Using Residual File Management Functions
Procedure
- Call the pgxc_get_residualfiles() function to obtain the name of the database that has residual files.
- Go to the databases where residual files exist and call the pgxc_verify_residualfiles() function to verify the residual files recorded in the current database.
- Call the pgxc_rm_residualfiles() function to delete all the verified residual files.
The pgxc residual file management function only operates on the CN and the current primary DN, and does not verify or clear residual files on the standby DN. Therefore, after the primary DN is cleared, you need to clear residual files on the standby DN or build the standby DN in a timely manner. This prevents residual files on the standby DN from being copied back to the primary DN due to incremental build after a primary/standby switchover.
Examples
The following example uses two user-created databases, db1 and db2.
- Run the following command to obtain all residual file records of the cluster on the CNs:
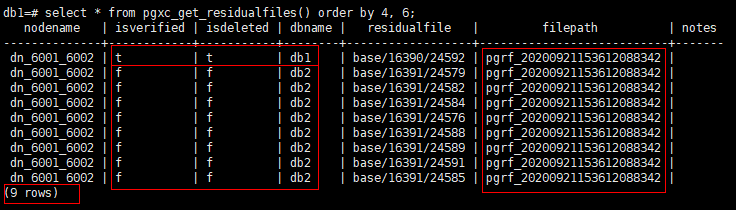
1db1=# select * from pgxc_get_residualfiles() order by 4, 6; -- order by is optional.
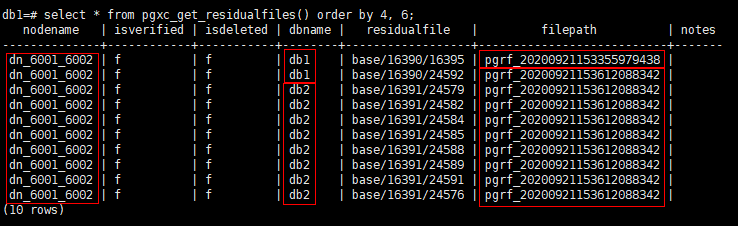
In the current cluster:
- Residual file records exist in the db1 and db2 databases on the dn_6001_6002 node (active node instance).
- Residual files are displayed in the residualfile column.
- The filepath column lists the files that record residual files. These files are stored in the pg_residualfiles directory under the instance data directory.
- Call the pgxc_verify_residualfiles() function to verify the db1 database.
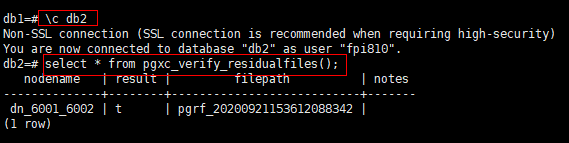
1db1=# SELECT * FROM pgxc_verify_residualfiles();
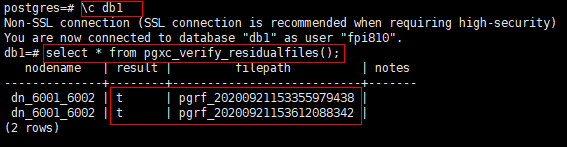
Verification functions are at the database level. Therefore, when a verification function is called in the db1 database, it only verifies residual files in db1.
You can call the get function again to check whether the verification is complete.
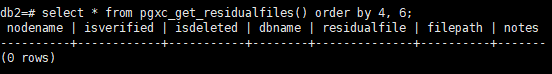
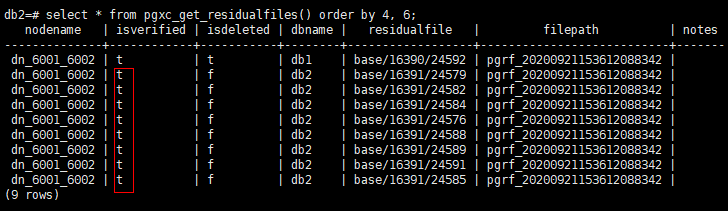
1db1=# SELECT * FROM pgxc_get_residualfiles() order by 4, 6;
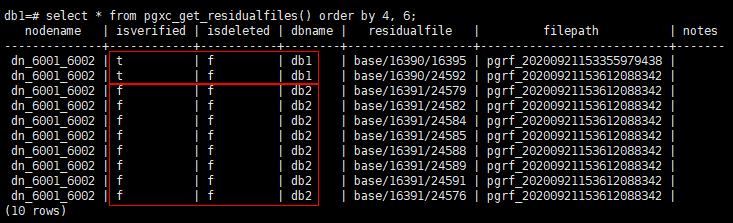
As shown in the preceding figure, the residual files in the db1 database have been verified, and the residual files in the db2 database are not verified.
- Call the pgxc_rm_residualfiles() function to delete residual files.
1db1=# SELECT * FROM pgxc_rm_residualfiles();
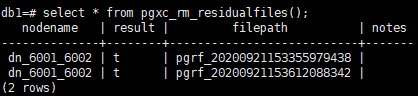
- Call the pgxc_get_residualfiles() function again to check the deletion result.
The result shows that the residual files in the db1 database are deleted (isdeleted is marked as t) and the residual files in the db2 database are not deleted.
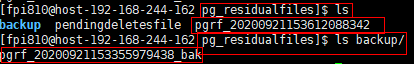
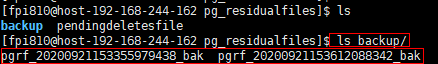
In addition, nine query results are displayed. Compared with the previous query results, a record for the residual file ending with 9438 is missing. This is because the record file that records the residual file ending with 9438 contains only one record, which is deleted in step 3. If all residual files in a record file are deleted, the record file is also deleted. Deleted files are backed up in the pg_residualfiles/backup directory.
- To delete files from the db2 database, you need to call the verify function in the db2 database and then call the rm function.
- Go to the db2 database and call the verification function.
Query the verification result:
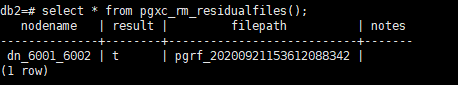
- Call the deletion function:
- Query the deletion result:
All residual files recorded in the record file whose name ends with 8342 have been deleted, so the record file is deleted and backed up in the backup directory. As a result, no records are found.
- Go to the db2 database and call the verification function.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot