CBH for DJCP (or MLPS)
This topic describes which CBH functions are useful for DJCP certification. So that you can use certain functions and provide supporting materials accordingly to win DJCP certification easily.
Articles Related to DJCP Level 3 Certification
The following part focuses on the following DJCP articles:
- Security audit should be performed on network borders and important network nodes. Every user's critical behaviors and security events shall be audited.
- Audit records shall include the event date and time, users, event types, whether the events succeeded, and other related audit information.
- Audit records shall be protected and backed up periodically to avoid unexpected deletion, modification, or overwriting.
- Behavior audit and analyses shall be separately performed for remote access user behaviors and Internet access user behaviors.
- The identity of the login user shall be identified and authenticated. The ID shall be unique, and the identity authentication information shall meet complexity requirements and be changed periodically.
- Response measures to login failures, including stopping sessions, restricting the number of illegal logins, and automatically logging off expired network connections, shall be configured and enabled.
- During remote management, necessary measures shall be taken to prevent authentication information from being intercepted during transmission.
- Two or more authentication methods, including tokens, passwords, and biometric technologies, shall be used to authenticate user identity. Password authentication must be used.
- Appropriate accounts and permissions shall be assigned to login users.
- Default accounts shall be renamed or deleted, and their passwords should be changed.
- Redundant or expired accounts should be deleted or disabled in time to avoid account sharing.
- The minimum permissions shall be granted to management users to implement separation of privilege.
- Access control policies should be configured by the authorization subject, and the access policy should specify the rules for the subject to access the authorized object.
- The security audit function must be provided for each user to audit important security incidents and user behavior.
- Audit records shall include the event date and time, users, event types, whether the events succeeded, and other related audit information.
Prerequisites
You have purchased a later bastion host of the standard edition or later and completed the bastion host configuration.
Security Zone Border: Security Audits
- DJCP article: Security audit should be performed on network borders and important network nodes. Every user's critical behaviors and security events shall be audited.
This clause focuses on whether security audit is performed. CBH supports monitoring and security audits for O&M activities on cloud servers.
- Log in to the CBH system using an account with the permission on the audit module. Choose .
Figure 1 Viewing historical sessions
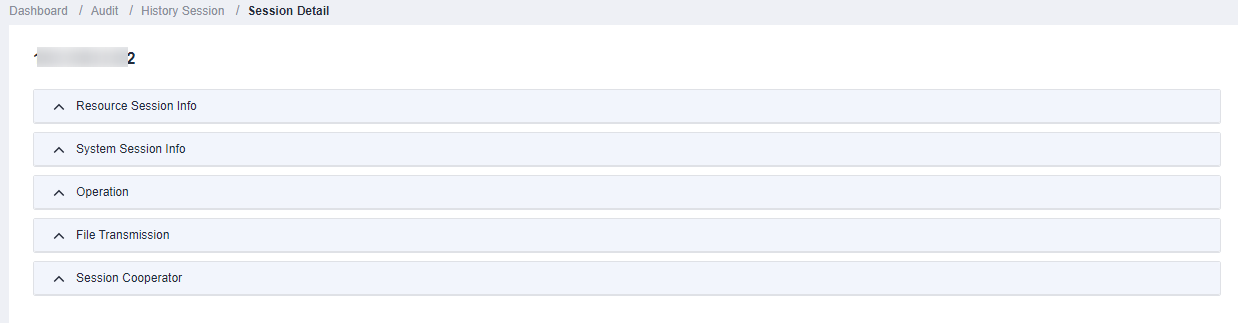
- On the history session page, you can view resource session information, system session information, operation records, file transmission records, and collaborative session records.
- Log in to the CBH system using an account with the permission on the audit module. Choose .
- DJCP article: Audit records shall include the event date and time, users, event types, whether the events succeeded, and other related audit information.
This article checks whether logs are recorded as required.
- Log in to the CBH system using the administrator account. Choose .
