Managing Real-Time Sessions
Scenarios
GaussDB allows you to view all real-time component-level sessions of an instance and kill specified sessions. You can also identify table names in SQL text using table definition query or query the table definition based on the table name, schema name, and database name.
Constraints
- Table definition query is available for instances whose DB engine version is V2.0-3.208.0 or later and kernel version is 503.1.0.SPC1200 or later. This function is only available for authorized users. To apply for the permissions needed, submit a service ticket.
- For details about how to query the version, see Checking the DB Engine and Kernel Engine Version of a GaussDB Instance.
- The system limits queries to return up to 200 real-time session records, ensuring requests do not time out from excessive data.
- If the normalized SQL ID is 0 or the user is a system user, SQL throttling tasks cannot be created.
- For distributed instances, memory information is only available when querying sessions of a single CN or DN. This is unavailable when querying sessions by all CNs, all session statuses, or CN drill-down sessions.
Viewing Real-Time Sessions
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose .
in the upper left corner of the page and choose . - On the Instances page, click the name of the target instance to go to the Basic Information page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Session Management to view real-time session information. In the search box, select the database, client IP address, username, or other filters to search for session data.
Table 1 Metrics for real-time sessions Metric
Description
Normalized SQL ID
If the normalized SQL ID is 0, SQL patches and SQL throttling tasks cannot be created.
Waiting
If the session is currently waiting for a lock, the value is true. Otherwise, the value is false.
Blocked Session ID
ID of the session that is blocking the current session from obtaining a lock.
Wait Event
Event that the current thread is waiting for.
Status
Overall state of the session. Enumerated values:
- active: The backend is executing a query.
- idle: The backend is waiting for a new client command.
- idle in transaction: The backend is in a transaction, but there is no statement being executed in the transaction.
- fastpath function call: The backend is executing a fast-path function.
- disabled: This state is displayed if track_activities is disabled in the backend.
- Select one or more sessions and click Kill Selected Sessions. In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
You can also click Kill Session in the Operation column of a specified session to kill it.
- Click Kill All Idle Sessions. In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
- You can click Configure Auto Killing to enable or disable automatic transaction killing and configure automatic killing rules for long transactions and large transactions.
Figure 1 Long transactions
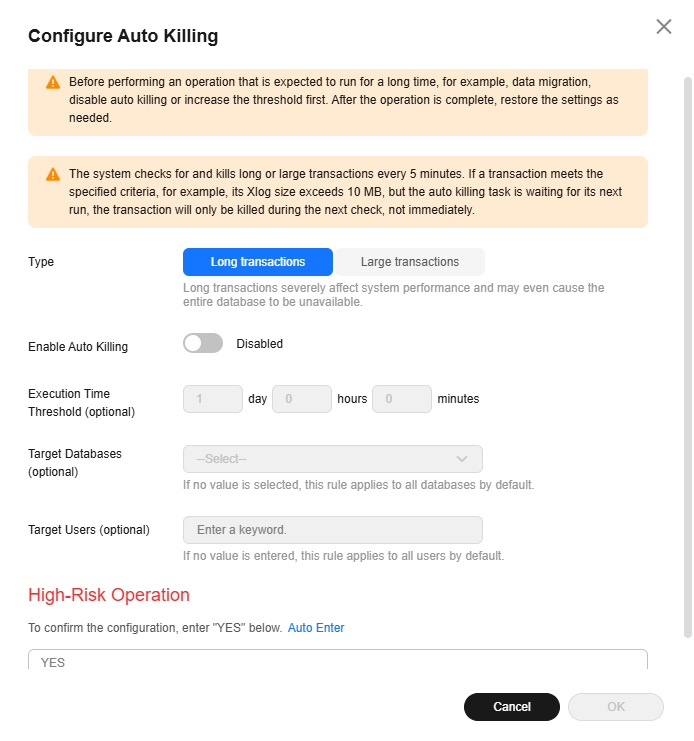 Figure 2 Large Transactions
Figure 2 Large Transactions
- Select the sessions for which you want to control their concurrency, and click Create SQL Throttling Task to limit the concurrency of the normalized SQL IDs involved in the selected sessions.
You can also click SQL Throttling in the Operation column of a specified session to limit the concurrency of the specified normalized SQL ID. For details about how to create a SQL throttling task, see Configuring SQL Throttling Rules.
- For a distributed instance, you can select All CNs or All session statuses from the drop-down list of the node filter. If you select All CNs, the sessions of all CNs are displayed. If you select All session statuses, the session thread statuses of all CNs and DNs are displayed.
Figure 3 All CNs/All session statuses

- An idle session is a session in the idle state. Sessions in the idle in transactions or active state are not regarded as idle sessions.
- Only sessions whose client IP addresses are not empty are displayed in the session list.
- Normalized SQL IDs cannot be queried for instances of V2.0-1.4 or earlier, so the normalized SQL ID column for such instances is empty.
- Real-time session statistics are only available for nodes with CNs or DNs (primary or standby DNs) deployed.
Creating a SQL Patch
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose .
in the upper left corner of the page and choose . - On the Instances page, click the name of the target instance to go to the Basic Information page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Session Management to view real-time session information.

If the normalized SQL ID is 0, SQL patches cannot be created.
- Locate a target SQL statement, click More, and click SQL Patch in the Operation column to go to the SQL Patch Details page.
- If no SQL patch is created, enter the patch name, and click OK.
Figure 4 SQL patch
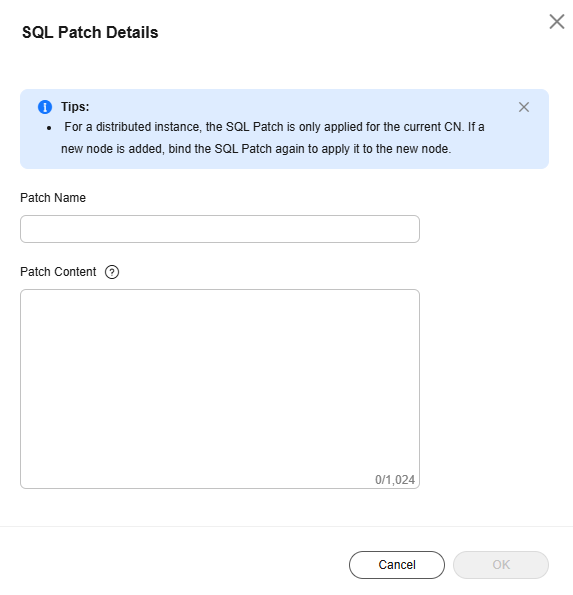
- If a SQL patch has been created, the SQL patch information is displayed.
Figure 5 Viewing SQL patch details
- Status: Click
 to enable or disable the SQL patch. If a SQL patch is disabled, the status is Disabled. If it is enabled, the status is Available.
to enable or disable the SQL patch. If a SQL patch is disabled, the status is Disabled. If it is enabled, the status is Available. - To delete a SQL patch, click Delete.
- Status: Click
- If no SQL patch is created, enter the patch name, and click OK.
Querying Table Definitions
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose .
in the upper left corner of the page and choose . - On the Instances page, click the name of the target instance to go to the Basic Information page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Session Management to view real-time session information.
- Click Table Definition in the Operation column. On the Table Definition page, view information in the Detected Tables area.
If no table is detected, click Add Table and enter a table name manually. If any detection result is incorrect, click Edit to modify, and then save the result.
- Click
 next to a table name to view its table definition.
Figure 6 Table Definition
next to a table name to view its table definition.
Figure 6 Table Definition
- Click the SQL statement in the table definition to view the definition details.
Figure 7 Table definition details

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





