ALTER BLOCK RULE
Function
This function modifies the attributes of a filtering rule, including the filtering rule name, bound client name, client IP address, user, and matching mode.
During routine database operations, executing abnormal SQL statements may use too many resources, affecting database performance and stability. You can create query filtering rules to intercept such SQL statements.
Precautions
- This syntax is supported only by clusters of version 9.1.0.100 or later.
- Only a user with the database owner permission or the gs_role_block role permission can run the ALTER BLOCK RULE statement. A system administrator has this permission by default.
- Common users cannot run CREATE BLOCK RULE. To run it, they must be authorized by the system administrator. The authorization syntax is as follows:
1GRANT gs_role_block TO user;
You are advised to narrow down the application scope when creating a query filtering rule to improve performance.
- The DEFAULT syntax is used to reset an attribute, but it applies only to optional options.
Syntax
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
ALTER BLOCK RULE block_name [ [ TO user_name@'host' ] | [ TO user_name ] | [ TO 'host' ] | [ TO DEFAULT ] ] | [ FOR UPDATE | SELECT | INSERT | DELETE | MERGE | DEFAULT ] | FILTER BY { SQL ( 'text' ) | TEMPLATE ( template_parameter = value ) } [ WITH ( { with_parameter = value }, [, ... ] ) ]; ALTER BLOCK RULE block_name RENAME to new_block_name; |
Parameter Description
|
Parameter |
Description |
Value Range |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
block_name |
Name of the query filtering rule whose attributes need to be modified. |
A string, which must comply with the naming convention. |
||||||
|
TO |
Specifies the object or client IP address that determines whether the filtering rule takes effect. The options are as follows:
|
The query filtering rule takes effect only when the client IP address is 192.168.0.59 and the login username is user1.
The query filtering rule takes effect only when the login username is user1, regardless of the client IP address.
The query filtering rule takes effect only when the client IP address is 192.168.0.59, regardless of the login user.
|
||||||
|
FOR |
Specifies the statement type. Its value can be UPDATE, SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, or MERGE INTO. |
- |
||||||
|
FILTER BY |
Specifies the filtering method. Value:
|
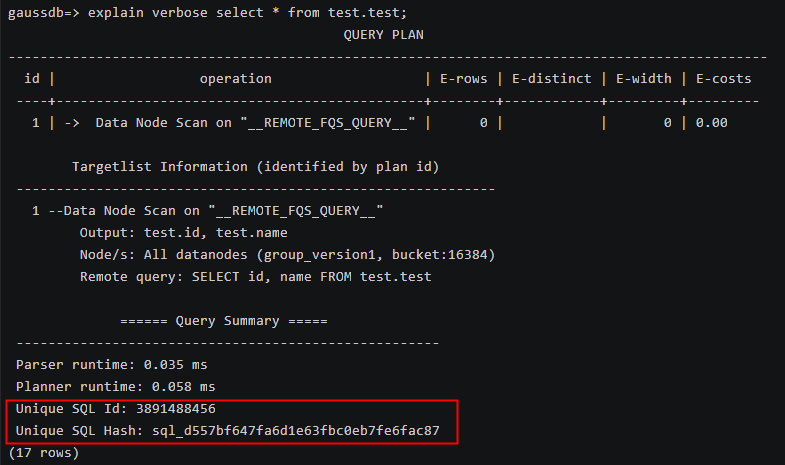
Query the values of unique_sql_id and sql_hash using EXPLAIN VERBOSE.
|
||||||
|
with_parameter |
Parameters for querying filter rule details. |
|
Examples
Create a query rule query_block.
1
|
CREATE BLOCK RULE query_block FILTER BY SQL('update table_table set a=1'); |
Modify the attributes of the query rule query_block.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
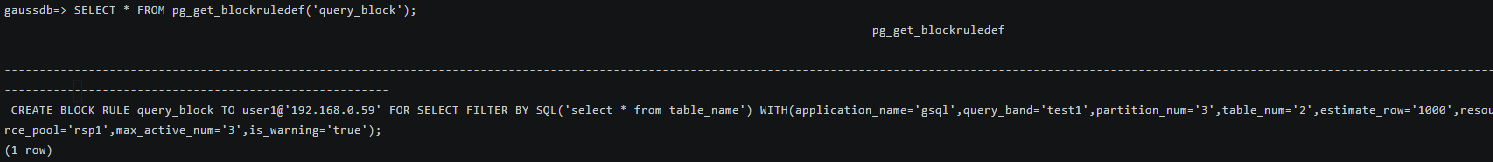
ALTER BLOCK RULE query_block TO user1@'192.168.0.59' FOR SELECT FILTER BY SQL('select * from table_name') WITH (application_name='gsql', query_band='test1', table_num='2', partition_num='3', estimate_row='1000', resource_pool='rsp1', max_active_num='3', is_warning='off' ); |
Query the modified filter rule through the pg_get_blockruledef view.
1
|
SELECT * FROM pg_get_blockruledef('query_block'); |
Rename the query rule query_block.
1
|
ALTER BLOCK RULE query_block RENAME TO query_block_new; |
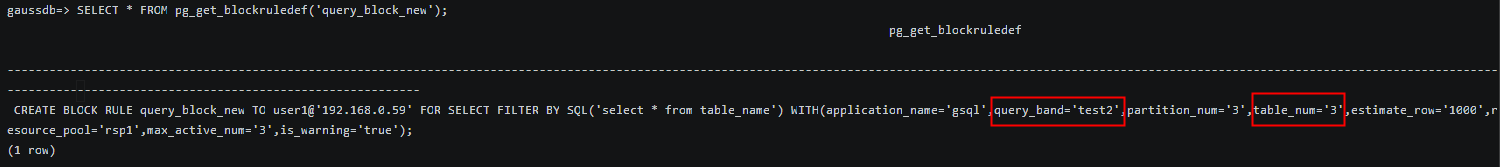
Note that if only some parameters are reset when the rule is modified, the original values of other parameters are retained. In other words, only the specified parameters are modified, and all parameters are not overwritten or cleared.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
ALTER BLOCK RULE query_block_new TO user1@'192.168.0.59' FOR SELECT FILTER BY SQL('select * from table_name') WITH ( query_band='test2', table_num='3'); SELECT * FROM pg_get_blockruledef('query_block_new'); |
The command output shows that only the values of query_band and table_num are changed, and the values of other parameters are retained.
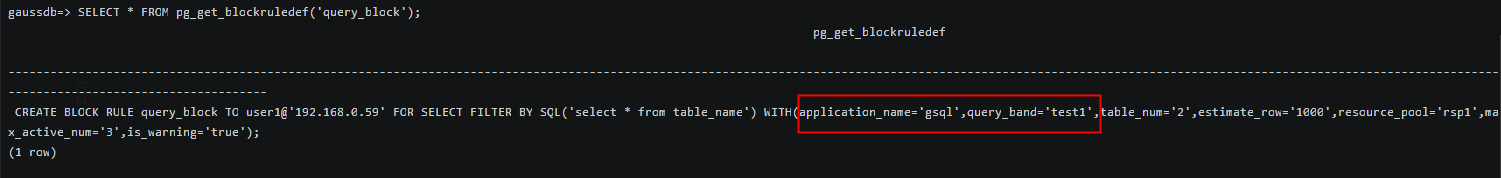
Similarly, new filter criteria will not clear the previous filter criteria. For example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
CREATE BLOCK RULE query_block_1 FILTER BY SQL('update table_table set a=1') WITH (application_name='gsql', query_band='test1'); ALTER BLOCK RULE query_block_1 FILTER BY SQL('update table_table set a=1') WITH ( table_num='2', partition_num='3', estimate_row='1000', resource_pool='rsp1', max_active_num='3', is_warning='off' ); SELECT * FROM pg_get_blockruledef('query_block'); |
The command output shows that the original application_name and query_band parameters are retained.
Helpful Links
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot