Connecting Services to AAD
Emergent Connection
If your service has been attacked or the origin server IP address has been blackholed before being connected to AAD, you are advised to handle the problem by referring to Table 1 when connecting your service to AAD.
If your service has been attacked before being connected to AAD, you are advised to change the IP address of the origin server. Prior to changing the IP address, verify if the client or application is hard-coded to the origin server's IP. Should this be the case, ensure you update the code within the client or application accordingly. This step is crucial to avoid any disruption in service accessibility following the IP address change. For details, see Changing an EIP.
|
Application scenarios |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Services are under DDoS attacks. |
Generally, after services are connected to AAD, they are protected based on the default protection configuration. |
|
The origin server IP address has been blackholed. |
If the origin server has been attacked and blackholed before being connected to AAD, change the origin server IP address in a timely manner. If your origin server is a Huawei Cloud load balancer, change the EIP of the load balancer. For details, see Changing an EIP.
NOTICE:
|
Prerequisites
- Services have been reviewed and preparations have been made accordingly.
- Domain name services have been connected to WAF.
Procedure
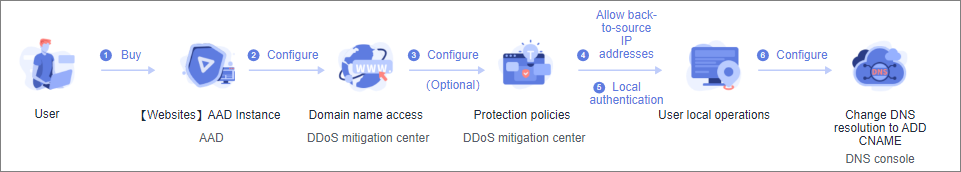
- Buy an AAD instance.
- If your service server is deployed in Chinese mainland, purchase an AAD instance.

- AAD instances do not support domain names that are not licensed by ICP. To use AAD to protect website services, ensure that the website domain name has an ICP license.
- AAD instances provide high-defense IPv4 addresses by default. If you need an IPv6 high-defense IP address, purchase a CNAD instance.
- If your service server is deployed outside the Chinese mainland and your primary user base is within, please note that the AAD (international edition) does not guarantee optimal access quality. Chinese mainland users may experience an average latency of approximately 300 ms. To enhance user experience, consider implementing these solutions:
If you only need to ensure the service access speed and stability for users of China Telecom, China Unicom, and other non-China Mobile lines in the Chinese mainland, you can purchase AAD with preferred lines (without protection).
- If your service server is deployed in Chinese mainland, purchase an AAD instance.
- Connect services to the AAD. For details, see Connecting Domain Name Services to the AAD.
- To prevent malicious attackers from bypassing Advanced Anti-DDoS to attack origin servers, you are advised to configure origin server protection.
For details about origin server protection, see Configuring Origin Server Protection.
- Configure protection policies against CC attacks.
- Services are not under attacks.
After connecting website services to AAD, you are recommended to examine the service application logs, which encompass URLs and the average access QPS per source IP, following a brief operational period (typically 2-3 days). Assess the normal QPS for individual source IP requests and establish frequency control along with custom rate limiting policies to proactively mitigate the impact of attacks.
- Services are under CC attacks.
Accessing AAD defense logs allows you to identify top URLs, IP addresses, source IPs, and user agents of domain-based requests. You can use such information to define frequency control rules and monitor the defense outcomes.
If the protection is not satisfying, it is recommended to consider acquiring Managed Detection Response to help you further analyze logs and formulate protection policies.
- Services are not under attacks.
- Verify the accuracy the configuration locally.
After the AAD protection policy is configured, you are advised to check whether the AAD configurations are correct by referring to Table 2 and Table 3.
For details about local verification, see Local Verification.
Table 2 Service verification items Service Type
Verification Item Description
Domain name services
Check whether the domain name configuration is correct.
Check whether the domain name is licensed.
Check whether the protocol configured for connecting to AAD is the same as the actual protocol.
Check whether the port configured for connecting to AAD is the same as the actual port.
Check whether the entered origin server IP is the real server IP address.
Check whether the certificate information is correctly uploaded.
Check certificate validity, such as ensuring compliance with encryption algorithm standards or confirming that the certificates correspond to correct domain names.
Check whether the certificate chain is complete.
Make sure you understand the elastic protection billing mode of AAD instances.
Check whether the WebSocket and WebSockets protocols are enabled.
Table 3 Service availability verification items Verification Item Type
Verification Item
Mandatory
Check whether services can be accessed normally.
Mandatory
Test the sticky session upon service login.
Mandatory
(For domain name services) Check the number of times that the service returns 4XX and 5XX response codes and ensure that the back-to-origin IP addresses are not blocked.
Suggestion
Check whether the backend server is configured to capture the true source IP address of incoming traffic.
Suggestion
(For domain name services) Check whether origin server protection is configured to prevent attackers from bypassing AAD to directly attack origin servers.
Mandatory
Check whether the TCP service ports can be accessed normally.
- Switch service traffic.
Upon successful local verification, it is advisable to sequentially update DNS resolution records and switch web service traffic to AAD, thereby mitigating the risk of service disruptions due to simultaneous changes. If an exception occurs during traffic switching, quickly restore DNS resolution records.

- After a DNS resolution record is modified, it takes about 10 minutes for the modification to take effect.
- After service traffic is switched, you need to perform the preceding service availability verification items again to ensure that services are running properly.
- Enable alarm notifications.
Once AAD alarm notifications are enabled, you will receive alarm notifications (via your chosen method of communication) under the following conditions to promptly identify any service exceptions.
Routine Maintenance Items After AAD Is Connected
After services are connected to AAD, you are advised to perform routine maintenance by referring to Table 4.
|
Maintenance Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Postpayment for elastic protection |
Before activating AAD's elastic protection feature, review the AAD pricing structure to ensure that the costs for elastic protection remain within your budget. For pricing details, see Product Pricing Details. |
|
Attack type identification |
If AAD suffers from both CC and DDoS attacks, you can view AAD protection logs to determine the attack type based on the attack traffic information.
|
|
Service access delay or packet loss |
If your origin server is situated outside of the Chinese mainland while your primary user base is within, experiencing significant delays or packet loss during access may indicate instability in the connection due to cross-network carrier issues. You are advised to purchase an AAD instance (international version) and choose an accelerated service line. |
|
Deletion of domain names or port forwarding configurations |
If you want to delete the port forwarding configuration record of a protected domain name, check whether the service has been connected to AAD.
NOTE:
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





