RELEASE SAVEPOINT
Description
RELEASE SAVEPOINT destroys a savepoint previously defined in the current transaction.
Destroying a savepoint makes it unavailable as a rollback point, but it has no other user visible behavior. It does not undo the effects of statements executed after the savepoint was established. To do that, use ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT. Destroying a savepoint when it is no longer needed allows the system to recycle some resources earlier than transaction end.
RELEASE SAVEPOINT also destroys all savepoints that were established after the named savepoint was established.
Precautions
- Releasing a savepoint name that was not previously defined will cause an error.
- It is not possible to release a savepoint when the transaction is in an aborted state.
- If multiple savepoints have the same name, only the one that was most recently defined is released.
Syntax
RELEASE [ SAVEPOINT ] savepoint_name;
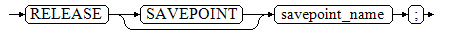
Parameters
- savepoint_name
Specifies the name of the savepoint to be destroyed.
Examples
-- Create a schema. gaussdb=#CREATE SCHEMA tpcds; -- Create a table. gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE tpcds.table1(a int); -- Start a transaction. gaussdb=#START TRANSACTION; -- Insert data. gaussdb=#INSERT INTO tpcds.table1 VALUES (3); -- Establish a savepoint. gaussdb=#SAVEPOINT my_savepoint; -- Insert data. gaussdb=#INSERT INTO tpcds.table1 VALUES (4); -- Delete the savepoint. gaussdb=#RELEASE SAVEPOINT my_savepoint; -- Query the table content, which should contain both 3 and 4. gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM tpcds.table1; a --- 3 4 (2 rows) -- Commit the transaction. gaussdb=#COMMIT; -- Query the table content again. You can see 3 and 4 at the same time. gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM tpcds.table1; a --- 3 4 (2 rows) -- Delete the table. gaussdb=#DROP TABLE tpcds.table1; -- Delete a schema. gaussdb=#DROP SCHEMA tpcds CASCADE;
Helpful Links
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





