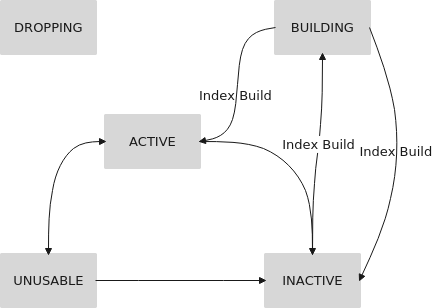
Changing the Status of HBase GSIs
Index Status
A GSI has the following states:
- ACTIVE: The index can be read and written normally.
- UNUSABLE: The index is disabled. Index data can be written normally but cannot be used for query.
- INACTIVE: The index is abnormal. The index data is inconsistent with that in the data table. The indexed data is skipped and the index cannot be used during data query.
- BUILDING: Index data is being generated in batches. After the generation is complete, the index is automatically switched to the ACTIVE state. In this state, data can be read and written properly.
- DROPPING: The index is being deleted. The indexed data is skipped, and the index cannot be used during data query.
You can change index status with the GSI tool. Figure 1 describes the states and transitions between them.
Scenario
You can use the GSI tool to disable or enable an index.
Usage
Run the following command on the HBase client to disable or enable an index:
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.hindex.global.mapreduce.GlobalTableIndexer -Dtablename.to.index='table' -D[idx_state_opt]='idx1'
The related parameters are described as follows:
- tablename.to.index: indicates the name of the data table whose index status needs to be changed.
- idx_state_opt: indicates the target status of the index to be modified. The options are as follows:
- indexnames.to.inactive: disables a specified index (INACTIVE).
- indexnames.to.active: enables a specified index (ACTIVE).
- indexnames.to.unusable: switches the specified index to UNUSABLE.
The following example changes the state of idx1 of table to UNUSABLE:
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.hindex.global.mapreduce.GlobalTableIndexer -Dtablename.to.index='table' -Dindexnames.to.unusable='idx1'
After the command is executed, check the index information.
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.hindex.global.mapreduce.GlobalTableIndexer -Dtablename.to.show='table'
As shown in Figure 2, the status of index idx1 is changed.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot