Releasing/Obtaining a Go Package via a Build Task
This practice describes how to release a private package to a Go repository via a build task and obtain a dependency from the repository for deployment.
Prerequisites
- You have purchased a CodeArts package.
- You already have a project. If no project is available, create one. For example, create a project named project01.
- You have created a Go repository in the self-hosted repo.
- You have permissions for the current repository. For details, see Managing Repository Permissions.
Releasing a Package to a Go Repository
- Download the configuration file.
- Use your Huawei Cloud account to access self-hosted repos.
- Select a Go repository. Click Tutorial on the right of the page.
- In the displayed dialog box, click Download Configuration File.
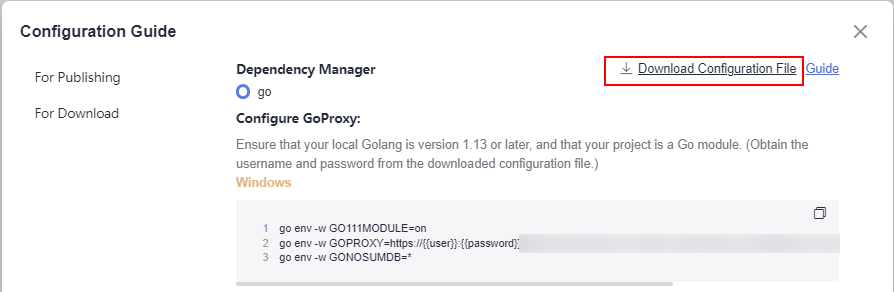
- Configure a repository.
- Go to CodeArts Repo. Create a Go repository. For details, see Creating a Repository This procedure uses the Go web Demo template.
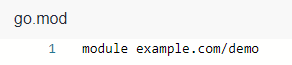
- Prepare the go.mod and upload it to the root directory of the repository. For details, see Uploading Code Files to CodeArts Repo The following figure shows the go.mod file used in this example.
- Configure and run a build task.
- On the Repo page, select the repository and click Create Build Task in the upper right.
Select Blank Template and click OK.
- Add the Build with Go action.
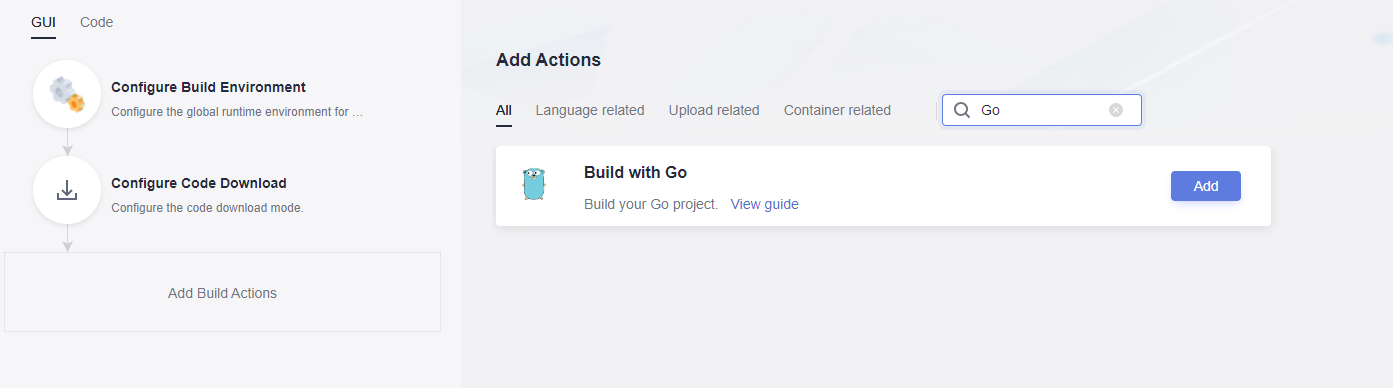
- Edit the Build with Go action.
- Select the desired tool version. In this example, go-1.13.1 is used.
- Delete the existing commands, open the configuration file downloaded in 1, and copy the commands for configuring Go environment variables in Linux to the command box.
- Copy the Go upload command segment in the configuration file to the command box, and replace the parameters in the commands by referring to Go Modules. (In this example, the package version is v1.0.0.)
- Click Save and Run on the right of the page to start the build task.
When the message build successful is displayed, go to the self-hosted repo page and find the uploaded Go package.
- On the Repo page, select the repository and click Create Build Task in the upper right.
Obtaining a Dependency from a Go Repository
The following procedure uses the Go package released in Releasing a Package to a Go Repository as an example to describe how to obtain a dependency from a Go repository.
- Download the configuration file by referring to Releasing a Package to a Go Repository.
- Go to Repo and create a Go repository. For details, see Creating a Repository This procedure uses the Go web Demo template.
- Configure and run a build task.
- On the Repo page, select the repository and click Create Build Task in the upper right.
Select Blank Template and click OK.
- Add the Build with Go action.
- Edit the Build with Go action.
- Select the desired tool version. In this example, go-1.13.1 is used.
- Delete the existing commands, open the downloaded configuration file, and copy the commands for configuring Go environment variables in Linux to the command box.
- Copy the Go download commands in the configuration file to the command box and replace the <modulename> parameter with the actual value. (In this example, the parameter is set to example.com/demo).
- On the Repo page, select the repository and click Create Build Task in the upper right.
- Click Save and Run on the right of the page to start the build task.
When the message build successful is displayed, view the task details. If information similar to the following is found in the log, the dependency has been downloaded from the Go repository.
Go Modules
This section describes how to build and upload Go packages through Go modules.
Perform the following steps:
- Create a source folder in the working directory.
mkdir -p {module}@{version} - Copy the code source to the source folder.
cp -rf . {module}@{version} - Compress the package into a ZIP package.
zip -D -r [package name] [package root directory]
- Upload the ZIP package and the go.mod file to the self-hosted repo.
curl -u {{username}}:{{password}} -X PUT {{repoUrl}}/{filePath} -T {{localFile}}
The package directory varies according to the package version. The version can be:
- Versions earlier than v2.0: The directory is the same as the path of the go.mod file. No special directory structure is required.
- v2.0 or later:
- If the first line in the go.mod file ends with /vX, the directory must contain /vX. For example, if the version is v2.0.1, the directory must contain v2.
- If the first line in the go.mod file does not end with /vN, the directory remains unchanged and the name of the file to be uploaded must contain +incompatible.
The following are examples of package directories for different versions:
- Versions earlier than v2.0
The go.mod file is used as an example.

- Create a source folder in the working directory.
- Copy the code source to the source folder.
The command is as follows (with the same parameter values as the previous command):
cp -rf . ~/example.com/demo@v1.0.0/
- Compress the package into a ZIP package.
Run the following command to go to the upper-level directory of the root directory where the ZIP package is located:
cd ~
Then, use the zip command to compress the code into a package. In this command, the package root directory is example.com and the package name is v1.0.0.zip. The command is as follows:
zip -D -r v1.0.0.zip example.com/
- Upload the ZIP package and the go.mod file to the self-hosted repo.
Parameters username, password, and repoUrl can be obtained from the configuration file.
- For the ZIP package, the value of filePath is example.com/demo/@v/v1.0.0.zip and that of localFile is v1.0.0.zip.
- For the go.mod file, the value of filePath is example.com/demo/@v/v1.0.0.mod and that of localFile is example.com/demo@v1.0.0/go.mod.
The commands are as follows (replace username, password, and repoUrl with the actual values):
curl -u {{username}}:{{password}} -X PUT {{repoUrl}}/example.com/demo/@v/v1.0.0.zip -T v1.0.0.zip curl -u {{username}}:{{password}} -X PUT {{repoUrl}}/example.com/demo/@v/v1.0.0.mod -T example.com/demo@v1.0.0/go.mod
- v2.0 and later, with the first line in go.mod ending with /vX
The go.mod file is used as an example.
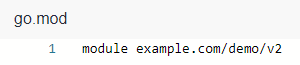
- Create a source folder in the working directory.
- Copy the code source to the source folder.
The command is as follows (with the same parameter values as the previous command):
cp -rf . ~/example.com/demo/v2@v2.0.0/
- Compress the package into a ZIP package.
Run the following command to go to the upper-level directory of the root directory where the ZIP package is located:
cd ~
Then, use the zip command to compress the code into a package. In this command, the package root directory is example.com and the package name is v2.0.0.zip. The command is as follows:
zip -D -r v2.0.0.zip example.com/
- Upload the ZIP package and the go.mod file to the self-hosted repo.
Parameters username, password, and repoUrl can be obtained from the configuration file.
- For the ZIP package, the value of filePath is example.com/demo/v2/@v/v2.0.0.zip and that of localFile is v2.0.0.zip.
- For the go.mod file, the value of filePath is example.com/demo/v2/@v/v2.0.0.mod and that of localFile is example.com/demo/v2@v2.0.0/go.mod.
The commands are as follows (replace username, password, and repoUrl with the actual values):
curl -u {{username}}:{{password}} -X PUT {{repoUrl}}/example.com/demo/v2/@v/v2.0.0.zip -T v2.0.0.zip curl -u {{username}}:{{password}} -X PUT {{repoUrl}}/example.com/demo/v2/@v/v2.0.0.mod -T example.com/demo/v2@v2.0.0/go.mod
- v2.0 and later, with the first line in go.mod not ending with /vX
The go.mod file is used as an example.
- Create a source folder in the working directory.
- Copy the code source to the source folder.
The command is as follows (with the same parameter values as the previous command):
cp -rf . ~/example.com/demo@v3.0.0+incompatible/
- Compress the package into a ZIP package.
Run the following command to go to the upper-level directory of the root directory where the ZIP package is located:
cd ~
Then, use the zip command to compress the code into a package. In this command, the package root directory is example.com and the package name is v3.0.0.zip. The command is as follows:
zip -D -r v3.0.0.zip example.com/
- Upload the ZIP package and the go.mod file to the self-hosted repo.
Parameters username, password, and repoUrl can be obtained from the configuration file.
- For the ZIP package, the value of filePath is example.com/demo/@v/v3.0.0+incompatible.zip and that of localFile is v3.0.0.zip.
- For the go.mod file, the value of filePath is example.com/demo/@v/v3.0.0+incompatible.mod and that of localFile is example.com/demo@v3.0.0+incompatible/go.mod.
The commands are as follows (replace username, password, and repoUrl with the actual values):
curl -u {{username}}:{{password}} -X PUT {{repoUrl}}/example.com/demo/@v/v3.0.0+incompatible.zip -T v3.0.0.zip curl -u {{username}}:{{password}} -X PUT {{repoUrl}}/example.com/demo/@v/v3.0.0+incompatible.mod -T example.com/demo@v3.0.0+incompatible/go.mod
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