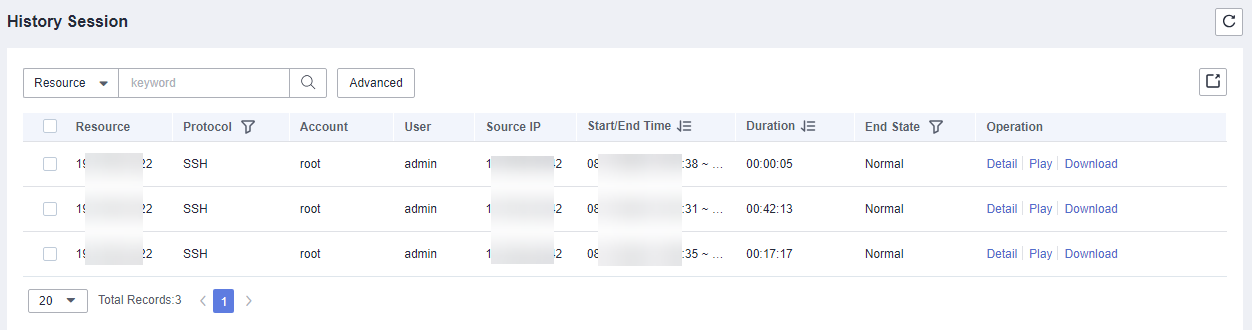
- For a history session, you can view the resource name, type, host IP address, account, start and end time, session duration, session size, operation user, source IP address and MAC address of the operation user, login mode, operation records, file transfer records, and session collaboration records.
Figure 2 Viewing historical sessions
- Audit records shall be protected and backed up periodically to avoid unexpected deletion, modification, or overwriting.
- Log in to the CBH system as the administrator, choose , and click Log Backup to go to the Log Backup page.
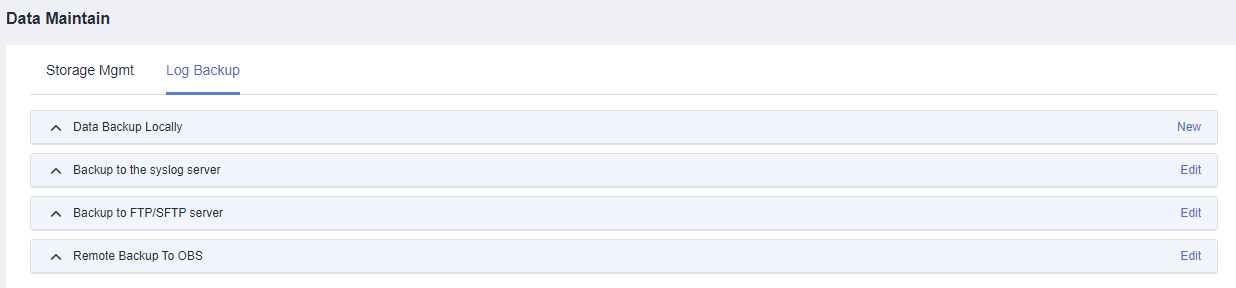
- On the Log Backup page, you can create and view log backups, including system login logs, resource login logs, command operation logs, file operation logs, and two-person authorization logs. Data can also be backed up to the Syslog server, FTP server, SFTP server, and an OBS bucket.
Figure 3 Creating a database backup
- Behavior audit and analyses shall be separately performed for remote access user behaviors and Internet access user behaviors.
This article checks whether remote access user activities and log data can be audited and analyzed.
Secure Computing Environment: Identity Authentication
- DJCP article: The identity of the login user shall be identified and authenticated. The ID shall be unique, and the identity authentication information shall meet complexity requirements and be changed periodically.
This clause focuses on the following three points:
- Check whether the login user is identified and authenticated. If the user accesses the bastion host page using a browser, the product functions can be used only after the user identity is authenticated.
Figure 4 CBH system login page
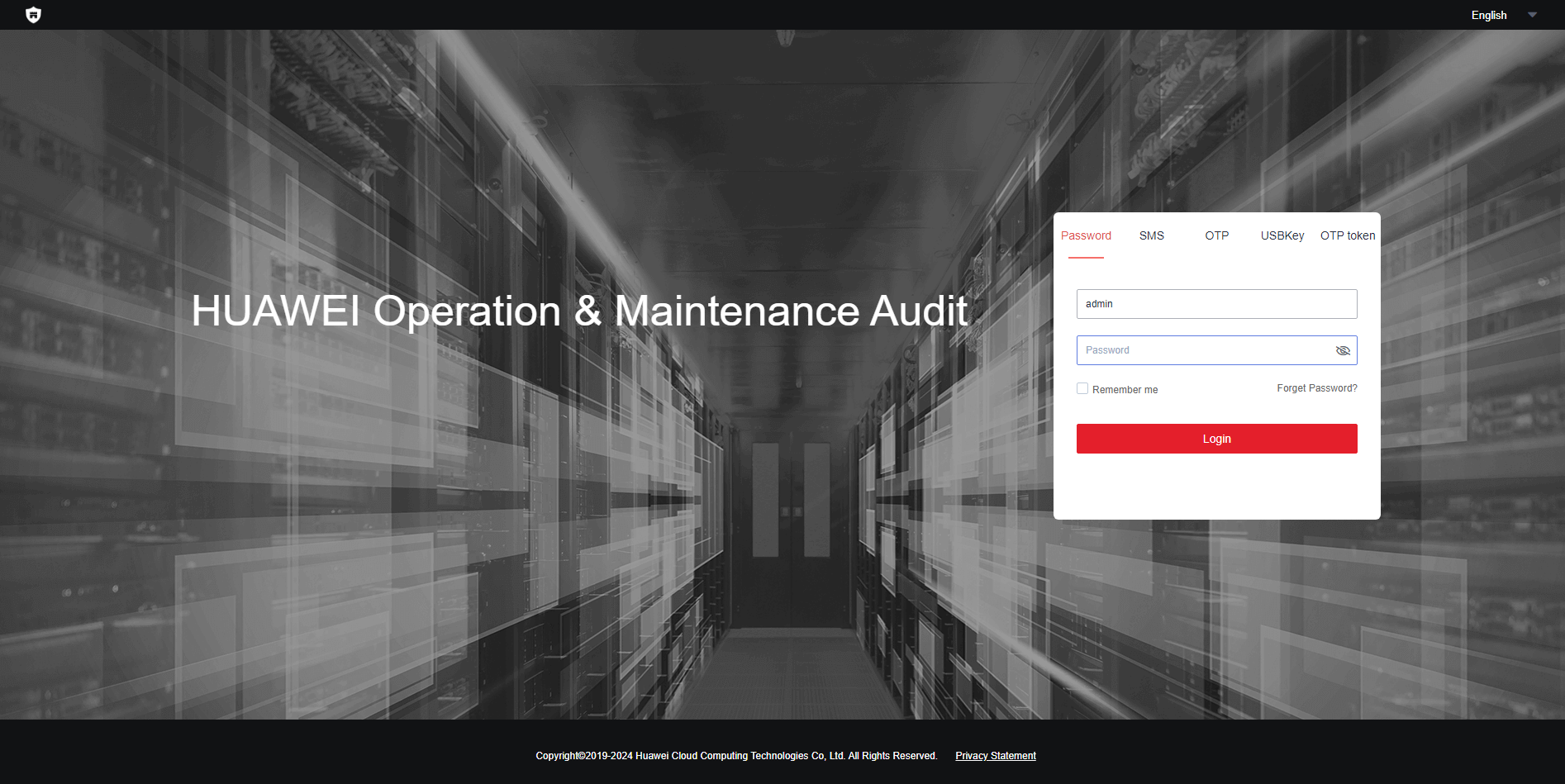
- Uniqueness: When creating users, the username, mobile number, email address, and role must be unique for each user. Only one role can be configured for a user. For details, see Creating a CBH System User.
Figure 5 Creating a user
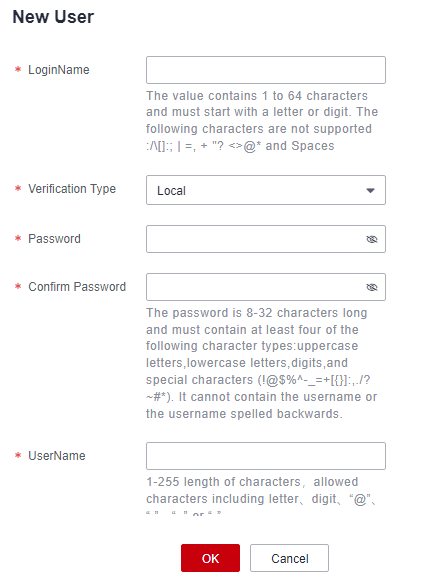
- Check whether password complexity and periodic change requirements on identity authentication are met. CBH supports manual, scheduled, and periodic password change methods. In addition, CBH supports generating different passwords, generating the same password, and specifying the same password for quickly change passwords for system users. For details, see CBH Password Change Rules.
Figure 6 Chpwd Rules
- Check whether the login user is identified and authenticated. If the user accesses the bastion host page using a browser, the product functions can be used only after the user identity is authenticated.
- DJCP article: Two or more authentication methods, including tokens, passwords, and biometric technologies, shall be used to authenticate user identity. Password authentication must be used.
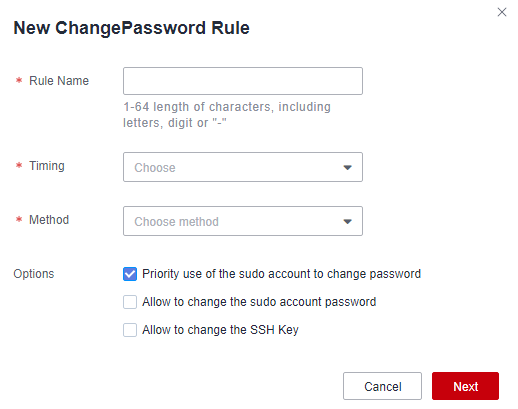
CBH uses multi-factor authentication. The login authentication methods include SMS messages, mobile phone tokens, USB keys, and dynamic OTPs.
Figure 7 Configuring Multifactor Verification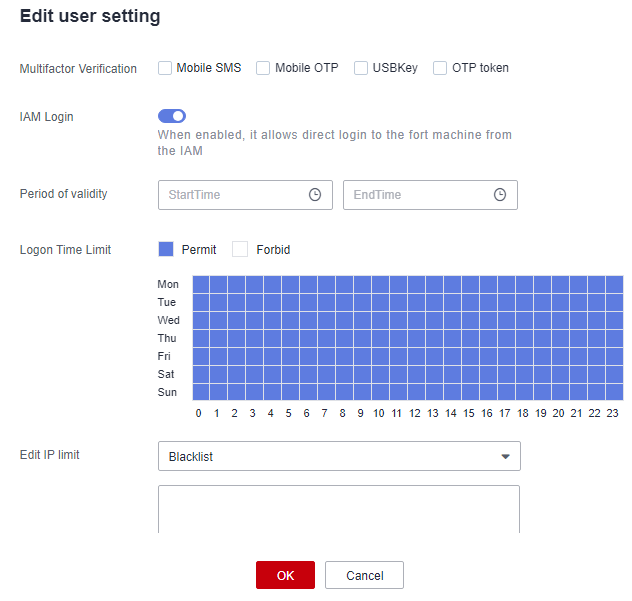
- DJCP article: Response measures to login failures, including stopping sessions, restricting the number of illegal logins, and automatically logging off expired network connections, shall be configured and enabled.
You can configure a security lock for user login, including the lock mode, lock duration, and maximum number of password attempts.
Figure 8 User login lockout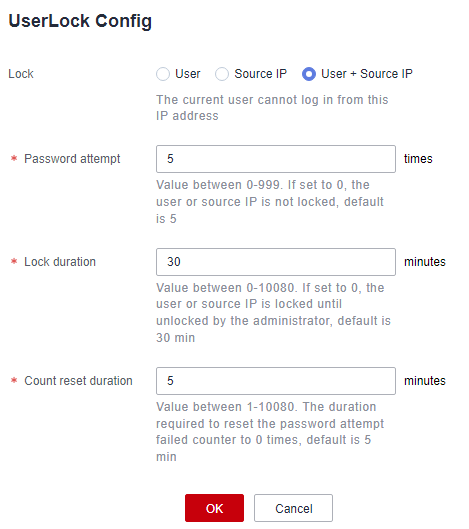
Access Control
- DJCP article: The minimum permissions shall be granted to management users to implement separation of privilege.
CBH supports three types of user operation permissions: access control, command control, and database control policies.
- CBH can control some operation permissions based on login user roles. For example, you can grant the permission to delete and modify proxy servers to the O&M manager account.
Figure 9 Fine-grained role permissions
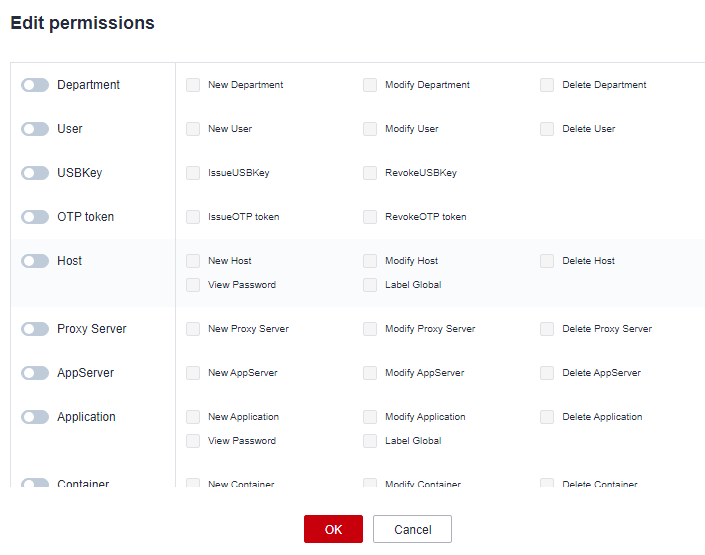
- You can control access to specific functions, such file management, upstream clipboard, downstream clipboard, watermark display, login time control, file upload, and file download. You can also allow or block the users of certain source IP addresses to access managed resources.
Figure 10 ACL Rules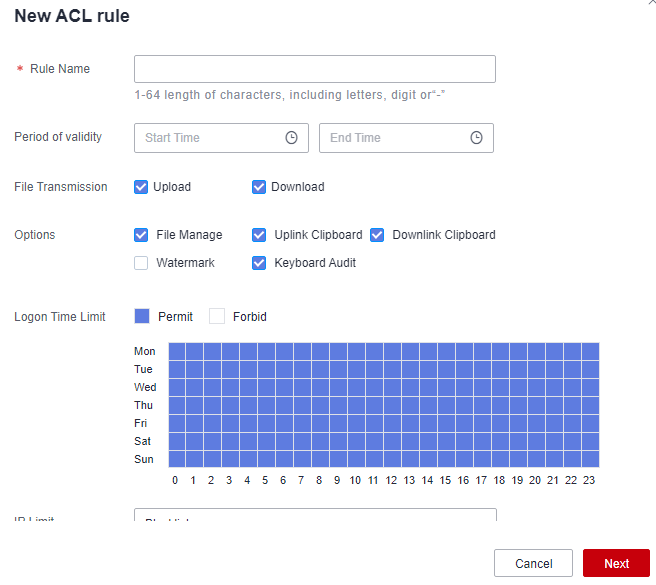
- CBH can control some operation permissions based on login user roles. For example, you can grant the permission to delete and modify proxy servers to the O&M manager account.
- DJCP article: Appropriate accounts and permissions shall be assigned to login users.
CBH allows you to assign roles to users and create user groups for users. For details, see User Role Management and CBH User Group Management in the Cloud Bastion Host User Guide.
Accounts that have not been used for a long time or have expired should be deleted in a timely manner. You can set a validity period for each CBH system user. Once the validity period expires, the corresponding account will be disabled as a zombie user.
Figure 11 Zombie user identification rule
Security Audits
- DJCP article: The security audit function must be provided for each user to audit important security incidents and user behavior.
CBH allows you to view real-time sessions, historical sessions, and system logs.
