Security Orchestration Overview
Security orchestration combines security functions of different systems or components in a system involved in security operations of enterprises and organizations based on certain logical relationships to complete a specific security operations process and procedure. It aims to help security teams of enterprises and organizations quickly and efficiently respond to network threats and implement efficient and automatic response and handling of security incidents.
In security orchestration, playbooks and workflows are core elements. They are associated, dependent on each other, and work together to enable efficient security operations. The following describes how they work together:
- Definition:
- A playbook is a formal representation of the security operations workflow in a security orchestration system. A playbook converts the security operations workflows and procedures into a machine-readable work flow. A playbook is a predefined, structured response plan used to handle specific types of incidents or threats. A playbook explicitly lists the steps and actions to be taken under certain trigger conditions, such as the detection of a specific security incident.
Playbooks embody the logic of security protection controls and schedule security capabilities. Playbooks are flexible and scalable. They can be modified and extended based on actual requirements to adapt to ever-changing security threats and service requirements.
A playbook can have only one workflow.
- A workflow is a collaborative work mode that integrates various capabilities related to security operation, such as tools, technologies, workflows, and personnel. It consists of multiple connected components. After defined in a workflow, these components can be triggered externally. For example, when a new service ticket is generated, the automatic service ticket review workflow is automatically triggered. You can use the visual canvas to define component actions for each node in a workflow.
A workflow is a response mode when a playbook is triggered. Workflows convert instructions and procedures in the corresponding playbook into specific actions and execution steps.
- A playbook is a formal representation of the security operations workflow in a security orchestration system. A playbook converts the security operations workflows and procedures into a machine-readable work flow. A playbook is a predefined, structured response plan used to handle specific types of incidents or threats. A playbook explicitly lists the steps and actions to be taken under certain trigger conditions, such as the detection of a specific security incident.
- Relationships and differences
- Relationship: A playbook provides guidance and rules for secure operations, and its workflow is responsible for converting these rules into specific execution steps and actions. A playbook and its workflow depend on each other. The playbook guides the execution of the workflow, while the workflow implements the intent and requirements of the playbook.
- Differences: There are also some differences between playbooks and workflows. First, playbooks focus more on defining and describing security operation processes and regulations, so they focus on the overall framework and policies. Workflows focus more on specific actions and execution steps, so they focus on how to convert requirements in playbooks into actual actions. Second, playbooks are flexible and scalable, and can be modified and extended as required. However, workflows are relatively fixed. Once the design is complete, they need to follow the specified steps.
Example: Take a specific cyber security incident response case as an example. When an organization suffers from a network attack, the security orchestration system first identifies the attack type and severity based on the preset playbook. Then, the system automatically triggers corresponding security measures based on the workflow defined in the playbook, such as isolating the attacked system, collecting attack data, and notifying the security team. During the process, playbooks and workflows work closely to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of security responses.
Security Orchestration Process
The process of using security orchestration is as follows.
|
No. |
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
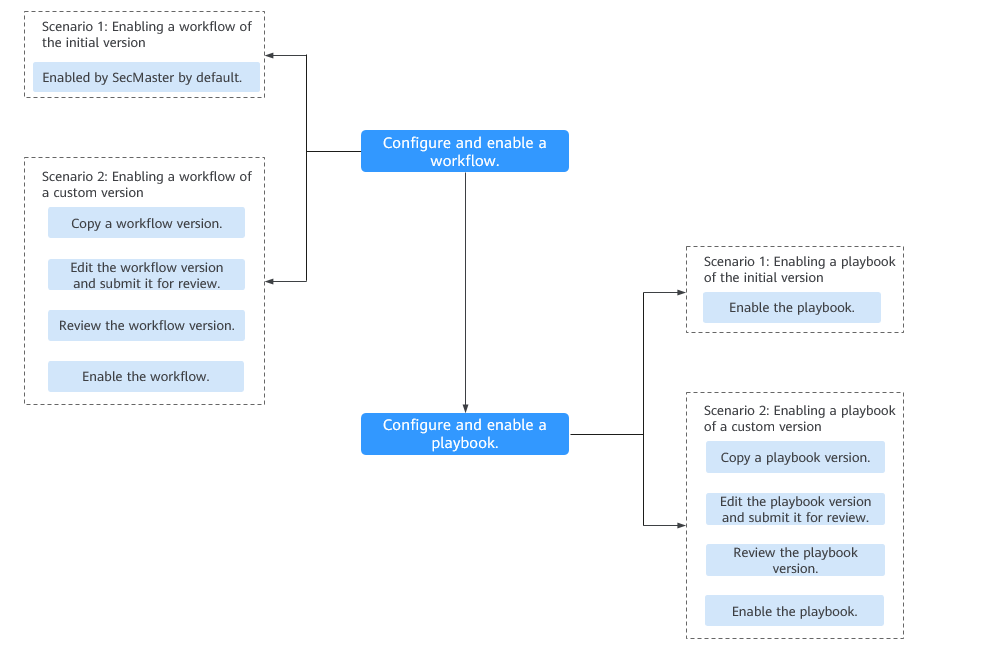
A workflow determines how a playbook responds to threats when it is triggered. SecMaster provides some preconfigured workflows, such as WAF one-click unblocking, HSS alert synchronization, and alert metric extraction. Workflows can be enabled in the following scenarios:
|
|
|
2 |
A playbook describes how SecMaster handles a type of security issues. Playbooks express security operations process of SecMaster in the entire security orchestration system. By default, SecMaster provides playbooks such as Fetching indicator from alert, Synchronization of HSS alert status, and Automatic closing of repeated alerts. The initial version (V1) of the playbooks has been activated. You only need to enable them. If you need to edit a playbook, you can copy the initial version and edit it. Playbooks can be enabled in the following scenarios:
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





