSS to Scan and Fix Vulnerabilities
- Using HSS to Prevent Weak Passwords
- Using HSS to Scan for Trojans
- Using HSS to Handle Mining Attacks
- Using HSS to Monitor the Integrity of Linux Server Files
- Whitelist Can Be Used to Avoid False Alarm Reporting
-
API Reference
- Before You Start
- Calling APIs
-
API Description
-
Asset Management
- Collecting Asset Statistics, Including Accounts, Ports, and Processes
- Querying the Account List
- Querying Open Port Statistics
- Querying the Process List
- Querying the Software List
- Querying Automatic Startup Item Information
- Querying the Server List of an Account
- Querying the Open Port List of a Single Server
- Querying the Server List of the Software
- Querying the Service List of Auto-Started Items
- Obtaining the Account Change History
- Obtaining the Historical Change Records of Software Information
- Obtaining the Historical Change Records of Auto-started Items
- Asset Fingerprints - Process - Server List
- Asset Fingerprints - Port - Server List
- Querying the Middleware List
- Querying the Server List of a Specified Middleware
-
Ransomware Prevention
- Querying the Servers Protected Against Ransomware
- Querying the Protection Policy List of Ransomware
- Modifying Ransomware Protection Policies
- Enabling Ransomware Prevention
- Disabling Ransomware Prevention
- Querying the Backup Policy Bound to HSS Protection Vault
- Modifying the Backup Policy Bound to Vault
-
Baseline Management
- Querying the Weak Password Detection Result List
- Querying the Password Complexity Policy Detection Report
- Querying the Result List of Server Security Configuration Check
- Querying the Check Result of a Security Configuration Item
- Querying the Checklist of a Security Configuration Item
- Querying the List of Affected Servers of a Security Configuration Item
- Querying the Report of a Check Item in a Security Configuration Check
- Ignoring, Unignoring, Repairing, or Verifying the Failed Configuration Check Items
- Quota Management
- Container Management
- Event Management
- Intrusion Detection
- Server Management
-
Container Image
- Querying the Image List in the SWR Image Repository
- Scanning Images in the Image Repository in Batches
- Querying the Local Image List
- Querying Image Vulnerability Information
- CVE Information Corresponding to the Vulnerability
- Synchronizing the Image List from SWR
- Querying the List of Image Security Configuration Detection Results
- Querying the Check Item List of a Specified Security Configuration Item of an Image
- Querying the Mirror Configuration Check Report
- Policy Management
-
Vulnerability Management
- Querying the Vulnerability List
- Exporting Information About Vulnerabilities and Their Affected Servers
- Querying the Servers Affected by a Vulnerability
- Changing the Status of a Vulnerability
- Querying Vulnerability Information About a Server
- Creating a Vulnerability Scan Task
- Querying a Vulnerability Scan Policy
- Modifying a Vulnerability Scan Policy
- Querying the Vulnerability Scan Tasks
- Querying the List of Servers Corresponding to a Vulnerability Scan Task
- Querying Vulnerability Management Statistics
- Web Tamper Protection
- Tag Management
- Cluster Management
- Installation and Configuration
-
Asset Management
- Appendixes
- SDK Reference
-
FAQs
-
About HSS
- What Is Host Security?
- What Is Container Security?
- What Is Web Tamper Protection?
- What Are the Relationships Between Images, Containers, and Applications?
- How Do I Use HSS?
- Can HSS Protect Local IDC Servers?
- Is HSS in Conflict with Any Other Security Software?
- What Are the Differences Between HSS and WAF?
- Can HSS Be Used Across Accounts?
- What Is the HSS Agent?
- Can HSS Be Used Across Clouds?
- Does HSS Support Version Upgrade?
- Can HSS Automatically Detect and Remove Viruses?
-
Agent
- Do I Need to Install the HSS Agent After Purchasing HSS?
- Is the Agent in Conflict with Any Other Security Software?
- How Do I Uninstall the Agent?
- What Should I Do If Agent Installation Failed?
- How Do I Fix an Abnormal Agent?
- What Is the Default Agent Installation Path?
- How Many CPU and Memory Resources Are Occupied by the Agent When It Performs Scans?
- Do Different HSS Editions Share the Same Agent?
- How Do I View Servers Where No Agents Have Been Installed?
- How Do I Upgrade the Agent?
- What Do I Do If the HSS Upgrade Fails?
- What Resources Will Be Accessed by the Agent After It Is Installed on a Server?
- How Do I Use Images to Install Agents in Batches?
- What Do I Do If I Cannot Access the Download Link of the Windows Or Linux Agent?
- What Do I Do If Agent Upgrade Fails and the Message "File replacement failed" Is Displayed?
- What Can I Do If Agents Failed to Be Installed in Batches and a Message Is Displayed Indicating that the Network Is Disconnected?
- How Do I Verify the Connection Between My Server and the HSS Server?
- Protection
-
Vulnerability Management
- How Do I Fix Vulnerabilities?
- What Do I Do If an Alarm Still Exists After I Fixed a Vulnerability?
- Why a Server Displayed in Vulnerability Information Does Not Exist?
- Do I Need to Restart a Server After Its Vulnerabilities Are Fixed?
- Can I Check the Vulnerability and Baseline Fix History on HSS?
- What Do I Do If Vulnerability Fix Failed?
- Why Can't I Select a Server During Manual Vulnerability Scanning or Batch Vulnerability Fixing?
- What Do I Do If a Vulnerability Scan Failed?
- Do I Need to Subscribe to Ubuntu Pro to Fix Ubuntu Vulnerabilities?
-
Detection & Response
- How Do I View and Handle HSS Alarm Notifications?
- What Do I Do If My Servers Are Subjected to a Mining Attack?
- Why a Process Is Still Isolated After It Was Whitelisted?
- Why an Attack Is Not Detected by HSS?
- Can I Unblock an IP Address Blocked by HSS, and How?
- Why a Blocked IP Address Is Automatically Unblocked?
- How Often Is Malware Scan and Removal?
- How Often Are the HSS Virus Database and Vulnerability Database Updated?
- What Do I Do If an IP Address Is Blocked by HSS?
- How Do I Defend Against Ransomware Attacks?
- Why Can't I Receive Alarms After the HSS Is Upgraded?
- How Do I Add High-risk Command Execution Alarms to the Whitelist?
- Why Doesn't HSS Generate Alarms for Some Web Shell Files?
- Abnormal Logins
-
Brute-force Attack Defense
- How Does HSS Intercept Brute Force Attacks?
- How Do I Handle a Brute-force Attack Alarm?
- How Do I Defend Against Brute-force Attacks?
- How Do I Unblock an IP Address?
- What Do I Do If HSS Frequently Reports Brute-force Alarms?
- What Do I Do If a Huawei Cloud IP Address Trigger a Brute-force Attack Alarm?
- What Do I Do If the Port in Brute-force Attack Records Is Not Updated?
-
Baseline Inspection
- Why Are Weak Password Alarms Generated After the Weak Password Detection Policy Is Disabled?
- How Do I Install a PAM and Set a Proper Password Complexity Policy in a Linux OS?
- How Do I Set a Proper Password Complexity Policy in a Windows OS?
- How Do I Handle Unsafe Configurations?
- How Do I View Configuration Check Reports?
- How Do I Handle a Weak Password Alarm?
- How Do I Set a Secure Password?
-
Web Tamper Protection
- Why Do I Need to Add a Protected Directory?
- How Do I Modify a Protected Directory?
- What Should I Do If WTP Cannot Be Enabled?
- How Do I Modify a File After WTP Is Enabled?
- What Can I Do If I Enabled Dynamic WTP But Its Status Is Enabled but not in effect?
- What Are the Differences Between the Web Tamper Protection Functions of HSS and WAF?
-
Container Security
- How Do I Disable Node Protection?
- How Do I Switch from CGS to HSS?
- How Do I Enable Node Protection?
- How Do I Enable the API Server Audit for an On-Premises Kubernetes Container?
- What Do I Do If the Container Cluster Protection Plug-in Fails to Be Uninstalled?
- What Do I Do If the Cluster Connection Component (ANP-Agent) Failed to Be Deployed?
- What Do I Do If Cluster Permissions Are Abnormal?
- Failed to Upload the Image to the Private Image Repository
- What Do I Do If I Failed to Enable Protection for a CCE Cluster?
- Ransomware Prevention
- Region and AZ
-
Security Configurations
- How Do I Clear the SSH Login IP Address Whitelist Configured in HSS?
- What Can I Do If I Cannot Remotely Log In to a Server via SSH?
- How Do I Use 2FA?
- What Do I Do If I Cannot Enable 2FA?
- Why Can't I Receive a Verification Code After 2FA Is Enabled?
- Why Does My Login Fail After I Enable 2FA?
- How Do I Add a Mobile Number or Email Address for 2FA?
- Do I Use a Fixed Verification Code for 2FA?
- Will I Be Billed for Alarm Notifications and SMS?
- How Do I Modify Alarm Notification Recipients?
- Why No Topics Are Available for Me to Choose When I Configure Alarm Notifications?
- Can I Disable HSS Alarm Notifications?
- How Do I Modify Alarm Notification Items?
- How Do I Disable the SELinux Firewall?
-
Protection Quota
- How Do I Extend the Validity Period of HSS Quotas?
- How Do I Filter Unprotected Servers?
- Why Can't I Find the Servers I Purchased on the Console?
- What Do I Do If My Quotas Are Insufficient and I Failed to Enable Protection?
- How Do I Allocate My Quota?
- If I Change the OS of a Protected Server, Does It Affect My HSS Quota?
- Why Doesn't an HSS Edition Take Effect After Purchase?
- How Do I Change the Protection Quota Edition Bound to a Server?
- Can I Bind a Server to an HSS Quota If They Are in Different Enterprise Projects?
- Billing, Renewal, and Unsubscription
-
Others
- How Do I Use the Windows Remote Desktop Connection Tool to Connect to a Windows Server?
- How Do I Check HSS Log Files?
- How Do I Enable Logging for Login Failures?
- How Do I Clear an Alarm on Critical File Changes?
- Why Can't I View All Projects in the Enterprise Project Drop-down List?
- How Do I Enable or Disable HSS Self-protection?
- What Do I Do If Windows Self-Protection Cannot Be Disabled?
- Why Is a Deleted ECS Still Displayed in the HSS Server List?
-
About HSS
- Videos
-
More Documents
-
User Guide (Ankara Region)
- Introduction
- Enabling HSS
- Server Security Dashboard
- Asset Management
- Risk Prevention
- Prevention
- Intrusion Detection
- Security Operations
- Security Report
- Installation & Configuration
- Permissions Management
-
FAQs
-
About HSS
- What Is HSS?
- What Is Container Security Service?
- What Is Web Tamper Protection?
- What Are the Relationships Between Images, Containers, and Applications?
- How Do I Use HSS?
- Can HSS Protect Local IDC Servers?
- Is HSS in Conflict with Any Other Security Software?
- What Are the Differences Between HSS and WAF?
- What Is the HSS Agent?
-
Agent FAQs
- Is the Agent in Conflict with Any Other Security Software?
- How Do I Install the Agent?
- How Do I Uninstall the Agent?
- What Should I Do If Agent Installation Failed?
- How Do I Fix an Abnormal Agent?
- What Is the Default Agent Installation Path?
- How Many CPU and Memory Resources Are Occupied by the Agent When It Performs Scans?
- Do WTP and HSS Use the Same Agent?
- How Do I View Servers Where No Agents Have Been Installed?
-
Brute-force Attack Defense
- How Does HSS Intercept Brute Force Attacks?
- How Do I Handle a Brute-force Attack Alarm?
- How Do I Defend Against Brute-force Attacks?
- How Do I Do If the Account Cracking Prevention Function Does Not Take Effect on Some Linux Accounts?
- How Do I Unblock an IP Address?
- What Do I Do If HSS Frequently Reports Brute-force Alarms?
- What Do I Do If My Remote Server Port Is Not Updated in Brute-force Attack Records?
- Weak Passwords and Unsafe Accounts
-
Intrusions
- What Do I Do If My Servers Are Subjected to a Mining Attack?
- Why a Process Is Still Isolated After It Was Whitelisted?
- What Do I Do If a Mining Process Is Detected on a Server?
- Why Some Attacks on Servers Are Not Detected?
- Can I Unblock an IP Address Blocked by HSS, and How?
- Why a Blocked IP Address Is Automatically Unblocked?
- How Often Does HSS Detect, Isolate, and Kill Malicious Programs?
- What Do I Do If an IP Address Is Blocked by HSS?
- How Do I Defend Against Ransomware Attacks?
- Abnormal Logins
- Unsafe Settings
- Vulnerability Management
-
Web Tamper Protection
- Why Do I Need to Add a Protected Directory?
- How Do I Modify a Protected Directory?
- What Should I Do If WTP Cannot Be Enabled?
- How Do I Modify a File After WTP Is Enabled?
- What Can I Do If I Enabled Dynamic WTP But Its Status Is Enabled but not in effect?
- What Are the Differences Between the Web Tamper Protection Functions of HSS and WAF?
- Container Guard Service
- Ransomware Protection
-
Security Configurations
- How Do I Clear the SSH Login IP Address Whitelist Configured in HSS?
- What Can I Do If I Cannot Remotely Log In to a Server via SSH?
- How Do I Use 2FA?
- What Do I Do If I Cannot Enable 2FA?
- Why Can't I Receive a Verification Code After 2FA Is Enabled?
- Why Does My Login Fail After I Enable 2FA?
- How Do I Add a Mobile Phone Number or Email Address for Receiving 2FA Verification Notifications?
- If I Choose to Use Verification Code for 2FA, How Do I Get the Code?
- How Do I Disable the SELinux Firewall?
- Quotas
-
Others
- How Do I Use the Windows Remote Desktop Connection Tool to Connect to a Server?
- How Do I Check HSS Log Files?
- How Do I Enable Logging for Login Failures?
- How Do I Clear an Alarm on Critical File Changes?
- Is HSS Available as Offline Software?
- How Do I Enable HSS Self-Protection?
- What Do I Do If HSS Self-Protection Cannot Be Disabled?
-
About HSS
- Change History
-
User Guide (ME-Abu Dhabi Region)
- Introduction
- Enabling HSS
- Server Security Dashboard
- Asset Management
- Risk Prevention
-
Prevention
- Application Protection
- WTP
- Ransomware Prevention
- File Integrity Monitoring
-
Container Firewalls
- Container Firewall Overview
- Creating a Policy (for a Cluster Using the Container Tunnel Network Model)
- Creating a Policy (for a Cluster Using the VPC Network Model)
- Managing Policies (for a Cluster Using the Container Tunnel Network Model)
- Managing Policies (for a Cluster Using the VPC Network Model)
- Intrusion Detection
- Security Operations
- Security Report
- Installation & Configuration
- Audit
- Permissions Management
- Manually Upgrading HSS
-
FAQs
- About HSS
-
Agent FAQs
- Is the Agent in Conflict with Any Other Security Software?
- How Do I Uninstall the Agent?
- What Should I Do If Agent Installation Failed?
- How Do I Fix an Abnormal Agent?
- What Is the Default Agent Installation Path?
- How Many CPU and Memory Resources Are Occupied by the Agent When It Performs Scans?
- Do WTP and HSS Use the Same Agent?
- How Do I View Servers Where No Agents Have Been Installed?
- What Can I Do If the Agent Status Is Still "Not installed" After Installation?
- What Do I Do If the HSS Upgrade Fails?
-
Brute-force Attack Defense
- How Does HSS Intercept Brute Force Attacks?
- How Do I Handle a Brute-force Attack Alarm?
- How Do I Defend Against Brute-force Attacks?
- What Do I Do If the Account Cracking Prevention Function Does Not Take Effect on Some Accounts for Linux Servers?
- How Do I Unblock an IP Address?
- What Do I Do If HSS Frequently Reports Brute-force Alarms?
- What Do I Do If My Remote Server Port Is Not Updated in Brute-force Attack Records?
- Weak Passwords and Unsafe Accounts
-
Intrusions
- What Do I Do If My Servers Are Subjected to a Mining Attack?
- Why a Process Is Still Isolated After It Was Whitelisted?
- What Do I Do If a Mining Process Is Detected on a Server?
- Why Some Attacks on Servers Are Not Detected?
- Can I Unblock an IP Address Blocked by HSS, and How?
- Why a Blocked IP Address Is Automatically Unblocked?
- How Often Does HSS Detect, Isolate, and Kill Malicious Programs?
- What Do I Do If an IP Address Is Blocked by HSS?
- How Do I Defend Against Ransomware Attacks?
- Abnormal Logins
- Unsafe Settings
- Vulnerability Management
-
Web Tamper Protection
- Why Do I Need to Add a Protected Directory?
- How Do I Modify a Protected Directory?
- What Should I Do If WTP Cannot Be Enabled?
- How Do I Modify a File After WTP Is Enabled?
- What Can I Do If I Enabled Dynamic WTP But Its Status Is Enabled but not in effect?
- What Are the Differences Between the Web Tamper Protection Functions of HSS and WAF?
- Container Guard Service
-
Security Configurations
- What Can I Do If I Cannot Remotely Log In to a Server via SSH?
- How Do I Use 2FA?
- Why Can't I Receive a Verification Code After 2FA Is Enabled?
- Why Does My Login Fail After I Enable 2FA?
- How Do I Add a Mobile Phone Number or Email Address for Receiving 2FA Verification Notifications?
- How Do I Disable the SELinux Firewall?
- Others
- Change History
-
User Guide (Paris)
- Introduction
- Enabling HSS
- Server Security Dashboard
-
Asset Management
- Asset Management
- Server Fingerprints
- Container Fingerprints
- Server Management
- Container Management
- Risk Prevention
-
Prevention
- WTP
- Ransomware Prevention
- File Integrity Monitoring
-
Container Firewalls
- Container Firewall Overview
- Creating a Policy (for a Cluster Using the Container Tunnel Network Model)
- Creating a Policy (for a Cluster Using the VPC Network Model)
- Managing Policies (for a Cluster Using the Container Tunnel Network Model)
- Managing Policies (for a Cluster Using the VPC Network Model)
- Intrusion Detection
- Security Operations
- Security Report
- Installation & Configuration
- Audit
- Permissions Management
- Manually Upgrading HSS
-
FAQs
- About HSS
-
Agent FAQs
- Is the Agent in Conflict with Any Other Security Software?
- How Do I Uninstall the Agent?
- What Should I Do If Agent Installation Failed?
- How Do I Fix an Abnormal Agent?
- What Is the Default Agent Installation Path?
- How Many CPU and Memory Resources Are Occupied by the Agent When It Performs Scans?
- Do WTP and HSS Use the Same Agent?
- How Do I View Servers Where No Agents Have Been Installed?
- What Can I Do If the Agent Status Is Still "Not installed" After Installation?
- What Addresses Do ECSs Access After the Agent Is Installed?
-
Brute-force Attack Defense
- How Does HSS Intercept Brute Force Attacks?
- How Do I Handle a Brute-force Attack Alarm?
- How Do I Defend Against Brute-force Attacks?
- What Do I Do If the Account Cracking Prevention Function Does Not Take Effect on Some Accounts for Linux Servers?
- How Do I Unblock an IP Address?
- What Do I Do If HSS Frequently Reports Brute-force Alarms?
- What Do I Do If My Remote Server Port Is Not Updated in Brute-force Attack Records?
- Weak Passwords and Unsafe Accounts
-
Intrusions
- What Do I Do If My Servers Are Subjected to a Mining Attack?
- Why a Process Is Still Isolated After It Was Whitelisted?
- What Do I Do If a Mining Process Is Detected on a Server?
- Why Some Attacks on Servers Are Not Detected?
- Can I Unblock an IP Address Blocked by HSS, and How?
- Why a Blocked IP Address Is Automatically Unblocked?
- How Often Does HSS Detect, Isolate, and Kill Malicious Programs?
- What Do I Do If an IP Address Is Blocked by HSS?
- How Do I Defend Against Ransomware Attacks?
- Abnormal Logins
- Unsafe Settings
-
Vulnerability Management
- How Do I Fix Vulnerabilities?
- What Do I Do If an Alarm Still Exists After I Fixed a Vulnerability?
- Why a Server Displayed in Vulnerability Information Does Not Exist?
- Do I Need to Restart a Server After Fixing its Vulnerabilities?
- Can I Check the Vulnerability and Baseline Fix History on HSS?
- What Do I Do If Vulnerability Fix Failed?
- Why Can't I Select a Server During Manual Vulnerability Scanning or Batch Vulnerability Fixing?
-
Web Tamper Protection
- Why Do I Need to Add a Protected Directory?
- How Do I Modify a Protected Directory?
- What Should I Do If WTP Cannot Be Enabled?
- How Do I Modify a File After WTP Is Enabled?
- What Can I Do If I Enabled Dynamic WTP But Its Status Is Enabled but not in effect?
- What Are the Differences Between the Web Tamper Protection Functions of HSS and WAF?
- Container Guard Service
-
Security Configurations
- How Do I Clear the SSH Login IP Address Whitelist Configured in HSS?
- What Can I Do If I Cannot Remotely Log In to a Server via SSH?
- How Do I Use 2FA?
- What Do I Do If I Cannot Enable 2FA?
- Why Can't I Receive a Verification Code After 2FA Is Enabled?
- Why Does My Login Fail After I Enable 2FA?
- How Do I Add a Mobile Phone Number or Email Address for Receiving 2FA Verification Notifications?
- If I Choose to Use Verification Code for 2FA, How Do I Get the Code?
- How Do I Modify Alarm Notification Recipients?
- Why No Topics Are Available for Me to Choose When I Configure Alarm Notifications?
- Can I Disable HSS Alarm Notifications?
- How Do I Modify Alarm Notification Items?
- How Do I Disable the SELinux Firewall?
-
Others
- How Do I Use the Windows Remote Desktop Connection Tool to Connect to a Server?
- How Do I Check HSS Log Files?
- How Do I Enable Logging for Login Failures?
- How Do I Clear an Alarm on Critical File Changes?
- Is HSS Available as Offline Software?
- Why Is a Deleted ECS Still Displayed in the HSS Server List?
- Change History
-
User Guide (Ankara Region)
- General Reference
Copied.
Adding a Protected Directory
WTP monitors website directories in real time, backs up files, and restores tampered files using the backup, protecting websites from Trojans, illegal links, and tampering.
Constraints and Limitations
- Only the servers that are protected by the HSS WTP edition support the operations described in this section.
- The constraints on protected directories are as follows:
- For Linux,
- A server can have up to 50 protected directories.
- The complete path of a protected directory cannot exceed 256 characters.
- The folder levels of a protected directory cannot exceed 100.
- The total folders in protected directories cannot exceed 900,000.
- For Windows,
- A server can have up to 50 protected directories.
- The complete path of a protected directory cannot exceed 256 characters.
- For Linux,
- The constraints on local backup paths are as follows:
- Local backup is supported only in Linux.
- The local backup path must be valid, or web tamper protection will not take effect.
- The local backup path cannot overlap with the added protected directory.
- The available capacity of the disk where the local backup path is located is greater than the size of all protected directories.
Adding a Protected Directory
- Log in to the management console.
- In the upper left corner of the page, select a region, click
 , and choose Security & Compliance > HSS.
, and choose Security & Compliance > HSS. - Choose Server Protection > Web Tamper Protection. Click Configure Protection in the Operation column.
NOTE:
If your servers are managed by enterprise projects, you can select an enterprise project to view or operate the asset and scan information.
Figure 1 Entering the page of protection settings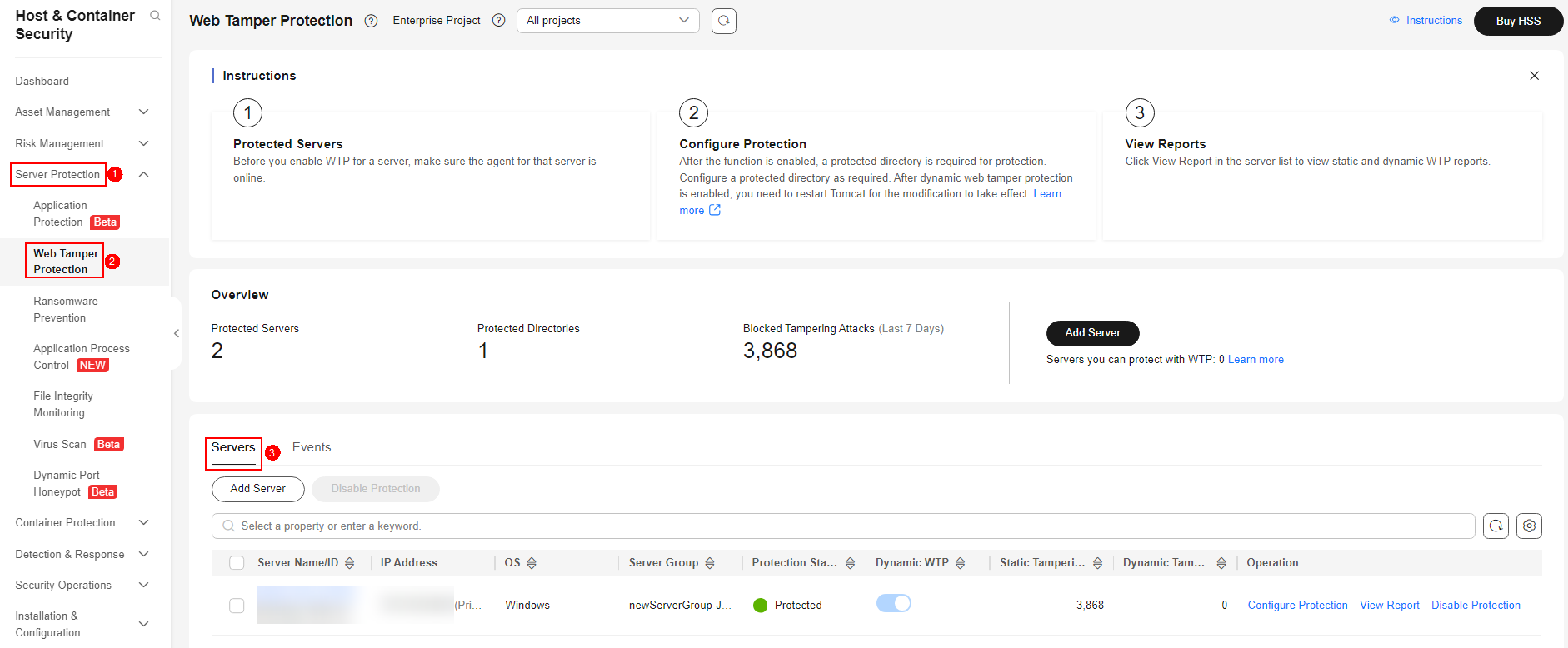
- Click Settings under Protected Directory Settings.
Figure 2 Page for setting a protected directory

- You can add a maximum of 50 protected directories.
- Click Add. In the Add Protected Directory dialog box, set required parameters. For details, see Table 1.
Figure 3 Adding a protected directory

Table 1 Parameters for adding a protected directory Parameter
Description
Example Value
Protected Directory
Directory to be protected.
- Only one protected directory can be added. The directory length cannot exceed 256 characters.
- Do not add an OS directory as a protected directory.
- After a directory is added, the files and folders in the protected directory are read-only and cannot be modified directly.
- Linux: /etc/lesuo
- Windows: d:\web
Excluded Subdirectory
Subdirectories that do not need to be protected in the protected directory, such as temporary file directories.
A maximum of 10 subdirectories can be added. Separate multiple subdirectories with semicolons (;). Each subdirectory can contain a maximum of 256 characters.
- Linux: lesuo/test
- Windows: web\test
Excluded File Types
Types of files that do not need to be protected in the protected directory, such as log files.
- The file type can contain only letters and numbers. A maximum of 10 file types can be added. Each file type can contain a maximum of 10 characters. Multiple file types are separated by semicolons (;).
- To record the running status of the server in real time, exclude the log files in the protected directory. You can grant high read and write permissions for log files to prevent attackers from viewing or tampering with the log files.
log;pid;text
Local Backup Path
Set this parameter if your server runs the Linux OS.
Set a local backup path for files in protected directories. After WTP is enabled, files in the protected directory are automatically backed up to the local backup path.
The backup rules are described as follows:
- The local backup path must be valid and cannot overlap with the protected directory path.
- Excluded subdirectories and types of files are not backed up.
- Generally, the backup completes within 10 minutes. The actual duration depends on the size of files in the protected directory.
- If WTP detects that a file in a protected directory is tampered with, it immediately uses the backup file on the local server to restore the file.
/etc/backup
Excluded File Path
Set this parameter if your server runs the Linux OS.
Files that do not need to be protected in the protected directory.
A maximum of 50 paths can be added. Separate multiple paths with semicolons (;). Each path can contain a maximum of 256 characters.
lesuo/data;lesuo/list
- Click OK.
If you need to modify files in the protected directory, stop protection for the protected directory first. After the files are modified, resume protection for the directory in a timely manner.
- Click Add. In the Add Protected Directory dialog box, set required parameters. For details, see Table 1.
- Enable remote backup.
By default, HSS backs up the files from the protected directories (excluding specified subdirectories and file types) to the local backup directory you specified when adding protected directories. To protect the local backup files from tampering, you must enable the remote backup function.
For details about how to add a remote backup server, see Configuring Remote Backup.
- On the Protected Directory Settings page, click Enable Remote Backup.
Figure 4 Enabling remote backup

- Select a backup server from the drop-down list box.
- Click OK.
- On the Protected Directory Settings page, click Enable Remote Backup.
Related Operations
- Export a protected directory: If you have configured a large number of protected directories, you can click
 on the protected directory configuration page to export the configurations of all protected directories to your local PC.
on the protected directory configuration page to export the configurations of all protected directories to your local PC. - Suspend protection: You can suspend WTP for a directory if needed. It is recommended that you resume WTP in a timely manner to prevent the files in the directory from being tampered with.
- Edit a protected directory: You can modify the added protected directory as needed.
- Delete a protected directory: You can delete the directories that do not need to be protected.
 NOTICE:
NOTICE:
- After you suspend protection for a protected directory, delete it, or modify its path, files in the directory will no longer be protected. Before performing these operations, ensure you have taken other measures to protect the files.
- After you suspend protection for a protected directory, delete it, or modify its path, if you find your files missing in the directory, search for them in the local or remote backup path.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot



