Application Integration
How Do an Application Call a Platform API for Authentication?
A customer application can call the IAM API to obtain the X-Auth-Token or integrate the SDK to use the AK/SK authentication. The password of a Huawei Cloud account may need to be updated periodically. It is recommended that the production system integrate the SDKs for the Application Side of IoTDA and use AK/SK authentication.
What Can I Do If the SDK on the Application Side Reports the Missing request header'X-Auth-Token' for method parameter of type String?
Description:
An application is integrated with the IoTDA SDK and uses the AK/SK for authentication. However, the status code 400 is returned, and the error message is Missing request header 'X-Auth-Token' for method parameter of type String.
Possible Causes:
The AK/SK signature algorithm does not match the signature algorithm supported by the cluster.
Solutions:
- Use the common AK/SK Signature Algorithm to access the access address of ab IoTDA basic edition instance in the CN North-Beijing4 region.
- When accessing the access address of an IoTDA standard or enterprise edition instance, you need to specify the derived AK/SK signature algorithm. For details, see SDKs for the Application Side.
How Do I Obtain the Access Addresses and Certificates of the Old and New Domain Names?
No CA certificate is provided for the new domain name. For details about the access addresses of the new and old domain names and the certificate for the old domain name, see Obtaining Resources.
What Are the Differences in Access Authentication If I Use the New or Old Domain Names?
When you use the new domain name, the IAM API for authentication is called, and the Huawei Cloud account and password need to be carried in the request. When you use the old domain name, the authentication API of the IoT platform is called, and the application ID and secret need to be carried.
How Does an Application Obtain Data Reported by Devices to the IoT Platform?
Data forwarding rules are configured based on the rule engine.
- Data forwarding rules are configured based on the rule engine. The IoT platform calls the configured rules to forward device data to other Huawei Cloud services (such as Kafka, DIS, and OBS), third-party applications
- The IoT platform calls the configured rules to forward device data to third-party cloud services (such as Kafka, DIS, and OBS), from which you can obtain the data to implement your service.
How Do I Obtain the ID and Secret of an Application?
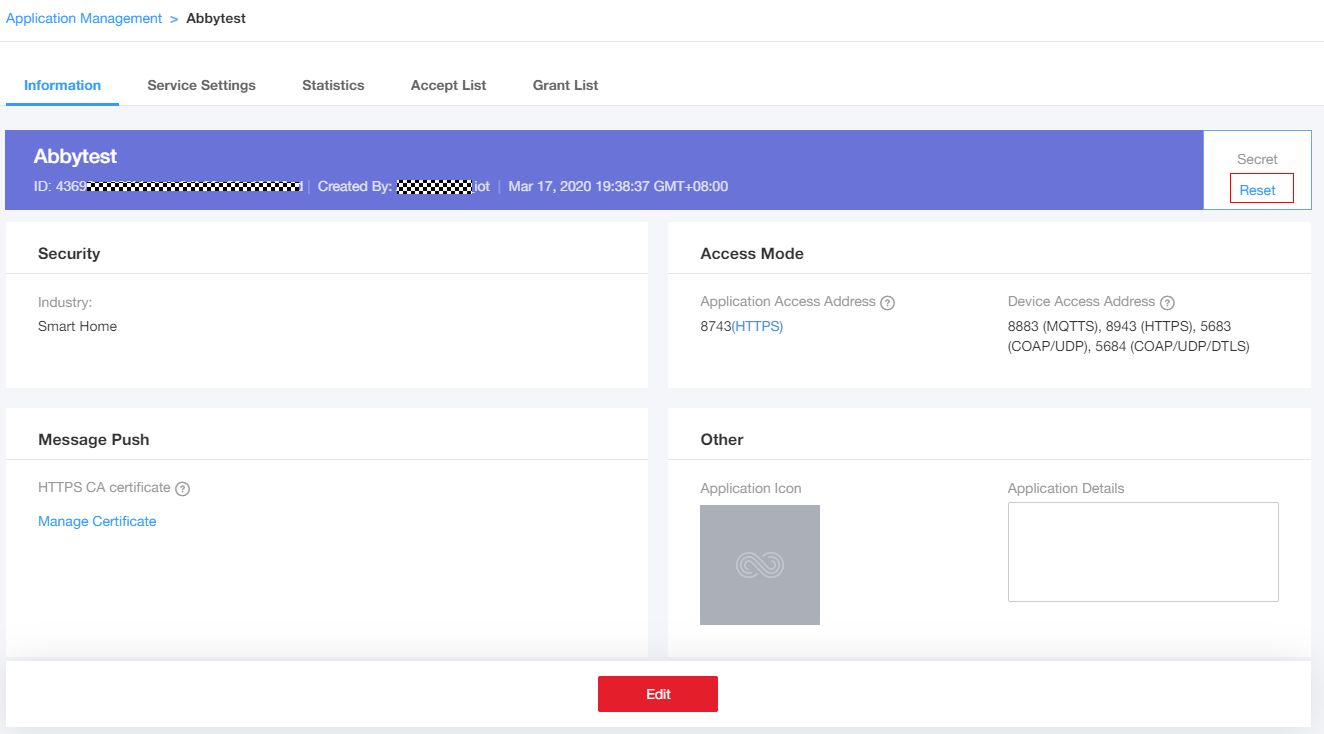
If you have enabled IoTDA before 00:00 on March 20, 2020 (GMT+08:00), you can perform the preceding operations to obtain the ID and secret. Otherwise, submit a service ticket to contact technical support.
- Check the access address and certificate of the API of the earlier version and click the button to access IoTDA.
- Select an application in the application list. The application ID is shown on the displayed page. Click Reset to obtain the secret.
Figure 1 Application details page
Why Did an Application Fail to Call an API?
- Check whether the network connection of the application is normal.
- Check whether the application access address and port number of the IoT platform in the request are correct.
- Run ping {application access address of the platform} to check whether the application can access the application access address of the platform.
- Run telnet {application access address of the platform } {port number} to check whether the application access port of the platform can be enabled.
- Check whether the application is integrated with the platform certificate. The certificate can be downloaded from Obtaining Resources.
- Check whether the parameters are correctly set based on the API Reference.
- When V3 APIs are used, the validity period of accessToken returned by calling the authentication API is 1 hour. After the validity period expires, other APIs cannot be called. In this case, call the authentication API to obtain the new accessToken and then call other APIs again.
- When V5 APIs are used, the validity period of X-Auth-Token returned by calling the authentication API is 24 hours. After the validity period expires, other APIs cannot be called. In this case, call the authentication API to obtain the new X-Auth-Token and then call other APIs again.
- If the previous steps do not resolve the issue, troubleshoot based on the error code returned when the API was called. For details about the error codes, see Error Codes. If an application has encapsulated error codes, you can use Postman to call the same API to obtain the original error code and description returned by IoTDA, and then rectify the fault based on the recommendations provided.
For example, if a message is displayed indicating that the node ID already exists when the API Creating a Device is called, check whether a device with the same node ID exists under your account. If no device with the same node ID is found under your account, submit a service ticket and contact technical support to check whether the node ID is used for device access.
How Does an Application Obtain Device IMEIs?
After the bindDevice notification is subscribed to, the IoT platform pushes the IMEI and deviceId to the application when a device is connected to the platform. For details, see the description of the API for subscribing to service data.
How Does an Application Deliver a Cached Command?
Set expireTime to a value greater than 0 when calling the API for creating a command.
expireTime indicates the validity period of a command, which is measured in seconds. The command will not be delivered after the specified time elapses. If this parameter is not specified, the default validity period is 48 hours (172,800 seconds).
Do I Have to Use Java to Call the APIs of the IoT Platform?
No. The APIs of the platform are standard RESTful APIs that support multiple languages such as Java, Python, and Go. For details, see SDKs for the Application Side.
Why Were Devices Registered on the IoT Platform Deleted After a Period of Time?
When a device is registered by calling an API, the timeout parameter must be configured. After the registration is complete, if the device is not bound to the platform within the time specified by timeout, the platform will delete the device.
The value range of timeout is 0 to 2147483647 (68 years), which is measured in units of seconds. When this parameter is set to 0, the timer never expires and the device is never deleted as a result of a timeout.
Can I Create the Same Product in Different Instances? Can the Product Name and Product ID Be the Same in Different Resource Spaces or the Same Resource Space?
The same product can be created in different instances. The same product can be created in different resource spaces of the same instance.
Can I Create the Same Device in Different Instances?
The same device can be created in different instances. The same device cannot be created under the same instance.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





