Workload Abnormalities
What Do I Do If There Is a Workload Abnormality?
If a workload is in the abnormal state, check the events first.
Log in to the CCI console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Workloads. Click the name of the abnormal workload. On the details page that is displayed, view the latest event.
Image Pull Failure
If there is an event indicating that the image failed to be pulled, check the following items to locate the fault:
- imagePullSecret is not specified when you create a workload.
For example, when creating a Deployment named nginx, check whether the YAML file contains the imagePullSecrets field, which indicates the secret name during image pull.
To pull an image from SWR, set this field to imagepull-secret.
apiVersion: cci/v2 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx namespace: nginx-ns spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx strategy: type: RollingUpdate template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - image: nginx:alpine imagePullPolicy: Always name: nginx imagePullSecrets: - name: imagepull-secret
- The image address is incorrect.
CCI allows you to create workloads using images pulled from SWR.
SWR images can be obtained using the image pull command. After an image is pushed, you can obtain its address.
Figure 1 Image address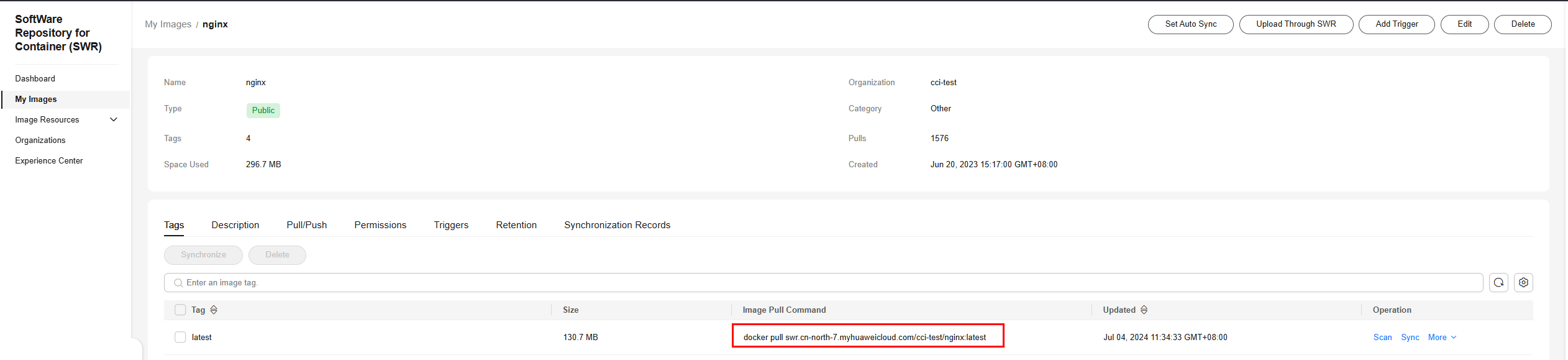
- IAM users do not have sufficient permissions to pull images.
If you have enabled Enterprise Project Management Service (EPS), you need to use your account to assign IAM users the permissions to access SWR so that the IAM users can pull private images in your account.
You can assign permissions to IAM users in either of the following ways:
- Assign permissions on the image details page. After permissions are granted, IAM users can read, edit, and manage the image. For details, see Granting Permissions of a Specific Image.
- Assign permissions on the organization details page. After permissions are granted, IAM users can read, edit, and manage all images in the organization. For details, see Granting Permissions of an Organization.
- The Docker version used for image packaging is outdated.
The image failed to be pulled, and the following error information is displayed:
failed to pull and unpack image "****": failed to unpack image on snapshotter devmapper: failed to extract layer sha256:xxxxxx: failed to get reader from content store: content digest sha256:xxxxxx: not found
Cause: The Docker version used to build the image is outdated (earlier than v1.10). Some image packaging standards are no longer supported by the community.
Solution: Use Docker v1.11 or later to rebuild the image and push it to SWR, upgrade the workload image tag and pull it again.
- VPC endpoints are not configured.
For details, see Buying a VPC Endpoint.
Solution: If you use a repository of SWR Enterprise Edition, configure a VPC endpoint for OBS and create the workload again. If you use an SWR public image repository, configure a VPC endpoint for OBS and a VPC endpoint for SWR and create the workload again.
Container Restart Failure
If the details page of a workload shows an event indicating that the container failed to restart, perform the following operations to locate the fault:
- There are port conflicts.
- On the page that is displayed, click the pod of the abnormal workload.
- Locate the pod of the container that failed to be started and click View YAML to check whether the container port conflicts with that of another container.
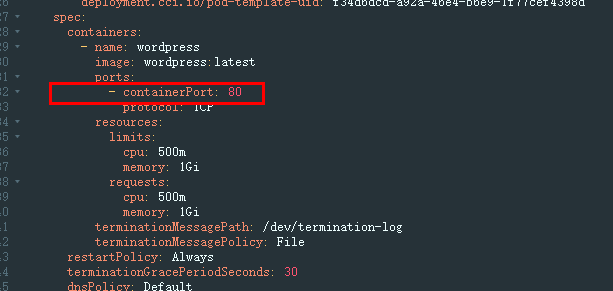
Solution: Create the workload again and configure a correct port. Ensure that the port does not conflict with other ports.
- The workload is abnormal.
Check whether the workload startup command is correctly executed or there is workload fault.
Solution: Create the workload again and configure a correct startup command.
- The workload health check failed.
If a liveness probe is configured for the workload and the number of health check failures exceeds the failure threshold, the container will be restarted. On the workload details page, if Kubernetes events contain "Liveness probe failed: ……", the health check fails.
Solution: Reconfigure the health check.
Other Check Items
- Configure the following startup command for the workload. In this way, the application will not be started after the pod is started, and no operation will be performed.
Before running the startup command, ensure that the /bin/bash command in the image is available.
- After the pod is started, locate the pod and click View Terminal in the Operation column. Then select the corresponding container, manually run the startup command, and locate and rectify the fault based on the error message.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






