Scaling Out or In an Elastic Resource Pool
Scaling out or in an elastic resource pool essentially means adjusting the actual CUs of the resource pool.
In an elastic resource pool:
- Actual CUs: actual size of resources currently allocated to the elastic resource pool (in CUs). That is, the number of compute resources actually owned.
The actual CUs used by an elastic resource pool are billed as follows:
- If pay-per-use billing is used, you are billed based on the number of actual CUs. Refer to Elastic Resource Pool Billing Modes.
- If yearly/monthly billing is used, the specifications are billed on a yearly/monthly basis, and the difference between the actual CUs and the specifications (actual CUs – specifications) is billed on a pay-per-use basis. To achieve more cost-effective billing, you can change the specifications of the elastic resource pool to match the actual CUs. This ensures that all actual CUs are billed on a yearly/monthly basis, resulting in overall cost savings compared to the original method. Detailed instructions can be found in Modifying Elastic Resource Pool Specifications.
- Elastic resource pool scaling out: It involves increasing the actual CUs, meaning increasing the number of compute resources within the resource pool. The upper limit for this expansion corresponds to the maximum value specified in the CU range of the elastic resource pool.
- Elastic resource pool scaling in: It involves decreasing the actual CUs, meaning decreasing the number of compute resources within the resource pool. The lower limit for this reduction corresponds to the minimum value specified in the CU range of the elastic resource pool.
That is, the actual CUs of the elastic resource pool dynamically change between the minimum value and the maximum value of the CU range.
For more information about basic concepts of elastic resource pools, see Basic Concepts.
Notes and Constraints
- Creating or deleting queues within an elastic resource pool triggers elastic resource scaling.
- Scaling in an elastic resource pool may affect nodes containing shuffle data, leading to the recomputation of Spark tasks. This causes automatic retries for Spark and SQL jobs, and if the retries exceed the limit, the job execution fails, requiring you to rerun the job.
- Spark 2.3 jobs need to be upgraded to a later Spark version to support dynamic scale-in of the jobs while they are running.
- Spark Streaming and Flink jobs cannot be scaled in while they are running. To perform a scale-in, suspend the jobs or migrate them to another elastic resource pool.
- Scale-out and scale-in triggered by the following operations take effect at the next full hour after the operations are performed:
- Adjusting the CU range of a queue
- Modifying the specifications of an elastic resource pool
- Setting CUs for an elastic resource pool
- You can add queues to adjust the actual CUs of an elastic resource pool. The adjustment takes effect immediately.
Triggering Methods for Scaling Out or In an Elastic Resource Pool
|
Operation |
Actual CU Change |
Trigger Method |
|---|---|---|
|
Scaling out |
Actual CUs increase. |
max{(min[sum(maximum CUs of queues), maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool]), minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool} > current actual CUs, the system automatically scales out. |
|
Scaling in |
Actual CUs decrease. |
max{(min[sum(maximum CUs of queues), maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool]), minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool} < current actual CUs, the system automatically scales in. |
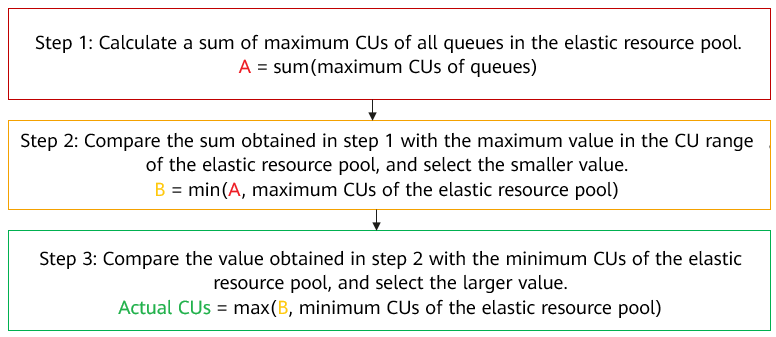
For details, see Figure 1.
Formula for Calculating Actual CUs of an Elastic Resource Pool
The actual CUs of an elastic resource pool must meet the following requirements:
- Meet the demands of all queues.
- Ensure that it does not exceed the upper limit of the CUs of the elastic resource pool.
- Ensure that it is not below the lower limit of the CUs of the elastic resource pool.
Examples
This part provides examples of scaling out and scaling in elastic resource pools under different billing modes.
- Scenario:
- Current specifications of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs
- CU range of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs to 128 CUs
- Actual CUs of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs
- Objective of the elastic resource pool: 128 CUs
- Procedure:
- Increase the maximum CUs of existing queues or create new queues to ensure that the total CUs of the queues are 128 CUs.
At the next full hour, the system automatically compares the actual CUs with max{(min[sum(maximum CUs of queues), maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool]), minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool}.
If max{(min[sum(maximum CUs of queues), maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool]), minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool} > current actual CUs, the system triggers scale-out. The calculation method for the actual CUs after scale-out can be found in Figure 1.
- Change the specifications of the elastic resource pool.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resources > Resource Pool.
- Locate the elastic resource pool you want to scale out, click More in the Operation column, and select Modify Yearly/Monthly CU.
- On the Modify Yearly/Monthly CU page, set Operation to Scale-out and adjust the specifications from 64 CUs to 128 CUs.
- The actual CUs become 128 CUs, and the minimum value of the CU range is automatically synchronized to 128 CUs.
- Increase the maximum CUs of existing queues or create new queues to ensure that the total CUs of the queues are 128 CUs.
- Result:
Actual CUs of the elastic resource pool: 128 CUs
CU range of the elastic resource pool: 128 CUs to 128 CUs
- Scenario:
- Current specifications of the elastic resource pool: 128 CUs
- CU range of the elastic resource pool: 128 CUs to 128 CUs
- Actual CUs of the elastic resource pool: 128 CUs
- Objective of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs
- Procedure:
- Reduce the maximum CUs of the queues or delete some queues so that the total CUs of the queues equal 64 CUs.
At the next full hour, the system automatically compares the actual CUs with max{(min[sum(maximum CUs of queues), maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool]), minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool}.
If max{(min[sum(maximum CUs of queues), maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool]), minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool} < current actual CUs, the system triggers scale-in. However, since the specifications remain at 128 CUs, the actual CUs will not automatically decrease.
Therefore, you need to proceed with the next steps.
- Change the specifications of the elastic resource pool from 128 CUs to 64 CUs.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resources > Resource Pool.
- Locate the elastic resource pool you want to scale out, click More in the Operation column, and select Modify Yearly/Monthly CU.
- On the Modify Yearly/Monthly CU page, set Operation to Scale-in and adjust the specifications from 128 CUs to 64 CUs.
- Manually change the CU range of the elastic resource pool to 64 CUs to 128 CUs.
- The actual CUs change to 64 CUs (the change takes effect at the next full hour).
- Reduce the maximum CUs of the queues or delete some queues so that the total CUs of the queues equal 64 CUs.
- Result:
Actual CUs of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs
CU range of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs to 128 CUs
- Scenario:
- CU range of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs to 128 CUs
- Actual CUs of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs
- Objective of the elastic resource pool: 96 CUs
- Procedure:
- Increase the maximum CUs of existing queues or create new queues to ensure that the total CUs of the queues are 96 CUs.
- The system triggers scale-out. The actual CUs change to max{(min[sum(maximum CUs of queues), maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool]), minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool}.
- The actual CUs automatically increase to 96 CUs.
- Result:
- Actual CUs of the elastic resource pool: 96 CUs
- CU range of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs to 128 CUs
The actual CUs of the pay-per-use resource pool dynamically change with the total CUs of queues.
- Scenario
- CU range of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs to 128 CUs
- Actual CUs of the elastic resource pool: 96 CUs
- Objective of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs
- Procedure
- Reduce the maximum CUs of the queues or delete some queues so that the total CUs of the queues equal 64 CUs.
- The system triggers scale-in. The actual CUs decrease to max{(min[sum(maximum CUs of queues), maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool]), minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool}.
- The actual CUs automatically decrease to 64 CUs.
- Result:
- Actual CUs of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs
- CU range of the elastic resource pool: 64 CUs to 128 CUs
Scaling in a pay-per-use resource pool also does not require manual specification changes.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot