Creating an Elastic Resource Pool and Creating Queues Within It
An elastic resource pool offers compute resources (CPU and memory) required for running DLI jobs, which can adapt to the changing demands of services.
You can create multiple queues within an elastic resource pool. These queues are associated with specific jobs and data processing tasks, and serve as the basic unit for resource allocation and usage within the pool. This means queues are specific compute resources required for executing jobs.
Queues within an elastic resource pool can be shared to execute jobs. This is achieved by correctly setting the queue allocation policy. This enhances queue utilization. This section describes how to create an elastic resource pool and create queues within it.
DLI elastic resource pools are physically isolated, while queues within the same elastic resource pool are logically isolated.
You are advised to create separate elastic resource pools for testing and production scenarios to ensure the independence and security of resource management through physical isolation.
Notes and Constraints
Creating an Elastic Resource Pool
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resources > Resource Pool.
- On the displayed page, click Buy Resource Pool in the upper right corner.
- On the displayed page, set the following parameters:
Table 2 Parameter descriptions Parameter
Description
Region
Select a region where you want to buy the elastic resource pool. A region refers to the location of the physical data center of an elastic resource pool. Select a region near you to ensure the lowest latency possible.
Project
Each region corresponds to a project.
Name
Name of the elastic resource pool.
- Only digits, letters, and underscores (_) are allowed. The value cannot contain only digits or start with an underscore (_) or digit.
- The value can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
NOTE:The elastic resource pool name is case-insensitive. Uppercase letters will be automatically converted to lowercase letters.
Type
- Basic edition: offers 16 CUs to 64 CUs
- This edition is suitable for testing scenarios with low resource consumption and low requirements for resource reliability and availability.
- High reliability and availability are not supported.
- Job priorities cannot be set.
- Standard edition: offers at least 64 CUs
This edition offers powerful computing capabilities, high availability, and flexible resource management. It is suitable for large-scale computing tasks and business scenarios with long-term resource planning needs.
CU Range
The maximum and minimum CUs allowed for the elastic resource pool.
CU settings are used to control the maximum and minimum CU ranges for elastic resource pool scaling to prevent unlimited resource expansion risks.
In CU Range, set the minimum CUs on the left and the maximum CUs on the right.
- The total minimum CUs of all queues in an elastic resource pool must be no more than the minimum CUs of the pool.
- The maximum CUs of any queue in an elastic resource pool must be no more than the maximum CUs of the pool.
An elastic resource pool should at least ensure that all queues in it can run with the minimum CUs and should try to ensure that all queues in it can run with the maximum CUs.
The specifications (yearly/monthly CUs) of an elastic resource pool are equal to the minimum CUs allocated during creation. This means that when the elastic resource pool is first created, the actual CUs will be equal to the specifications, which is also the minimum CUs.
Description
Description of the elastic resource pool
CIDR Block
CIDR block the elastic resource pool belongs to. If you use an enhanced datasource connection, this CIDR block cannot overlap that of the data source. Once set, this CIDR block cannot be changed.
Recommended CIDR blocks:
10.0.0.0–10.255.0.0/16–19
172.16.0.0–172.31.0.0/16–19
192.168.0.0–192.168.0.0/16–19
IPv6
After IPv6 is enabled, the elastic resource pool can communicate with data sources (the CIDR block of which have IPv6 enabled) using IPv6 addresses.
If IPv6 is enabled, an IPv6 CIDR block will be automatically allocated to the elastic resource pool.
- IPv6 can only be enabled during creation.
- After enabling, both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses will be available, allowing for both private and public network access. IPv6 cannot be used independently.
- The IPv6 CIDR block cannot be specified; it is allocated by the system.
- IPv6 cannot be disabled after being enabled.
Enterprise Project
If the created elastic resource pool belongs to an enterprise project, select the enterprise project.
Enterprise projects let you manage cloud resources and users by project.
For how to set enterprise projects, see Enterprise Management User Guide.
NOTE:This parameter is available only for users who have subscribed to the Enterprise Management Service.
Tags
Tags used to identify cloud resources. A tag includes the tag key and tag value. If you want to use the same tag to identify multiple cloud resources, that is, to select the same tag from the drop-down list box for all services, you are advised to create predefined tags on the Tag Management Service (TMS).
If your organization has configured tag policies for DLI, add tags to resources based on the policies. If a tag does not comply with the tag policies, resource creation may fail. Contact your organization administrator to learn more about tag policies.
For details, see Tag Management Service User Guide.
NOTE:- A maximum of 20 tags can be added.
- Only one tag value can be added to a tag key.
- The key name in each resource must be unique.
- Tag key: Enter a tag key name in the text box.
NOTE:
A tag key can contain a maximum of 128 characters. Only letters, digits, spaces, and special characters (_.:+-@) are allowed, but the value cannot start or end with a space or start with _sys_.
- Tag value: Enter a tag value in the text box.
NOTE:
A tag value can contain a maximum of 255 characters. Only letters, digits, spaces, and special characters (_.:+-@) are allowed.
- Click Buy and confirm the configurations.
- Click Pay. Wait until the status of the elastic resource pool changes to Available. The elastic resource pool is successfully created.
- Refer to Example Use Case: Creating an Elastic Resource Pool and Running Jobs and Example Use Case: Configuring Scaling Policies for Queues in an Elastic Resource Pool to perform subsequent operations as needed.
Creating Queues Within an Elastic Resource Pool
Create one or more queues within an elastic resource pool to run jobs. This section describes how to create a queue within an elastic resource pool.
Queues added to an elastic resource pool are not billed separately, but billed as billing items of the elastic resource pool.
Creating a queue within an elastic resource pool will trigger changes of elastic resource CUs.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resources > Resource Pool.
- Locate the elastic resource pool in which you want to create queues and click Add Queue in the Operation column.
- On the Add Queue page, set basic queue parameters based on the table below.
Table 3 Basic parameters for adding a queue Parameter
Description
Name
Name of the queue to add
Type
- For SQL: The queue is used to run SQL jobs.
- For general purpose: The queue is used to run Spark and Flink jobs.
Engine
If Type is For SQL, the queue engine can be Spark or HetuEngine.
If HetuEngine is selected, the minimum number of CUs of the SQL queue cannot be fewer than 96 CUs.
To use HetuEngine to submit SQL jobs, you need to configure a DLI job bucket. For details, see Configuring a DLI Job Bucket.
Enterprise Project
Select the enterprise project the queue belongs to. Queues under different enterprise projects can be added to an elastic resource pool.
Enterprise projects let you manage cloud resources and users by project.
For how to set enterprise projects, see Enterprise Management User Guide.
NOTE:This parameter is available only for users who have subscribed to the Enterprise Management Service.
Description
Description about the queue.
Tags
Tags used to identify cloud resources. A tag includes the tag key and tag value. If you want to use the same tag to identify multiple cloud resources, that is, to select the same tag from the drop-down list box for all services, you are advised to create predefined tags on the Tag Management Service (TMS).
If your organization has configured tag policies for DLI, add tags to resources based on the policies. If a tag does not comply with the tag policies, resource creation may fail. Contact your organization administrator to learn more about tag policies.
For details, see Tag Management Service User Guide.
NOTE:- A maximum of 20 tags can be added.
- Only one tag value can be added to a tag key.
- The key name in each resource must be unique.
- Tag key: Enter a tag key name in the text box.
NOTE:
A tag key can contain a maximum of 128 characters. Only letters, digits, spaces, and special characters (_.:+-@) are allowed, but the value cannot start or end with a space or start with _sys_.
- Tag value: Enter a tag value in the text box.
NOTE:
A tag value can contain a maximum of 255 characters. Only letters, digits, spaces, and special characters (_.:+-@) are allowed.
- Click Next. On the displayed page, configure a scaling policy for the queue in the elastic resource pool.
Figure 1 Configuring a scaling policy when adding a queue
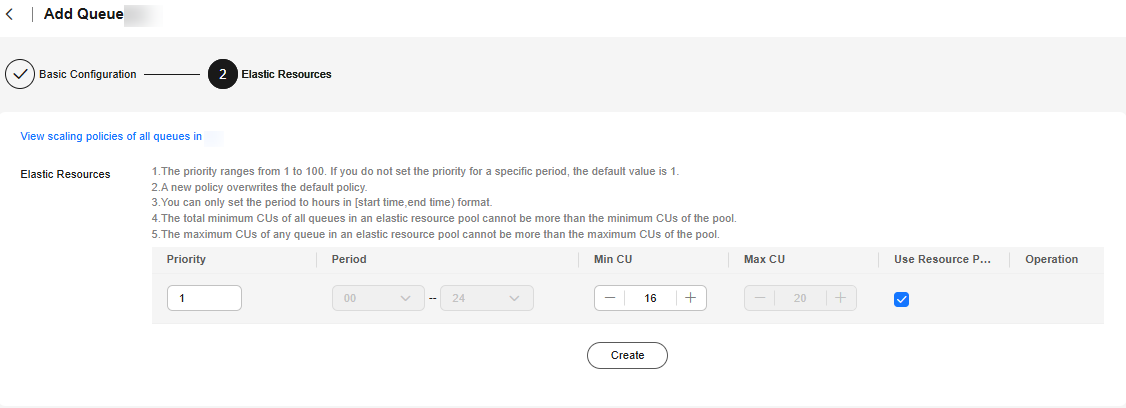
Click Create to add a scaling policy with varying priority, period, minimum CUs, and maximum CUs. The parameters of each scaling policy are:
Table 4 Scaling policy parameters Parameter
Description
Priority
Priority of the scaling policy in the current elastic resource pool. A larger value indicates a higher priority. You can set a number ranging from 1 to 100.
Period
Time segment when the policy takes effect. It can be set only by hour. The start time is on the left, and the end time is on the right.
- The time range includes the start time but not the end time, that is, [start time, end time).
For example, if you set Period to 01 and 17, the scaling policy takes effect at 01:00 a.m. till 05:00 p.m.
- The periods of scaling policies with different priorities should not overlap.
Min CU
Minimum number of CUs allowed by the scaling policy.
- In any time segment of a day, the total minimum CUs of all queues in an elastic resource pool cannot be more than the minimum CUs of the pool.
- If the minimum CUs of the queue are fewer than 16 CUs, both Max. Spark Driver Instances and Max. Prestart Spark Driver Instances set in the queue properties do not apply. Refer to Setting Queue Properties.
For a HetuEngine SQL queue, there must be at least 96 CUs.
Max CU
Maximum number of CUs allowed by the scaling policy.
In any time segment of a day, the maximum CUs of any queue in an elastic resource pool cannot be more than the maximum CUs of the pool.
- The maximum CUs of a queue in the elastic resource pool of the basic edition must be a multiple of 4.
- The maximum CUs of a queue in the elastic resource pool of the standard edition must be a multiple of 16.
Use Resource Pool's Max CU
When selected, the maximum CUs of queues equal the maximum CUs of the resource pool within the period specified by the current scaling policy.
Increasing the maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool automatically adjusts the queue's maximum CUs to match without manual intervention.
The setting takes effect only within the period specified by the current scaling policy. You need to manually configure CU limits for other periods.
- The first scaling policy is the default policy, and its Period parameter configuration cannot be deleted or modified.
- Flink jobs cannot trigger automatic scaling of queues in an elastic resource pool.
- The time range includes the start time but not the end time, that is, [start time, end time).
- Click OK. View all queues and scaling policies added to the elastic resource pool by referring to Adjusting Scaling Policies for Queues in an Elastic Resource Pool.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





