Step 2: Add an Agent
Add a new agent or choose an existing agent for the database to be audited, depending on your database type. The agent will obtain database access traffic, upload traffic statistics to the audit system, receive audit system configuration commands, and report database monitoring data.

Currently, only the following types of databases support agent-free installation: After the database is added, you do not need to install the agent and can directly go to Step 4: Add a Security Group Rule.
- RDS for SQLServer
- RDS for MySQL
- 5.6 (5.6.51.1 or later)
- 5.7 (5.7.29.2 or later)
- 8.0 (8.0.20.3 or later)
- GaussDB(DWS): 8.2.0.100 or later
- PostgreSQL
- 14 (14.4 or later)
- 13 (13.6 or later)
- 12 (12.10 or later)
- 11 (11.15 or later)
- 9.6 (9.6.24 or later)
- 9.5 (9.5.25 or later)
- RDS for MariaDB
Prerequisites
The database audit instance is in the Running state.
Scenarios
Determine where to add the agent based on how your database is deployed. Common database deployment modes are as follows:
- Deploy DBSS for databases built on ECS/BMS. For details, see Figure 1 and Figure 2.
- Deploy DBSS for RDS databases. For details, see Figure 3 and Figure 4.
Table 1 provides more details.

- If your applications and databases (databases built on ECS/BMS) are deployed on the same node, add the agent on the database side.
- For easier O&M, you can deploy the database audit agent in a large number of containerized applications or databases in batches. This makes configuration quicker and easier. For details, see Container-based database audit agent
|
Scenario |
Where to Add the Agent |
Audit Scope |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Databases built on ECS/BMS |
Database or application |
All access records of applications that have accessed the database |
|
|
RDS database |
Application (if applications are deployed on the cloud) |
Access records of all the databases connected to the application |
|
|
Proxy side (if applications are deployed off the cloud) |
Only the access records between the proxy and database. Those between the applications and database cannot be audited. |
|
Adding an Agent (User-built Databases on ECS/BMS)
- For details, see Step 1.
- Log in to the management console.
- Select a region, click
 , and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed.
, and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed. - In the navigation tree on the left, choose Databases.
- In the Instance drop-down list, select the instance whose agent is to be added.
- In the Agent column of the desired database, click Add.
Figure 5 Adding an agent
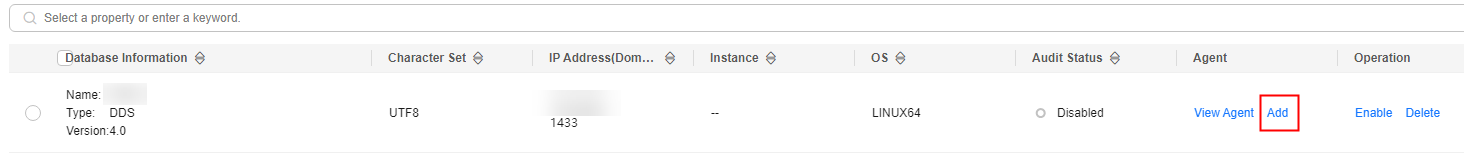
- In the displayed dialog box, select an add mode, as shown in Figure 6. For details about related parameters, see Table 2.
Table 2 Parameters for adding an agent (user-built databases on ECS/BMS) Parameter
Description
Example Value
Add Mode
Mode for adding an agent- Select an existing agent
If an agent has been installed on a database connected to the same application as the desired database, select Select an existing agent.
- Create an agent
If no agent is available, select Create an agent to create one.
Create an agent
Database Name
Optional. If you select Select an existing agent for Add Mode, you need to select a database that already has an agent.
test1
Agent ID
This parameter is mandatory when Add Mode is set to Select an existing agent.
Select an added agent ID of the instance. The agent ID is automatically generated by the system.
-
Installing Node Type
This parameter is mandatory when Add Mode is set to Create an agent.
When auditing user-installed databases on ECS/BMS, select Database or Application for Installing Node Type.
Database
Installing Node IP Address
This parameter is mandatory if Installing Node Type is set to Application. IP address of the application node to be audited. You can enter only one IP address.
The IP address must be the internal IP address of the application node. IPv4 and IPv6 formats are both supported.
192.168.1.1
OS
This parameter is mandatory when Add Mode is set to Create an agent.
OS of the database to be audited. The value can be LINUX64_x86 , LINUX64_Arm, or WINDOWS64.
NOTE:Select an OS version based on the server architecture.
LINUX64_X86
CPU Threshold (%)
Optional. CPU threshold of the application node to be audited. The default value is 80.
80
Memory Threshold (%)
Optional. Memory threshold of the application node to be audited. The default value is 80.
80
- Select an existing agent
- Click OK.
- In the Agent column of the desired database, click View Agent. In the Agents area, view information about the added agent.
Figure 7 Successfully adding an agent
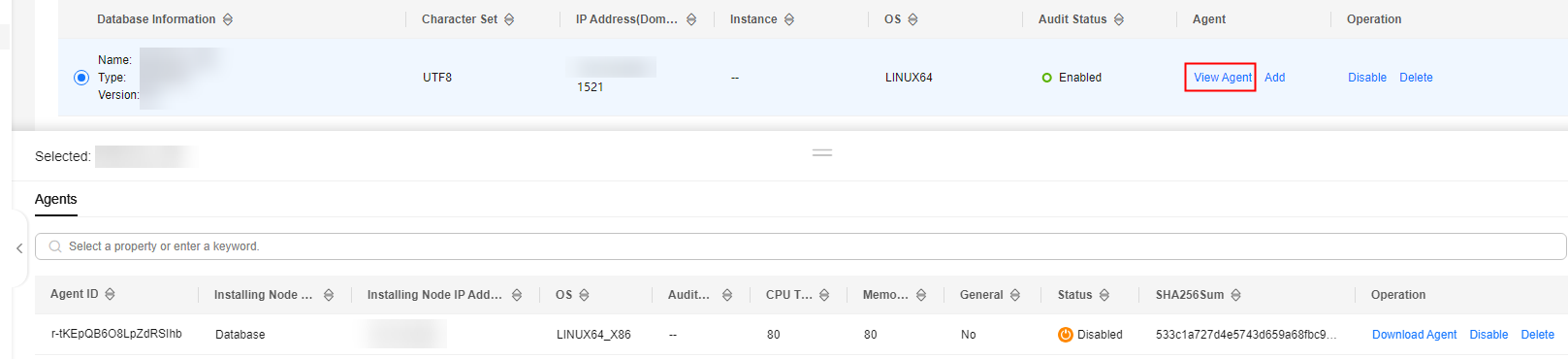

After adding the agent, confirm that the agent information is correct. If the agent is incorrectly added, click Delete in the Operation column of the row to delete it, and add an agent again.
Adding an Agent (RDS Databases)
If an application connects to multiple RDS databases, be sure to:
- Add an agent to each of the RDS databases.
- Select Select an existing agent if one of the databases already has an agent. Add that agent for the rest of the databases.
- For details, see Step 1.
- Log in to the management console.
- Select a region, click
 , and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed.
, and choose . The Dashboard page is displayed. - In the navigation tree on the left, choose Databases.
- In the Instance drop-down list, select the instance whose agent is to be added.
- In the Agent column of the desired database, click Add.
Figure 8 Adding an agent
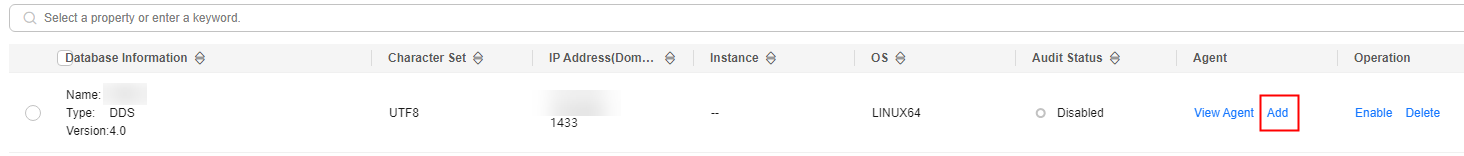
- In the displayed dialog box, select an add mode, as shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10. For details about related parameters, see Table 3.
- Select Select an existing agent for Add Mode.
For details about when you should select this option, see When Should I Select an Existing Agent?
- Set Add Mode to Create an agent.
If no agent is available, select Create an agent to create one.
Table 3 Parameters for adding an agent (RDS databases) Parameter
Description
Example Value
Add Mode
Mode for adding an agent- Selecting an existing agent
If an agent has been installed on a database connected to the same application as the desired database, select Select an existing agent.
- Create an agent
If no agent is available, select Create an agent to create one.
Create an agent
Database Name
Optional. If you select Select an existing agent for Add Mode, you need to select a database that already has an agent.
tesT
Agent ID
This parameter is mandatory when Add Mode is set to Select an existing agent.
Select an added agent ID of the instance. The agent ID is automatically generated by the system.
-
Installing Node Type
This parameter is mandatory when Add Mode is set to Create an agent.
To audit the RDS databases, select Application.
Application
Installing Node IP Address
This parameter is mandatory when Installing Node Type is set to Application. IP address of the application node to be audited. You can enter only one IP address.
The IP address must be the internal IP address of the application node. IPv4 and IPv6 formats are both supported.
NOTICE:To audit an RDS database connected to an off-cloud application, set this parameter to the IP address of the proxy.
192.168.1.1
Audited NIC Name
Optional. This parameter is configurable if Installing Node Type is set to Application.
Name of the network interface card (NIC) of the application node to be audited
-
CPU Threshold (%)
Optional. This parameter is configurable if Installing Node Type is set to Application.
CPU threshold of the application node to be audited. The default value is 80.
NOTICE:If the CPU usage of a server exceeds the threshold, the agent on the server will stop running.
80
Memory Threshold (%)
Optional. This parameter is configurable if Installing Node Type is set to Application.
Memory threshold of the application node to be audited. The default value is 80.
NOTICE:If the memory usage of your server exceeds the threshold, the agent will stop running.
80
OS
Optional. This parameter is configurable if Installing Node Type is set to Application.
OS of the application node to be audited. The value can be LINUX64_X86, LINUX64_ARM, or WINDOWS64.
LINUX64_X86
- Select Select an existing agent for Add Mode.
- Click OK.
- In the Agent column of the desired database, click View Agent. In the Agents area, view information about the added agent.
Figure 11 Successfully adding an agent


After adding the agent, confirm that the agent information is correct. If the agent is incorrectly added, click Delete in the Operation column of the row to delete it, and add an agent again.
Follow-Up Procedure
Configure TCP (port 8000) and UDP (ports 7000 to 7100) in the security group inbound rule of the agent node to allow the agent to communicate with the audit instance. For details about how to add a security group rule, see Adding a Security Group Rule.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot












