kagent Add-on
kagent is an open-source programming framework designed for DevOps and platform engineers. It introduces powerful AI agent functions to Kubernetes clusters, automates O&M tasks, troubleshoots faults, and optimizes workflows in cloud native environments, helping teams solve complex technical challenges more efficiently. It provides:
- Automated O&M: AI agents automatically handle common faults (such as pod breakdown and network policy conflicts), reducing manual intervention.
- Knowledge accumulation: Team experience is converted into reusable diagnosis processes and policies to avoid repeated work.
- Collaboration platform: A custom agent development framework is provided to support sharable O&M solutions for scenarios such as ingresses and CRDs, accelerating problem handling.
Deep integration with kagent capabilities enables CCE standard and Turbo clusters to provide the out-of-the-box kagent add-on and one-click deployment of the production-grade AI O&M agent framework, achieving intelligent cluster management.
Basic Concepts
|
Concept |
Description |
Functions |
|---|---|---|
|
An AI agent is an AI-based application that can interact with users in natural language and execute tasks on behalf of users. |
|
|
|
Tools are executable functions or APIs used by AI agents to interact with environments. They enable agents to perform specific operations, not just generate text. |
|
For more concepts, see kagent.
Prerequisites
- You have created a CCE standard or Turbo cluster of v1.28 or later.
- You have deployed an inference service using the AI Inference Framework add-on by referring to AI Inference Framework Add-on.
Constraints
- kagent needs to be installed immediately after it is started. Ensure that the pods in the cluster can access the public network. You can configure an SNAT rule for the cluster to ensure that pods can access the public network. You will be billed for the SNAT rule. For details, see NAT Gateway Price Calculator.
- This add-on is being deployed. To view the regions where this add-on is available, see the console.
- This add-on is in the OBT phase. You can experience the latest add-on features. However, the stability of this add-on version has not been fully verified, and the CCE SLA is not valid for this version.
Installing the Add-on
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons. On the displayed page, locate kagent and click Install.
- On the Install Add-on page, configure the specifications.
Table 2 Add-on specifications Parameter
Description
Version
Select a version as needed.
Add-on Specifications
Currently, only the default specifications are supported.
openaiApiUrl
URL of the inference service. For details, see Prerequisites.
openaiApiKey
Authentication key for accessing the inference service. For details, see Prerequisites.
openaiModel
Model name used in the inference service. For details, see Prerequisites.
- Click Install in the lower right corner. If the status is Running, the add-on has been installed.
Components
|
Component |
Description |
Resource Type |
|---|---|---|
|
kagent |
kagent consists of the following:
|
Deployment |
Use Case
This example shows how to create a custom agent using the kagent add-on.
- Install kubectl on an existing ECS and access a cluster using kubectl. For details, see Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl.
- Run the following command to create a YAML file for the NodePort Service. You can use this Service to access the cceaddon-kagent workload in the kube-system namespace. Set both the access port and container port to 80.
vim kagent-svc.yamlThe file content is as follows:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: kagent-svc namespace: kube-system labels: app.kubernetes.io/instance: cceaddon-kagent app.kubernetes.io/name: kagent spec: ports: - name: ui protocol: TCP port: 80 targetPort: 80 nodePort: 30371 # Node port number - name: app protocol: TCP port: 8081 targetPort: 8081 nodePort: 30372 # Node port number selector: app.kubernetes.io/instance: cceaddon-kagent app.kubernetes.io/name: kagent type: NodePort sessionAffinity: None externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster ipFamilies: - IPv4 ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
- Create the Service.
kubectl apply -f kagent-svc.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
service/kagent-svc created
- Obtain the IP address of the Service.
kubectl get node -owide
Information similar to the following is displayed:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP 192.168.0.211 Ready <none> 12d 192.168.0.211 xx.xx.xx.xx 192.168.0.32 Ready,SchedulingDisabled <none> 7d16h 192.168.0.32 <none> 192.168.1.173 Ready,SchedulingDisabled <none> 12d 192.168.1.173 xx.xx.xx.xx
- Enter http://<EIP-of-any-node>:<node-port>/ in the address bar of a browser to access the kagent UI.
Figure 1 UI
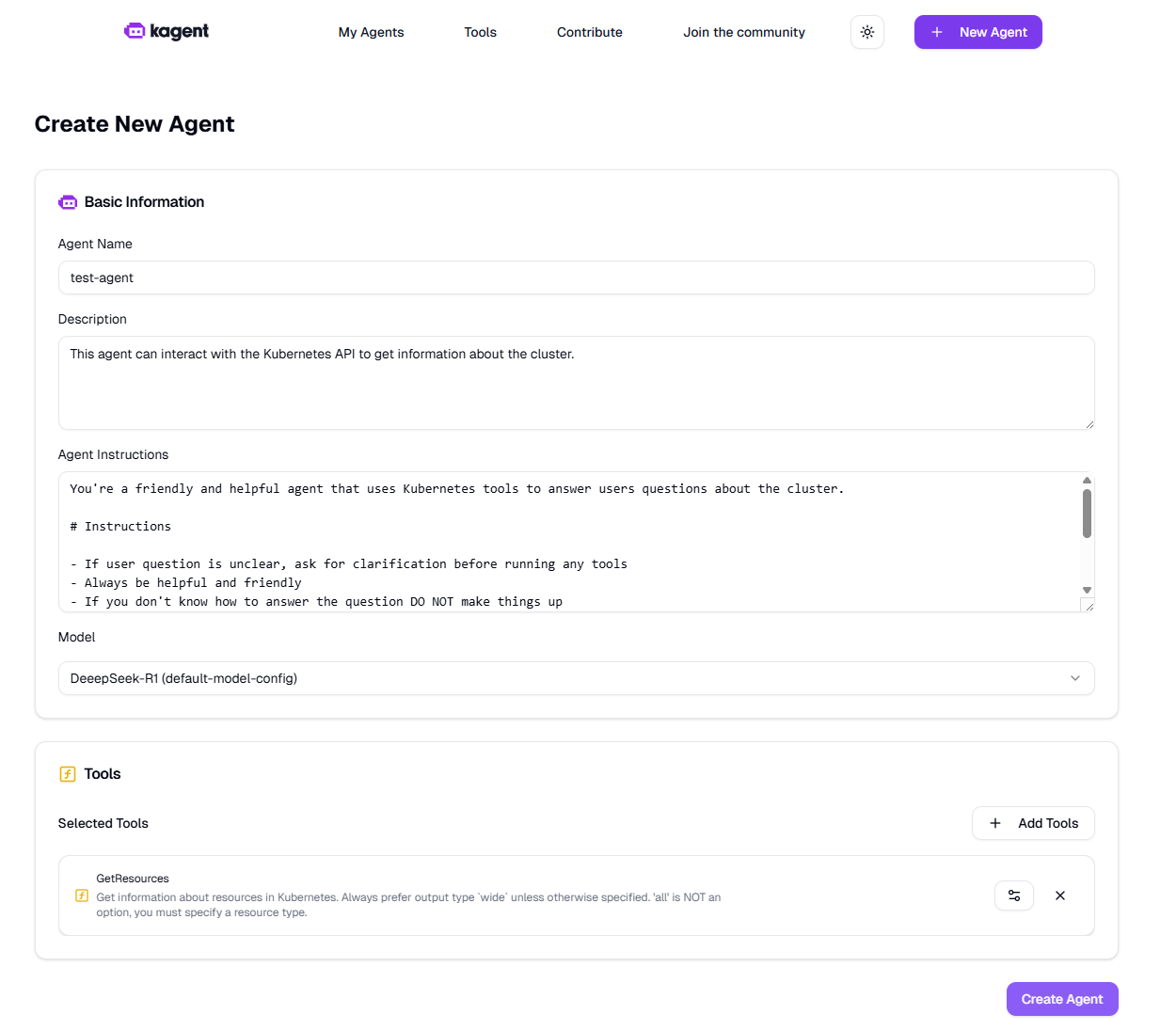
- Click New Agent to create an agent. By default, the inference service entered during add-on installation is used. For details about the parameters, see Figure 2.
- Click Create Agent. After the agent is created, you can use it.
Release History
|
Add-on Version |
Supported Cluster Version |
New Feature |
Community Version |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0.1.15 |
v1.28 v1.29 v1.30 v1.31 |
CCE standard and Turbo clusters support the kagent add-on. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot