Enabling Lite Cluster Resources
ModelArts Lite Cluster is a dedicated resource pool in Huawei Cloud ModelArts. Targeting at Kubernetes resource users, it provides hosted Kubernetes clusters, pre-installs mainstream AI development plug-ins and Huawei-developed acceleration plug-ins, and provides users with AI native resources and tasks in cloud native mode. You can directly perform operations on nodes and Kubernetes clusters in the resource pool, applicable to scenarios where cloud native resources are required.
Differences between ModelArts Lite Cluster and ModelArts Standard resource pools:
- ModelArts Lite resource pool: You can directly perform operations on nodes and Kubernetes clusters, applicable to scenarios where cloud native resources are required.
- ModelArts Standard resource pool: Provides upper-layer capabilities such as training, inference, and development environments, suitable for one-stop development.
This section describes how to enable a Lite Cluster resource pool.
Billing
- After Lite Cluster resources are enabled, compute resources are charged. For Lite Cluster resource pools, only the yearly/monthly billing mode is supported. For details, see Table 1.
Table 1 Billing items Billing Item
Description
Billing Mode
Billing Formula
Compute resource
Dedicated resource pool
Usage of compute resources.
For details, see ModelArts Pricing Details.
Yearly/Monthly
Specification unit price x Number of compute nodes x Purchase duration
- When purchasing a Lite Cluster resource pool, you need to select a CCE cluster. For details about CCE pricing, see CCE Price Calculator.
Process
The following figure shows the process of enabling cluster resources.

|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Before enabling resources, ensure that you have completed related preparations, including applying for required specifications and configuring permissions. |
|
|
Purchase Lite Cluster resources on the ModelArts console. |
Preparations
Before enabling resources, ensure that you have completed related preparations, including applying for required specifications and configuring permissions.
Purchasing a Lite Cluster Resource Pool
- Log in to the ModelArts console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Lite Cluster under Resource Management.
- Click Buy Lite Cluster. On the displayed page, configure parameters according to the following table.
Table 3 Parameters Parameter
Sub-Parameter
Description
Billing Mode
Yearly/Monthly
Yearly/Monthly is a prepaid billing mode in which your subscription is billed based on the required duration. This mode is more cost-effective when the usage duration is predictable.
For Lite Cluster resources, only the yearly/monthly billing mode is supported.
Cluster Flavor
Pool Name
The system provides an editable name.
Only lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-) are allowed. The value must start with a lowercase letter and cannot end with a hyphen (-).
Select CCE Cluster
Choose an existing CCE cluster from the drop-down list. Click Create Cluster on the right to create a cluster if none is available. For details about the required cluster version, see Software Versions Required by Different Models.
Create a Lite Cluster resource pool only when the CCE cluster is running.
CCE clusters of versions 1.23, 1.25, 1.28, and 1.31 are supported. CCE clusters of v1.28 and v1.31 can be created on the console or using APIs. CCE clusters of v1.23 and v1.25 can be created using APIs. For details about how to create CCE clusters of different versions, see Kubernetes Version Policy.
If you already have the CCE cluster but its version is earlier than 1.23, you shall upgrade it to 1.28 by referring to Cluster Upgrade Overview.
Node Pool Flavor
Node Pool Name
To help you better manage nodes in a Kubernetes cluster, ModelArts provides node pools.
Enter a custom node pool name.
Once a resource pool is created, the name of an existing node pool in the resource pool cannot be changed.
Node Type
- Common node: A physical or virtual server that provides independent basic compute, storage, and network resources.
- Supernode: A converged node that provides a large-scale compute resource pool and supports flexible allocation and high-density deployment Supernodes are specially designed to support large-scale model inference tasks. These servers are usually equipped with multiple compute PUs (such as Huawei Cloud AI NPUs) to provide powerful computing capabilities to meet heavy–load inference requirements. Supernode resources are available only in CN Southwest-Guiyang1, CN North-Beijing3, CN North-Ulanqab1, and CN East 2.
- Integrated rack: An entire physical server that provides exclusive resource access. It provides extremely high isolation, performance, and deterministic resource availability.
Resource Type
Select BMS or ECS as required.
- BMS: A BMS features both the scalability of Elastic Cloud Servers (ECSs) and high performance of physical servers, providing dedicated servers on the cloud for you and your enterprise.
- ECS: ECS provides secure, scalable, on–demand compute resources, enabling you to flexibly deploy applications and workloads.
CPU Architecture
The CPU architecture refers to the command set and design specifications for CPUs. The CPU supports x86 and Arm64 architectures, as well as heterogeneous scheduling for x86 and Arm64. Set this parameter as required.
- x86: applies to most general-purpose computing scenarios and supports a wide software ecosystem.
- Arm64: applies to specific optimization scenarios, such as mobile applications and embedded systems, features low power consumption.
Instance Specifications Type
Choose CPU, GPU, or Ascend chips as needed.
- CPU: general-purpose compute architecture, features low computing performance, is suitable for lightweight general tasks.
- GPU: parallel compute architecture, features high computing performance, is suitable for parallel tasks and scenarios such as deep learning training and image processing, and supports multi-PU distributed training.
- Ascend: dedicated AI architecture, features extremely high computing performance, is suitable for AI tasks and scenarios such as AI model training and inference acceleration, and supports multi-node distributed deployment.
Instance Specifications
Select required specifications. Due to system loss, the available resources are fewer than specified. After a resource pool is created, view the available resources in the Nodes tab on the details page.
AZ
Select Random or Manual as required. An AZ is a physical region where resources use independent power supplies and networks. AZs are physically isolated but interconnected over an intranet.
- Random: AZs are automatically allocated.
- Manual: Specify AZs for resource pool instances. To ensure system disaster recovery, deploy all instances in the same AZ. You can set the number of instances in an AZ.
Instances
Select the number of instances (nodes) in the Lite Cluster resource pool. A larger number indicates higher computing performance.
If AZ is set to Manual, you do not need to configure Instances.
Do not create more than 30 instances at a time. Otherwise, the creation may fail due to traffic limiting.
You can purchase instances by rack for certain specifications. The total number of instances is the number of racks multiplied by the number of instances per rack. Purchasing a full rack allows you to isolate tasks physically, preventing communication conflicts and maintaining linear computing performance as task scale increases. All instances in a rack must be created or deleted together.
You can purchase Snt9b23 instances with a custom step. The total number of instances is the number of instances multiplied by the step. The step is the minimum unit of each adjustment of the fault reporting quota. In the node binding scenario, nodes in each step are considered as a whole and belong to the same batch.
Storage Configuration
You can configure the following storage parameters:
- System Disk: Select the type and size of the system disk. The system disk can be a local disk or an EVS disk (including common SSD, high I/O, and ultra-high I/O). System disks of some specifications support only local disks.
- Container Disk: Select the type, size, and quantity of the container disk. The storage type of container disks of some specifications can be manually set. You can select local disks or EVS disks.
- Advanced Container Disk Configuration: You can specify the disk space, container engine space size, and write mode.
- Container Engine Space Size: The default container engine space size is 50 GiB. You can specify the container engine space or set the space to unlimited. The default and minimum values are 50 GiB. The maximum value depends on the specifications, and can be found in the console prompt.
- Write Mode: For some specifications, the write mode of container disks can be set to linear or striped. A linear logical volume integrates one or more physical volumes. Data is written to the next physical volume when the previous one is used up. A striped logical volume stripes data into blocks of the same size and stores them in multiple physical volumes in sequence. This allows data to be concurrently read and written. A storage pool consisting of striped volumes cannot be scaled out.
- Data Disk: Some specifications support common data disks. Multiple data disks can be mounted to a resource pool. The type, size, and quantity of data disks can be set.
The maximum number of disks varies depending on the flavor. For example, a maximum of four data disks can be mounted to a 300I Duo node.
- Advanced Data Disk Configuration: For some specifications, you can set the data disk mounting mode. The details are as follows:
- Default: The EVS disks are directly attached to the resource pool without any additional processing, such as partitioning.
- Specified Directory: You can set the path and write mode, which can be linear or striped.
- Local PV: You can set the PV write mode, which can be linear or striped. In this example, the write mode of all data disks is set.
- Ephemeral Volume: You can set the EV write mode, which can be linear or striped. In this example, the write mode of all data disks is set.
Network Settings
After you select Network Settings, you can set a VPC as the CCE cluster network.
- Virtual Private Cloud: VPC network where the CCE cluster is located and cannot be changed.
- Node subnet: Choose a subnet within the same VPC. New nodes will be created using this subnet.
- Associated Security Group: Specifies the security group used by nodes created in the node pool. A maximum of four security groups can be selected. Traffic needs to pass through certain ports in the node security group to ensure node communications. If no security group is associated, the cluster's default rules are applied.
Environment Settings
After you select Environment Settings, the following parameters can be set:
- Image Settings: You can specify the OS of the instance.
- Preset image: provided by ModelArts. ModelArts supports multiple OSs and has built-in AI drivers and software, offering a complete AI development environment for you to perform development and training directly without additional configuration.
- Private image: not provided by ModelArts. Private images must be fully verified in a test environment before being deployed in a production environment. Ensure that your image is stable and secure in the target CCE cluster environment, and is compatible with the environment, including the OS type, kernel version, container runtime, and driver. If your image is incompatible with the environment, the driver may fail to be installed, and AI services may fail to be deployed or run abnormally.
- Container Engine: Container engines, one of the most important components of Kubernetes, manage the lifecycle of images and containers. The kubelet interacts with a container runtime through the Container Runtime Interface (CRI). Docker and Containerd are supported. For details about the differences between Containerd and Docker, see Container Engines.
When creating a resource pool, you can choose a container engine. Alternatively, you can change the container engine on the scaling page after the resource pool is created.
The CCE cluster version determines the available container engines. If it is earlier than 1.23, only Docker is supported. If it is 1.27 or later, only containerd is supported. For all other versions, both Containerd and Docker are supported.
Node Pool Tag Management
Click
 to add a node pool tag.
to add a node pool tag.- Resource Tag: Add resource tags to classify resources. You can also modify the tags on the resource pool details page after the resource pool is created.
- Kubernetes Label: Add key/value pairs that are attached to Kubernetes objects, such as Pods. A maximum of 20 labels can be added. Labels can be used to distinguish nodes. With workload affinity settings, container pods can be scheduled to a specified node.
- Taint: This parameter is left blank by default. Configure anti-affinity by adding taints to nodes, with a maximum of 20 taints per node.
Add Node Pool
Click Add Node Pool to create node pools as required. Configure the node pool as required.
Plug-in Configuration
Select Plug-in
ModelArts offers several plug-ins to help you expand resource pool functions as needed.
Click Select Plug-in. In the displayed dialog box, select plug-ins you want to add and click OK.
Click View Details to view plug-in functions and version updates.
The following plug-ins are added by default:
- ModelArts Node Agent: a node problem detector that monitors cluster node exceptions and interconnects with third-party monitoring platforms. It is a daemon that runs on each node to collect node problems from different daemon processes.
- ModelArts Metric Collector: default built-in plug-in, which runs as a node daemon to collect monitoring metrics of nodes and jobs and report the metrics to AOM.
- AI Suite – Ascend NPU (ModelArts Device Plugin): a management plug-in that supports Huawei NPU devices in containers
It is automatically installed when Instance Specifications Type is set to Ascend.
- Volcano Scheduler: a batch scheduling platform based on Kubernetes. It provides a series of features required by machine learning, deep learning, bioinformatics, genomics, and other big data applications, as a powerful supplement to Kubernetes capabilities.
Resource Scheduling and Allocation
GPU/NPU Driver
This parameter is displayed if Custom Driver is enabled. You can select a GPU or NPU driver. The value depends on the driver you choose.
For details about the required gpu-driver version, see Software Versions Required by Different Models.
Advanced Config
Cluster Description
Enter a description.
User-defined Node Name Prefix
Choose whether to enable this function to add a node name prefix.
- After a prefix is added, a node name consists of a prefix and a random number.
- The value can contain 1 to 64 characters.
- The prefix starts with a lowercase letter and only contains lowercase letters and digits. It is separated from the node name by a hyphen (-), for example, node-com.
Tags
Click Add Tag to configure tags for the Lite resource pool so that resources can be managed by tag. The tag information can be predefined in Tag Management Service (TMS). You can also set tag information in the Tags tab of the details page after the Lite resource pool is created.
Management
Login Credential
Choose a cluster login mode, Password or Key pair.
- Password: The default username is root, and you can set a password.
- Key pair: Select an existing key pair or click Create Key Pair to create one.
Required Duration
N/A
Select the time length for which you want to use the resource pool. This parameter is mandatory only when the Yearly/Monthly billing mode is selected.
Auto-renewal is disabled by default. If you enable this function, the resource pool will be automatically renewed upon expiration. The fees generated by auto-renewal will be deducted from your account balance. For details, see Auto-Renewal. If the subscription is monthly, the subscription is automatically renewed for one month. If the subscription is yearly, the subscription is automatically renewed for one year.
- Click Buy Now and confirm the specifications. Confirm the information and click Submit.
- After a resource pool is created, its status changes to Running. Only when the number of available nodes is greater than 0, tasks can be delivered to this resource pool.
- Hover over Creating to view the details about the creation process. Click View Details to go the operation record page.
- You can view the task records of the resource pool by clicking Records in the upper right corner of the Lite resource pool list.
Figure 9 Operation records
 Figure 10 Viewing operation records
Figure 10 Viewing operation records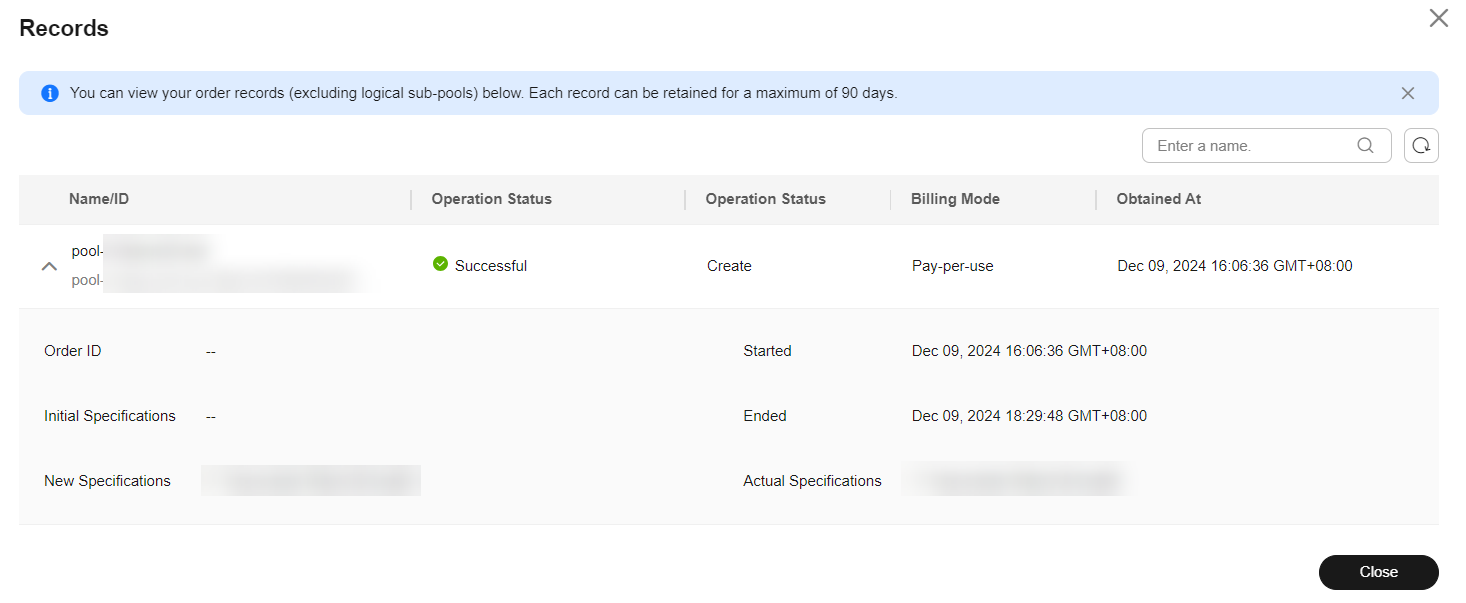
After a resource pool is created, its status changes to Running. Click the cluster resource name to go to the resource details page. Check whether the purchased specifications are correct.Figure 11 Viewing resource details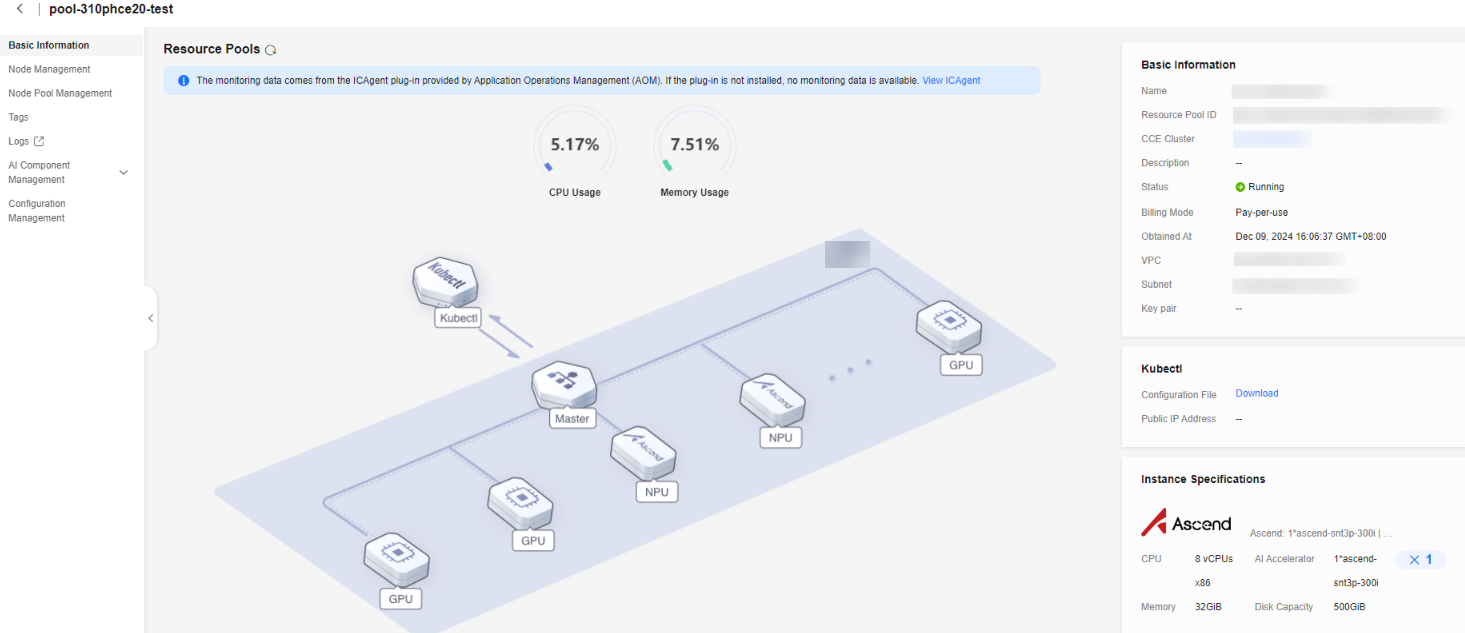
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot