Overview
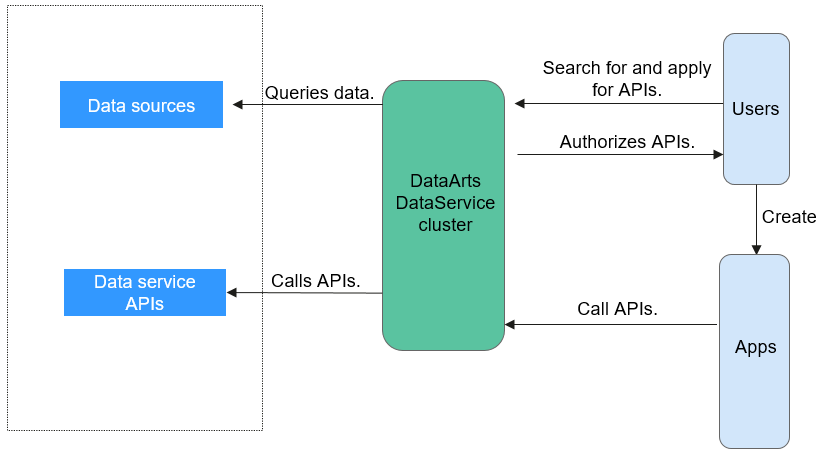
DataArts Studio DataArts DataService aims to build a unified data service bus for enterprises to centrally manage internal and external API services. DataArts DataService helps you quickly generate data APIs based on data tables and allows you manage the full lifecycle of APIs, covering API publishing, management, and O&M. With DataArts DataService, you can implement microservice aggregation, frontend-backend separation, and system integration, and provide functions and data for partners and developers easily and quickly at a low cost and risk.
- Unified interface standards reduce the workload for interconnection with upper-layer applications.
- Data logic is deployed on the data platform and is therefore decoupled from the application logic. This reduces repeated development of data models and avoids frequent changes caused by data logic adjustment.
- Data logic-related storage and compute resources are deployed on the data platform, reducing resource consumption on applications.
- A large amount of detailed and sensitive data is inaccessible to applications. In addition, DataArts DataService improves data security by means of API review and publishing, authentication and throttling, and dynamic anonymization.
DataArts DataService encapsulates data logic into RESTful APIs of a unified standard that can be used to access data. DataArts DataService applies to quick response to the requests for accessing a small amount of data. To open a large amount of data, you are advised to adopt data sharing and exchange or other solutions.
Publishing an API
- Managing Exclusive Clusters
If you want to use DataArts DataService, you must buy a DataArts DataService Exclusive cluster.
- Creating a Reviewer in DataArts DataService
Before creating an API, you need to create a reviewer.
- Creating an API
You can generate an API. An API can be generated using configuration or a script/MyBatis.
- Debugging an API
Debug the created API on the management console to check whether it runs properly.
- Publishing an API
The API can be called only after it is published.
- Managing APIs
You can manage the published API as needed.
- Orchestrating an API
API orchestration allows you to reorganize and reconstruct APIs in a visualized manner based on specific service logic and processes without compiling code. In this way, you can perform secondary development easily without affecting native APIs.
- (Optional) Configuring a Throttling Policy
To ensure the stability of backend services, you can perform throttling on the API.
- (Optional) Authorizing an API
An app defines the identity of an API caller. An API that uses app or IAM authentication must be authorized so that the authentication information for calling the API can be obtained.
Calling an API
- Obtain an API.
Obtain the API from the service catalog. An API can be called only after it is published.
- Applying for API Authorization
If you are an API developer and want to call an API which uses app or IAM authentication, you must apply for API authorization.
- Calling the API.
After completing the preceding steps, you can call the API.
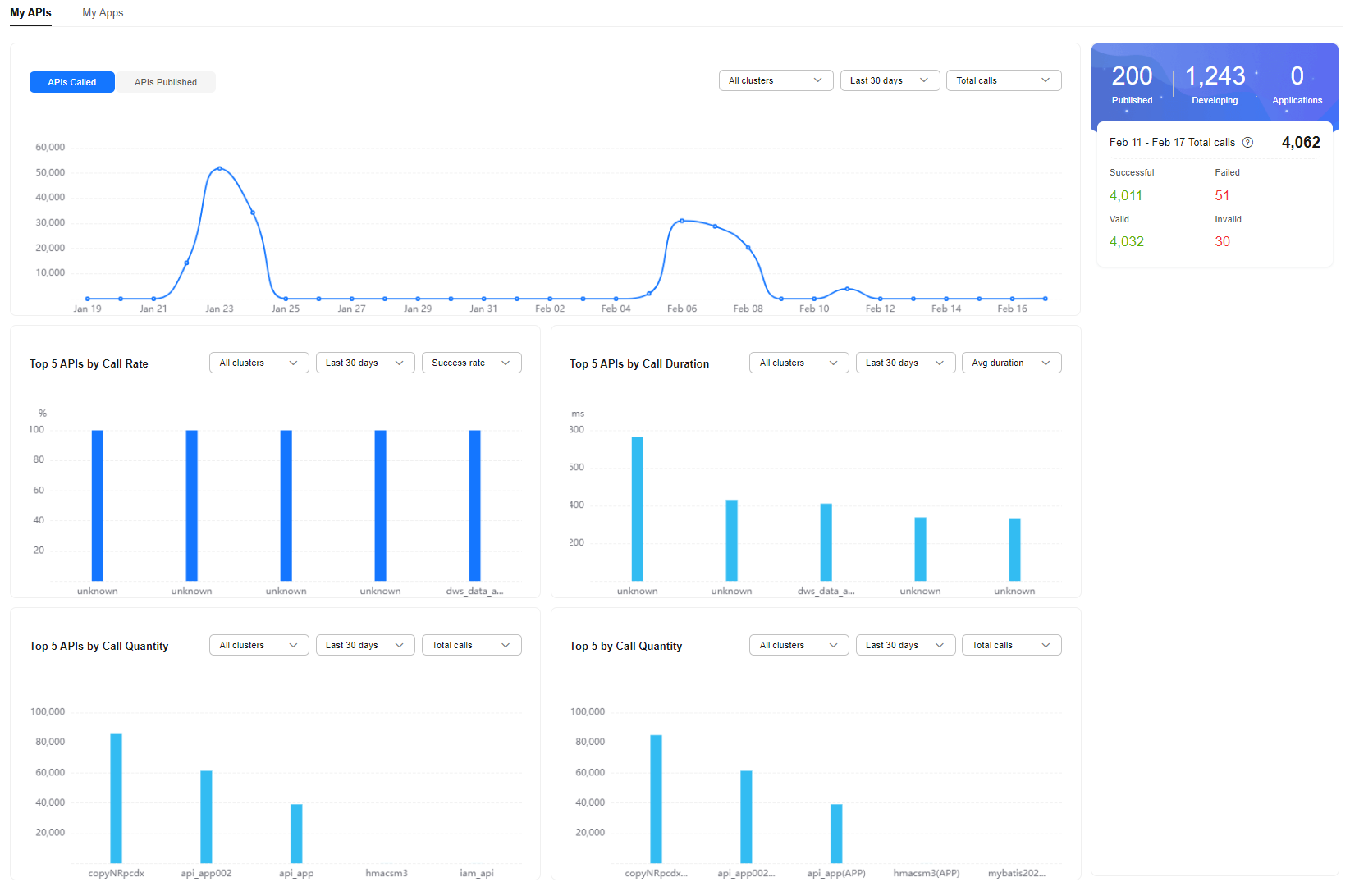
Overview Page
On the Overview page, you can view various monitoring data views. The Overview page displays information about APIs and apps.
|
Category |
Metric |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Data overview |
Published |
Number of APIs that have been published |
|
Developing |
Number of APIs that are being developed |
|
|
Applications |
Number of apps authorized by published APIs |
|
|
Total calls |
Number of calls to the APIs in all clusters over the last seven days (excluding the current day) |
|
|
Successful |
Number of successful API calls |
|
|
Failed |
Number of failed API calls |
|
|
Valid |
Number of valid API calls. Valid API calls refer to the calls that pass the verification. |
|
|
Invalid |
Number of invalid API calls. Invalid API calls refer to the calls that fail to pass the verification due to incorrect request parameters. |
|
|
Trend chart |
APIs Called |
Trend of the number of API calls in one or all clusters during a specified time period.
|
|
APIs Published |
Trend of the number of API publishing times in a specified time period
|
|
|
Top 5 statistics |
Top 5 APIs by Call Rate |
Top 5 APIs by call rate in one or all clusters during a specified time period
|
|
Top 5 APIs by Call Duration |
Top 5 APIs by call duration in one or all clusters during a specified time period
|
|
|
Top 5 APIs by Call Quantity |
Top 5 APIs by the number of calls in one or all clusters during a specified time period. (If an API is authorized to different apps, the number of calls made by those apps to the API is counted together.)
|
|
|
Top 5 by Call Quantity |
Top 5 APIs by the number of calls in one or all clusters during a specified time period. (If an API is authorized to different apps, the number of calls made by those apps to the API is counted separately.)
|
|
Category |
Metric |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Data overview |
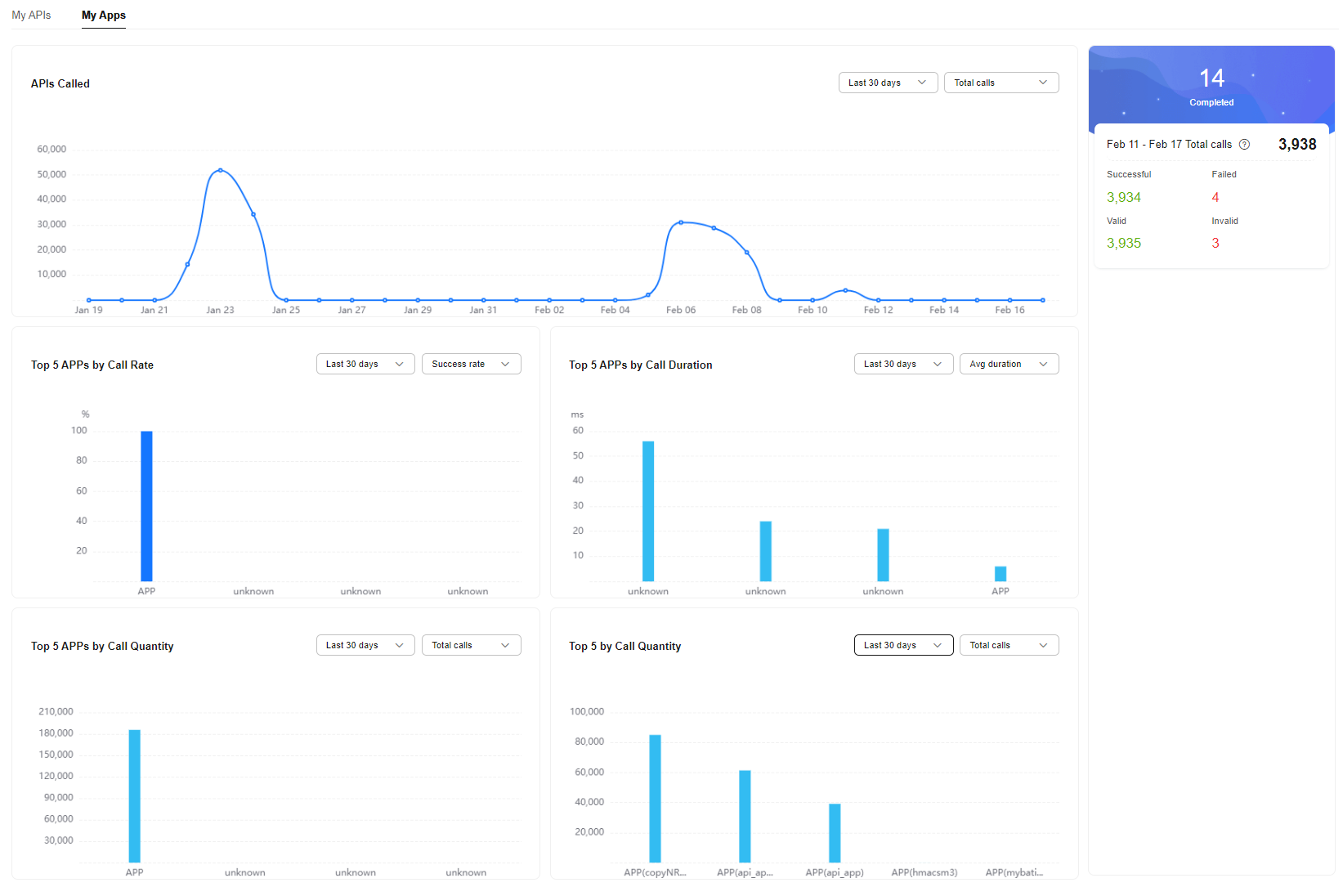
Completed |
Number of apps authorized by all APIs |
|
Total calls |
Number of calls to the APIs (that use app or IAM authentication) in all clusters over the last seven days (excluding the current day) |
|
|
Successful |
Number of successful calls to APIs that use app or IAM authentication. |
|
|
Failed |
Number of failed calls to APIs that use app or IAM authentication. |
|
|
Valid |
Number of valid calls to APIs that use app or IAM authentication. Valid API calls refer to the calls that pass the verification. |
|
|
Invalid |
Number of invalid calls to APIs that use app or IAM authentication. Invalid API calls refer to the calls that fail to pass the verification due to incorrect request parameters. |
|
|
Trend chart |
APIs Called |
Trend of the number of calls to APIs that use app or IAM authentication in all clusters during a specified time period.
|
|
Top 5 statistics |
Top 5 Apps by Call Rate |
Top 5 APIs (using app or IAM authentication) by call rate in all clusters during a specified time period
|
|
Top 5 Apps by Call Duration |
Top 5 APIs (using app or IAM authentication) by call duration in all clusters during a specified time period
|
|
|
Top 5 Apps by Call Quantity |
Top 5 APIs (using app or IAM authentication) by the number of calls in all clusters during a specified time period. (If an API is authorized to different apps, the number of calls made by those apps to the API is counted together.)
|
|
|
Top 5 by Call Quantity |
Top 5 APIs (using app or IAM authentication) by the number of calls in all clusters during a specified time period. (If an API is authorized to different apps, the number of calls made by those apps to the API is counted separately.)
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





