VALUES
Function
VALUES computes a row or a set of rows based on given values. It is most commonly used to generate a constant table within a large command.
Precautions
- VALUES lists with large numbers of rows should be avoided, as you might encounter out-of-memory failures or poor performance. VALUES appearing within INSERT is a special case, because the desired column types are known from the INSERT's target table, and need not be inferred by scanning the VALUES list. In this case, VALUE can handle larger lists than are practical in other contexts.
- If more than one row is specified, all the rows must have the same number of elements.
Syntax
1 2 3 4 |
VALUES {( expression [, ...] )} [, ...] [ ORDER BY { sort_expression [ ASC | DESC | USING operator ] } [, ...] ] [ { [ LIMIT { count | ALL } ] [ OFFSET start [ ROW | ROWS ] ] } | { LIMIT start, { count | ALL } } ] [ FETCH { FIRST | NEXT } [ count ] { ROW | ROWS } ONLY ]; |
Parameter Description
|
Parameter |
Description |
Value Range |
|---|---|---|
|
expression |
Specifies a constant or expression to compute and insert at the indicated place in the resulting table or set of rows. In a VALUES list appearing at the top level of an INSERT, an expression can be replaced by DEFAULT to indicate that the destination column's default value should be inserted. DEFAULT cannot be used when VALUES appears in other contexts. |
- |
|
sort_expression |
Specifies an expression or integer constant indicating how to sort the result rows. |
- |
|
ASC |
Indicates ascending sort order. |
- |
|
DESC |
Indicates descending sort order. |
- |
|
operator |
Specifies a sorting operator. |
- |
|
count |
Specifies the maximum number of rows to return. |
- |
|
start |
Specifies the number of rows to skip before starting to return rows. |
- |
|
FETCH { FIRST | NEXT } [ count ] { ROW | ROWS } ONLY |
The FETCH clause restricts the total number of rows starting from the first row of the return query result. |
The default value is 1. |
Inserting One or More Data Records
Create the reason_t1 table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS reason_t1; CREATE TABLE reason_t1 ( TABLE_SK INTEGER , TABLE_ID VARCHAR(20) , TABLE_NA VARCHAR(20) ); |
Insert one data record to the table.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1(TABLE_SK, TABLE_ID, TABLE_NA) VALUES (1, 'S01', 'StudentA'); |
Insert one data record into the table. This command is equivalent to the last one.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1 VALUES (1, 'S01', 'StudentA'); |
Insert records whose TABLE_SK is less than 1 into the table.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1 SELECT * FROM reason_t1 WHERE TABLE_SK < 1; |
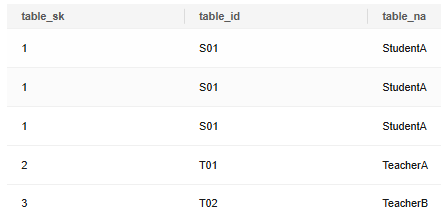
Insert records into the table.
1 2 |
INSERT INTO reason_t1 VALUES (1, 'S01', 'StudentA'),(2, 'T01', 'TeacherA'),(3, 'T02', 'TeacherB'); SELECT * FROM reason_t1 ORDER BY 1; |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





