Changing the Node Specifications and Storage Type of an Elasticsearch Cluster
If the workloads on an Elasticsearch cluster's data plane change, you can scale the cluster vertically by changing its node specifications or node storage type.
|
Change Type |
Scenario |
Change Process |
|---|---|---|
|
Changing node specifications |
Typically, you increase node specifications instead of decreasing them. Common scenarios include:
Alternatively, you may also decrease node specifications, but doing so will decrease the cluster's data processing and storage capacities. Exercise caution. |
The node specifications are changed one node at a time. This is to ensure that there are sufficient resources to keep services running. |
|
Changing the node storage type (disk type) |
Change the node storage type if disk I/O has become a performance bottleneck, which impacts query and write performance. |
The nodes are changed one at a time to prevent service interruptions. |
Impact on Billing
For a pay-per-use cluster, you can see its new price when confirming the node specifications or storage type change on the console. After the change is complete, the cluster will be billed based on the new price. For details, see Cloud Search Service Price Calculator.
For a yearly/monthly cluster, you can also see the new price when you confirm the change. In the case of an upgrade, a new order is triggered when you confirm the change; and in the case of a downgrade, a refund request is triggered when you do so.
Constraints
- The node specifications and storage type cannot be changed for nodes that use local disks.
- The node specifications and storage type cannot be changed at the same time.
- The node storage type can be changed only for data nodes and cold data nodes.
- When you change the node storage type, data needs to be migrated between different nodes. The timeout for data migration per node is 48 hours. Upgrade will fail if this timeout expires. When the cluster has large quantities of data, you are advised to manually adjust the data migration rate and avoid performing the migration during peak hours.
- For a cluster without master nodes, the node specifications and node storage type can be changed only if the number of data nodes plus cold data nodes is at least three.
- For a cluster with master nodes, this operation is allowed only if the cluster has at least two data nodes.
- During a node storage type change, there is always one node that is unavailable. To ensure service continuity, make sure the total number of data nodes and cold data nodes is greater than the maximum number of index replicas plus 1. For a single-AZ or dual-AZ cluster, also make sure there are at least two nodes of each type for the cluster in each of its AZs.
- During a node specifications change, nodes are brought offline in order to make the changes. To ensure service continuity, make sure all shards have replicas.
- Make sure the disk usage is always less than 80% during the change.
Change Impact
Before changing a cluster's node specifications or storage type, it is essential to assess the potential impacts and review operational recommendations. This enables proper scheduling of the change, minimizing service interruptions.
- Performance impact (only when the node storage type is changed)
Changing the node storage type does not interrupt services. However, data migration that occurs during this process consumes I/O performance, and taking individual nodes offline still has some impact on the overall cluster performance.
To minimize this impact, it is advisable to adjust the data migration rate based on the cluster's traffic cycle: increase the data migration rate during off-peak hours to shorten the task duration, and decrease it before peak hours arrive to ensure optimal cluster performance. The data migration rate is determined by the indices.recovery.max_bytes_per_sec parameter. The default value of this parameter is the number of vCPUs multiplied by 8 MB. For example, for four vCPUs, the data migration rate is 32 MB. You can adjust it based on the service requirements.PUT /_cluster/settings { "transient": { "indices.recovery.max_bytes_per_sec": "128MB" } } - Impact on request handling
Taking nodes offline one at a time usually does not interrupt services. However, requests sent to offline nodes may fail. To mitigate this impact, the following measures may be taken:
- Use a VPC endpoint or a dedicated load balancer to handle access requests to your cluster, which makes sure that requests are automatically routed to available nodes.
- Enable an exponential backoff & retry mechanism on the client (configure three retries).
- Perform this operation during off-peak hours.
- Impact on index replicas
Shards that have no replicas will become unavailable when the nodes that store them are taken offline, causing service interruptions. You are advised to add replicas for all important indexes before making the change described in this topic.
- Impact on Kibana and Cerebro
Changing the node storage type for a cluster will cause Kibana and Cerebro to be rebuilt. During this period, Kibana and Cerebro are temporarily unavailable. During a node specifications change, if Kibana and Cerebro become unavailable because the node that runs them is taken offline, refresh the web page or try to log in again, and the system will reschedule Kibana and Cerebro to an available node.
- Characteristics of this process
Once started, a change task cannot be stopped until it succeeds or fails. A change task failure only impacts a single node, and does not interrupt services if there are data replicas, but the failed node still needs to be restored promptly.
If a change of the node specifications or storage type is urgently needed, submit a service ticket to contact technical support and perform a pre-change evaluation and the necessary checks.
Change Durations
- The following formulas can be used to estimate how long the node specifications change will take:
Change duration (min) = 10 (min) x Total number of nodes to change + Data recovery duration (min)
where,- 10 minutes indicates how long non-data recovery operations (e.g., initialization) typically take per node. It is an empirical value.
- The total number of nodes is the sum of the number of data nodes, master nodes, client nodes, and cold data nodes in the cluster.
Data recovery duration (min) = Total data size (MB)/[Total number of vCPUs of the data nodes x 8 (MB/s) x 60 (s)]
where,- 8 MB/s indicates that each vCPU can process 8 MB of data per second. It is an empirical value.
- The formulas above use estimates under ideal conditions. The actual data recovery speed depends on cluster load.
- The following formulas can be used to estimate how long the node storage type change will take:
Change duration (min) = 15 (min) x Total number of nodes to change + Data migration duration (min)
where,- 15 minutes indicates how long non-data migration operations (e.g., initialization) typically take per node. It is an empirical value.
- The total number of nodes is the sum of the number of data nodes, master nodes, client nodes, and cold data nodes in the cluster.
Data migration duration (min) = Total data size (MB)/[Total number of vCPUs of the data nodes x 8 (MB/s) x 60 (s)]
where,- 8 MB/s indicates that each vCPU can process 8 MB of data per second. It is an empirical value.
- The formulas above use estimates under ideal conditions. The actual migration speed depends on cluster load.
Prerequisites
- The cluster status is Available, and there are no ongoing tasks.
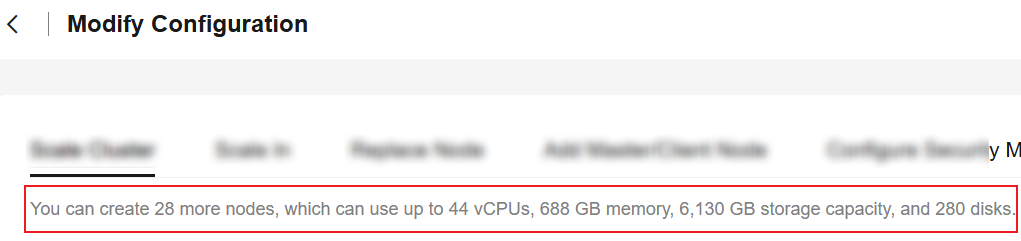
- Your CSS resource quotas are sufficient for the capacity expansion you are about to perform. You can check available resources on the Modify Configuration page.
Figure 1 Checking available resources
- All mission-critical data has been backed up before a node storage type change. This is to prevent data loss. For details, see Creating Snapshots to Back Up the Data of an Elasticsearch Cluster.
Changing the Node Specifications and Storage Type
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > Elasticsearch.
- Check that all service data has replicas so that services will not be interrupted during the change.
- In the displayed cluster list, find the target cluster, and click Access Kibana in the Operation column to log in to the Kibana console.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Dev Tools.
- Run the GET _cat/indices?v command in Kibana.
- If the returned rep value is greater than 0, data replicas exist. Go to the next step.
- If the returned rep value is 0, there are no data replicas. You are advised to manually create a snapshot for the cluster before moving on to the next step. For details, see Creating Snapshots to Back Up the Data of an Elasticsearch Cluster.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and choose More > Modify Configuration in the Operation column. The Modify Configuration page is displayed.
- Click the Scale Cluster tab.
- Click Change specifications to set parameters.
Table 2 Changing the node specifications and storage type Parameter
Description
Action
Select Change specifications.
Resources
Shows the change of resources for this operation.
Nodes
Configure the changes you want to make.
- Select a node type in the Node Type column.
- Select a new flavor in the Node Specifications column, or select a new storage type in the Node Storage column.
The node specifications and storage type cannot be changed at the same time.
Figure 2 Changing node specifications
- Click Next.
- Confirm the information and click Submit.
- In the displayed dialog box, confirm check items, and click OK to start the specifications change.
- Check items for node specifications change: Verify index copies & nodes and Cluster status check.
- Check items for node storage type change: Check cluster load.
Table 3 Check item description Item
Description
Verify index replicas & nodes
- Verifying the existence of index replicas helps improve data security. You can skip this step, but the absence of index replicas may impact data reliability during a node specifications change.
- Verifying data nodes ensures the cluster has enough capacity to handle requests. Skipping this check risks service interruptions when changing node specifications. Proceed with caution.
Verification rules:
- If you select Verify index copies & nodes and the cluster has no master nodes, each index is required to have at least one replica and the cluster must have at least three data nodes plus cold data nodes.
- If you select Verify index copies & nodes and the cluster has a master node, each index is required to have at least one replica, but there is no requirement on how many nodes the cluster must have.
Cluster status check
During a node specifications change, the cluster status is checked by default to improve the success rate and ensure data security. The nodes are changed one at a time. For each node, the system changes its specifications, restarts it, and checks that all its processes are started successfully before moving on to the next node.
In emergencies (for example, when a cluster is overloaded and services are faulty, which may prevent a specifications change request from being delivered), you can skip cluster status check so that more resources can be made available for cluster recovery. However, doing so may cause the cluster to become faulty and interrupt services. Exercise caution.
Check cluster load
During a node storage type change, data migration between nodes and the stopping and restarting of nodes will consume cluster resources, causing the cluster load to increase. A cluster load check can identify possible overload risks for a cluster and reduce the likelihood of an overload condition causing the node storage type change to fail.
The cluster load check items are as follows:
- nodes.thread_pool.search.queue < 1000: Check that the maximum number of requests in the search queue is less than 1000.
- nodes.thread_pool.write.queue < 200: Check that the maximum number of requests in the write queue is less than 200.
- nodes.process.cpu.percent < 90: Check that the maximum CPU usage is less than 90%.
- nodes.os.cpu.load_average/Number of vCPUs < 80%: Check that the number of running processes plus the number of processes waiting for CPUs is less than 80% of the total number of vCPUs.
If the change request fails to be submitted and a message is displayed indicating that the cluster needs to be upgraded, it means the current cluster version does not support a node storage type change. Upgrade the cluster to the latest image version and then try again. For a detailed upgrade guide, see Upgrading the Version of an Elasticsearch Cluster.
- Click Back to Cluster List to go back to the Clusters page. The Cluster Status is Configuration modified. When Cluster Status changes to Available, the cluster node specifications have been successfully changed.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





