Help Center/
GaussDB/
Developer Guide(Distributed_V2.0-8.x)/
Stored Procedures/
Arrays, Collections, and Records/
Arrays/
Use of Array Types
Updated on 2025-09-22 GMT+08:00
Use of Array Types
Before the use of arrays, an array type needs to be defined:
Syntax
Define an array type immediately after the AS keyword in a stored procedure. Run the following statement:
TYPE array_type IS VARRAY(size) OF data_type;
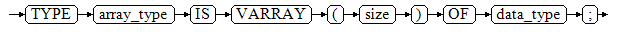
Related parameters are as follows:
- array_type: indicates the name of the array type to be defined.
- size: indicates the maximum number of members in the array type to be defined. The value is a positive integer.
- data_type: indicates the types of members in the array type to be created.
Precautions
- GaussDB supports access to array elements using index syntax (enclosed by parentheses ()) and provides various dedicated functions (such as EXTEND, COUNT, FIRST, LAST, PRIOR, EXISTS, TRIM, NEXT, and DELETE) for flexible array operations and management.
- In GaussDB, an array automatically increases. If an access violation occurs, a NULL value will be returned, and no error message will be reported.
- The scope of an array type defined in a stored procedure takes effect only in this storage process.
- size is used only for syntax compatibility and has no actual meaning.
- data_type can also be the record type defined in a stored procedure (anonymous blocks are not supported) or collection type, but cannot be the array or cursor type defined in the stored procedure.
- When data_type is collection, multi-dimensional arrays are not supported.
- The constructors of the array type can be used only in ORA-compatible mode.
- The constructor of the array type cannot be used as the default value of a function or stored procedure parameter.
- If the elements of an array are of the collection type and data_type of the array is set to VARCHAR or NUMERIC that can define the length and precision, you need to enable the tableof_elem_constraints option for GUC parameter behavior_compat_options to verify the element length of the array or convert the element to the corresponding precision.
- After enable_recordtype_check_strict is set to on, if the member is of the record type and a column of the record type has the not null or default attribute, an error is reported during stored procedure or package compilation.
- If the stored procedure contains DML statements (SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, or DELETE), DML statements can access array elements only using brackets. In this way, it may be separated from the function expression area.
- Elements of varray variables cannot be accessed in DML statements.
- NOT NULL syntax is not supported.
Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 |
-- Perform array operations in the stored procedure. gaussdb=#CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE array_proc AS DECLARE TYPE ARRAY_INTEGER IS VARRAY(1024) OF INTEGER;-- Define the array type. ARRINT ARRAY_INTEGER: = ARRAY_INTEGER(); -- Declare the variable of the array type. BEGIN ARRINT.EXTEND(10); FOR I IN 1..10 LOOP ARRINT(I) := I; END LOOP; DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT.COUNT); DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT(1)); DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT(10)); DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT(ARRINT.FIRST)); DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT(ARRINT.LAST)); DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT(ARRINT.NEXT(ARRINT.FIRST))); DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT(ARRINT.PRIOR(ARRINT.LAST))); ARRINT.TRIM(); IF ARRINT.EXISTS(10) THEN DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE('Exist 10th element'); ELSE DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE('Not exist 10th element'); END IF; DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT.COUNT); DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT(ARRINT.FIRST)); DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(ARRINT(ARRINT.LAST)); ARRINT.DELETE(); END; / -- Call the stored procedure. gaussdb=#CALL array_proc(); 10 1 10 1 10 2 9 Not exist 10th element 9 1 9 array_proc ------------ (1 row) -- Drop the stored procedure. gaussdb=#DROP PROCEDURE array_proc; |
Parent topic: Arrays
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
The system is busy. Please try again later.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