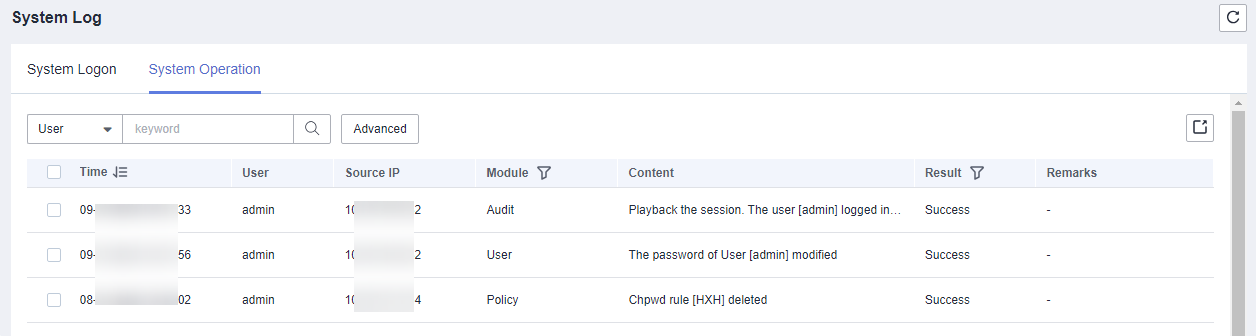
You can view system login logs, including the login time, login user, source IP address, log content, login mode, login result, and remarks.Figure 12 System logon logs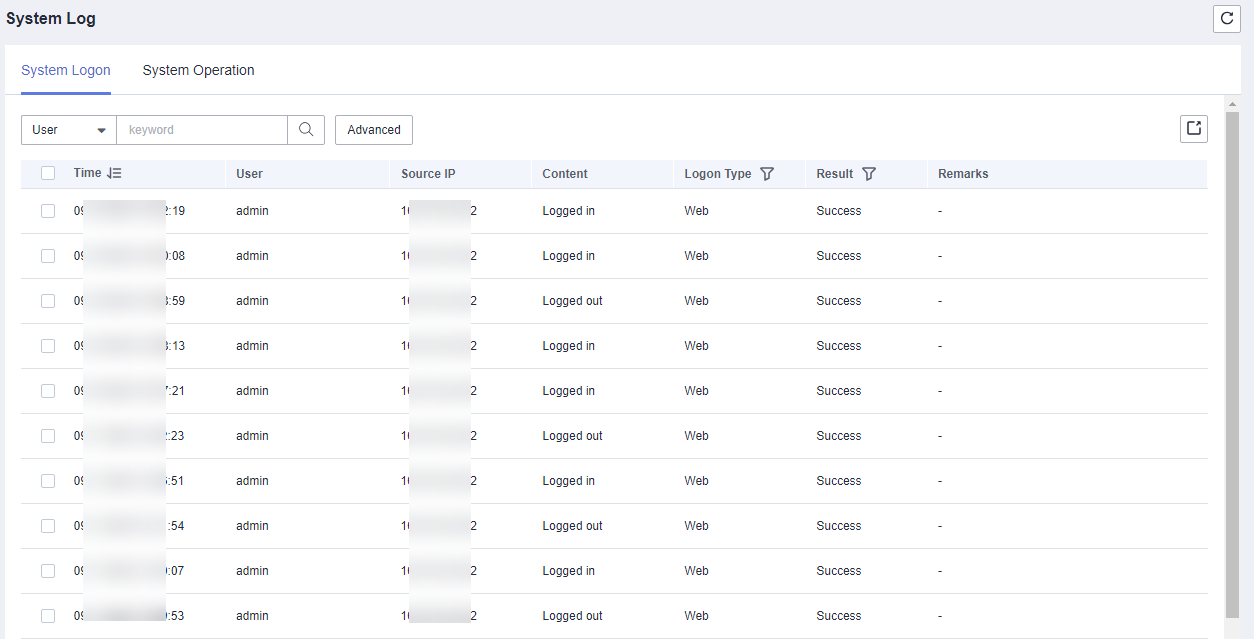
- DJCP article: Audit records shall include the event date and time, users, event types, whether the events succeeded, and other related audit information.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot