Database Audit Is Unavailable
Symptom
After the database traffic is triggered, you cannot find the audit information about an executed statement in the SQL statement list.
In this case, perform the following operations to troubleshoot the problem:
Checking Database Information and Audit Function Settings
- Log in to the management console.
- Select a region, click
 , and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed.
, and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed. - In the navigation tree on the left, choose Databases.
- Select an instance where the database is located from the Instance drop-down list.
- View the database information.
- Check whether the database information is correct.
- Check whether the database audit function is enabled.
- If Audit Status is Enabled, go to Checking Audited Database Settings.
- If Audit Status is Disabled, click Enable to enable the database audit function.
- If the fault is rectified, no further operation is required.
- If the problem persists, go to Checking Audited Database Settings.
Checking Audited Database Settings
In the navigation tree on the left, choose Database Audit > Rules. The Audit Scope page is displayed.
- If Status is Enabled, go to Checking Database Agent Status.
- If Status is Disabled, click Enable to enable the desired audit scope rule of the database.
- If the fault is rectified, no further operation is required.
- If the problem persists, go to Checking Database Agent Status.
Checking Database Agent Status
- Log in to the node where the agent is installed as user root by using a cross-platform remote access tool (for example, PuTTY) via SSH.
- Run the following command to view the running status of the agent program:
- Run the following command to restart the agent:
service audit_agent restart
- If the fault is rectified, no further operation is required.
- If the problem persists, go to 4.
- Run the following command to check the communication status between the agent and database audit instance:
tailf /opt/dbss_audit_agent/log/audit_agent.log
- If information similar to the following is displayed, the communication between the agent and database audit instance is normal. Go to Verifying the Result.
Figure 1 Normal communication
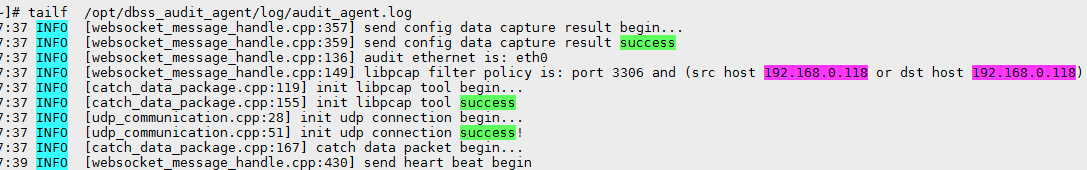
- If information similar to the following is displayed, the communication between the agent and database audit instance is abnormal. Go to Checking the Security Group Rules of the Database Audit Instance.
Figure 2 Communication error
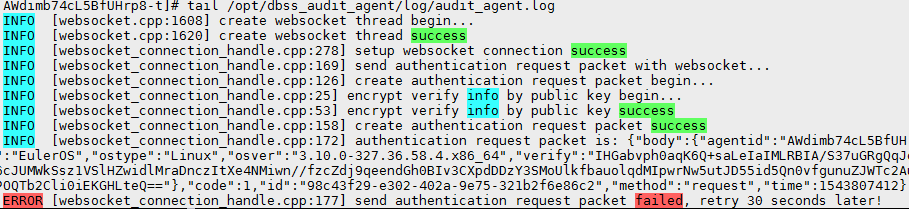
- If information similar to the following is displayed, the communication between the agent and database audit instance is normal. Go to Verifying the Result.
Checking the Security Group Rules of the Database Audit Instance
- Go to the Database Security Service page.
- In the navigation tree on the left, choose Database Audit > Databases. The Databases page is displayed.
- Select an instance where the database is located from the Instance drop-down list.
- Record the IP address of the agent node.
Click
 next to the database to view the information of its agent, and record Installing Node IP Address.
next to the database to view the information of its agent, and record Installing Node IP Address. - Click Add Security Group Rule.
- In the displayed dialog box, record the security group name (for example, default) of the database audit instance.
- Click Go to VPC.
- In the security group list, enter the group name default in the search box in the upper right corner of the list, and click
 or press Enter. The group information is displayed in the list.
or press Enter. The group information is displayed in the list. - Click the name of the security group default. Click the Inbound Rules tab.
- Check the inbound access rules of the security group.
Check whether TCP (port number 8000) and UDP protocols (port number from 7000 to 7100) are configured in the inbound rules of the security group for the IP address of the installing node in 4.
- If the inbound rules of the security group have been configured for the installing node, go to Verifying the Result.
- If no inbound rules of the security group have been configured for the installing node, go to 11.
- Add an inbound rule for the installing node.
- On the Inbound Rules tab, click Add Rule.
- In the Add Inbound Rule dialog box, add TCP (port number 8000) and UDP protocols (port number from 7000 to 7100) for the installing node IP address.
- Click OK.
Verifying the Result
- If the SQL statement is found, the problem has been solved.
- If the SQL statement is not found, the problem persists. Contact customer service.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





