INSERT
Function
INSERT inserts new rows into a table.
Precautions
- For details about how to use INSERT, see the INSERT Operation.
- You must have the INSERT permission on a table in order to insert into it.
- Use of the RETURNING clause requires the SELECT permission on all columns mentioned in RETURNING.
- If you use the query clause to insert rows from a query, you of course need to have the SELECT permission on any table or column used in the query.
- Using the OVERWRITE clause requires both SELECT and TRUNCATE permissions on the table since it deletes existing data before inserting new records.
- When you connect to a database compatible to Teradata and td_compatible_truncation is on, a long character string will be automatically truncated. If later INSERT statements (not involving foreign tables) insert long strings to columns of char- and varchar-typed columns in the target table, the system will truncate the long strings to ensure no strings exceed the maximum length defined in the target table.

If inserting multi-byte character data (such as Chinese characters) to database with the character set byte encoding (SQL_ASCII, LATIN1), and the character data crosses the truncation position, the string is truncated based on its bytes instead of characters. Unexpected result will occur in tail after the truncation. If you want correct truncation result, you are advised to adopt encoding set such as UTF-8, which has no character data crossing the truncation position.
Syntax
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
[ WITH [ RECURSIVE ] with_query [, ...] ] INSERT [/*+ plan_hint */] [ IGNORE | OVERWRITE ] INTO table_name [ partition_clause ] [ AS alias ] [ ( column_name [, ...] ) ] { DEFAULT VALUES | VALUES {( { expression | DEFAULT } [, ...] ) }[, ...] | query } [ ON DUPLICATE KEY duplicate_action | ON CONFLICT [ conflict_target ] conflict_action ] [ RETURNING {* | {output_expression [ [ AS ] output_name ] }[, ...]} ]; where partition_clause can be: PARTITION ( partition_name ) | PARTITION FOR ( partition_key_value [, ...] ) and duplicate_action can be: UPDATE { column_name = { expression | DEFAULT } | ( column_name [, ...] ) = ( { expression | DEFAULT } [, ...] ) } [, ...] and conflict_target can be one of: ( { index_column_name | ( index_expression ) } [ COLLATE collation ] [ opclass ] [, ...] ) [ WHERE index_predicate ] ON CONSTRAINT constraint_name and conflict_action is one of: DO NOTHING DO UPDATE SET { column_name = { expression | DEFAULT } | ( column_name [, ...] ) = ( { expression | DEFAULT } [, ...] ) } [, ...] [ WHERE condition ] |
Parameter Description
|
Parameter |
Description |
Value Range or Example |
|---|---|---|
|
WITH [ RECURSIVE ] with_query [, ...] |
The WITH clause allows you to specify one or more subqueries that can be referenced by name in the primary query, equal to temporary table. If RECURSIVE is specified, it allows a SELECT subquery to reference itself by name. The format of with_query is as follows: with_query_name [ ( column_name [, ...] ) ] AS
( {select | values | insert | update | delete} )
with_query_name specifies the name of the result set generated by a subquery. Such names can be used to access the result sets of subqueries in a query. column_name specifies the column name displayed in the subquery result set. Each subquery can be a SELECT, VALUES, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE statement. |
Generating Temporary Tables with WITH and Inserting Data into Another Table |
|
plan_hint clause |
Following the keyword in the /*+ */ format, hints are used to optimize the plan generated by a specified statement block. For details, see Hint-based Tuning. |
- |
|
IGNORE |
Specifies that the data that duplicates an existing primary key or unique key value will be ignored. For details, see UPSERT. |
|
|
OVERWRITE |
Specifies the overwrite mode. After this mode is used, the original data is cleared and only the newly inserted data exists. This parameter is available only for clusters of version 8.1.1 or later. You can specify the columns on which OVERWRITE takes effect, and the other columns will keep their original data. If a column has no original data, its value is NULL. INSERT OVERWRITE constraint:
|
- |
|
table_name |
Specifies the name of the target table. |
An existing table name. |
|
AS |
Specifies an alias for the target table table_name. alias indicates the alias name. |
- |
|
column_name |
Specifies the name of a column in a table.
|
An existing column name. |
|
partition_name |
Specifies the name of a partition. |
Name of an existing partition. |
|
partition_key_value |
Specifies the key value of a partition. The value specified by PARTITION FOR ( partition_key_value [, ...] ) can uniquely identify a partition. Multiple partition key values can be specified. Use commas (,) to separate multiple partition key values. |
Value range of the partition key of the partition to be renamed. |
|
expression |
Specifies an expression or a value to assign to the corresponding column.
|
|
|
DEFAULT |
Specifies the default value of the corresponding field name. |
The value is NULL if no specified default value has been assigned to it. For details, see Using the Default Value of a Column When Writing Data. |
|
query |
Specifies a query statement (SELECT statement) that uses the query result as the inserted data. |
|
|
ON DUPLICATE KEY |
Specifies that the data that duplicates an existing primary key or unique key value will be updated. duplicate_action specifies the columns and data to be updated. For details, see UPSERT. |
Inserting Data with ON DUPLICATE KEY for Handling Primary Key/Unique Conflicts |
|
ON CONFLICT |
Specifies that the data that duplicates an existing primary key or unique key value will be ignored or updated. conflict_target specifies the column name index_column_name, expression index_expression that contains multiple column names, or constraint name constraint_name. It is used to infer whether there is a unique index from the column name, the expression that contains multiple column names, or the constraint name. index_column_name and index_expression must comply with the index column format of CREATE INDEX. conflict_action specifies the policy to be executed upon a primary key or unique constraint conflict. There are two available actions:
For details, see UPSERT. |
|
|
RETURNING |
Returns the inserted rows. The syntax of the RETURNING list is identical to that of the output list of SELECT. |
|
|
output_expression |
An expression used to calculate the output of the INSERT command after each row is inserted. |
The expression can use any column names of the table. Write * to return all columns of the inserted row(s). |
|
output_name |
Specifies a name to use for a returned column. |
A string, which must comply with the naming convention. For details, see Identifier Naming Conventions. |
Inserting One or More Data Records
Create the reason_t1 table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS reason_t1; CREATE TABLE reason_t1 ( TABLE_SK INTEGER , TABLE_ID VARCHAR(20) , TABLE_NA VARCHAR(20) ); |
Insert one data record to the table.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1(TABLE_SK, TABLE_ID, TABLE_NA) VALUES (1, 'S01', 'StudentA'); |
Insert one data record into the table. This command is equivalent to the last one.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1 VALUES (1, 'S01', 'StudentA'); |
Insert records whose TABLE_SK is less than 1 into the table.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1 SELECT * FROM reason_t1 WHERE TABLE_SK < 1; |
Insert records into the table.
1 2 |
INSERT INTO reason_t1 VALUES (1, 'S01', 'StudentA'),(2, 'T01', 'TeacherA'),(3, 'T02', 'TeacherB'); SELECT * FROM reason_t1 ORDER BY 1; |
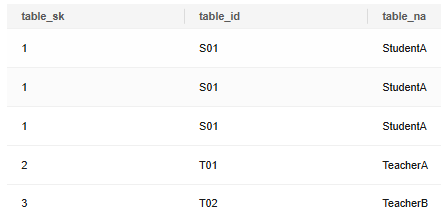
Inserting Query Results into a Table
Insert data back into the reason_t1 table.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1 SELECT * FROM reason_t1; |
Using RETURNING to Return Insertion Results
Insert table data and return the values of table_id and table_na corresponding to the inserted data.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1 SELECT * FROM reason_t1 RETURNING table_id, table_na; |
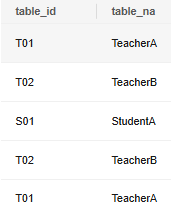
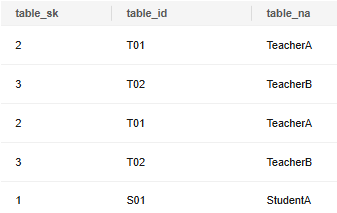
Insert data and return all column values of the inserted data.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1 SELECT * FROM reason_t1 RETURNING *; |
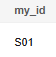
Insert data and return the value of the renamed column my_id.
1
|
INSERT INTO reason_t1 VALUES (1, 'S01', 'StudentA') RETURNING table_id AS my_id; |
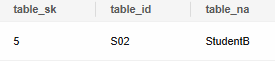
Using INSERT OVERWRITE to Insert Data in Overwriting Mode
Use INSERT OVERWRITE to update data in a table, that is, insert data in overwriting mode (clear the data in the target table first).
1 2 |
INSERT OVERWRITE INTO reason_t1 values (5, 'S02', 'StudentB'); SELECT * FROM reason_t1 ORDER BY 1; |
Using the Default Value of a Column When Writing Data
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS products; CREATE TABLE products ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(50), price DECIMAL(10, 2) DEFAULT 0.00 ); |
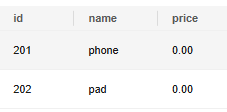
Insert a data record. If the value of the price column is not defined, 0.00 is used by default.
1
|
INSERT INTO products (id, name)VALUES (201, 'phone'); -- The price column uses the default value 0.00. |
Insert a data record and explicitly use the default value.
1 2 |
INSERT INTO products (id, name, price)VALUES (202, 'pad', DEFAULT); -- Explicitly use the default value. SELECT * FROM product; |
Generating Temporary Tables with WITH and Inserting Data into Another Table
Insert some data in a table to another table: Use the WITH subquery to obtain a temporary table temp_t, and then insert all data in temp_t to another table reason_t1.
1
|
WITH temp_t AS (SELECT * FROM reason_t1) INSERT INTO reason_t1 SELECT * FROM temp_t ORDER BY 1; |
Using IGNORE to Ignore Primary Key Conflicts
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS users; CREATE TABLE users ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, username VARCHAR(50) ) DISTRIBUTE BY HASH (id); |
Insert two records whose primary keys are both 1. A conflict occurs and the operation cannot be performed.
1 2 3 4 |
INSERT INTO users (id, username) VALUES (1, 'john_doe'), (2, 'jane_smith'), (1, 'duplicate_user'); --Primary key conflict. Insertion failed. |
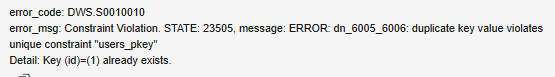
Use IGNORE to ignore the conflict. The conflicting data is ignored and skipped.
1 2 3 4 5 |
INSERT IGNORE INTO users (id, username) VALUES (1, 'john_doe'), (2, 'jane_smith'), (1, 'duplicate_user'); -- Conflicting data will be ignored. SELECT * FROM users; |
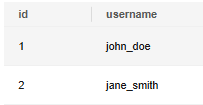
Inserting Data with ON DUPLICATE KEY for Handling Primary Key/Unique Conflicts
1 2 3 4 5 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user_logins; CREATE TABLE user_logins (user_id int primary key, login_count int) DISTRIBUTE BY HASH (user_id); |
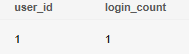
Insert two records. The primary key of the second record conflicts with that of the first record. The insertion fails.
1 2 3 |
INSERT INTO user_logins VALUES (1, 1); INSERT INTO user_logins VALUES (1, 1); --Primary key conflict. Insertion failed. SELECT * FROM user_logins; |
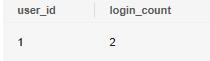
If a duplicate key exists, increment the login_count field by 1 using the ON DUPLICATE KEY clause.
1 2 |
INSERT INTO user_logins VALUES (1, 1) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE login_count = login_count + 1; SELECT * FROM user_logins; |
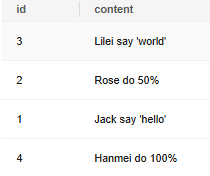
Inserting an Expression or Value into a Column
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
CREATE TABLE tt01 (id int,content varchar(50)); INSERT INTO tt01 values (1,'Jack say ''hello'''); --Insert "Jack say'hello'" and add single quotation marks to escape. INSERT INTO tt01 values (2,'Rose do 50%'); INSERT INTO tt01 values (3,'Lilei say ''world'''); --Insert "Lilei say'world'" and add single quotation marks to escape. INSERT INTO tt01 values (4,'Hanmei do 100%'); SELECT * FROM tt01; |
Inserting Data into a Specified Partition of a Partitioned Table
Insert data into a specified partition of a partitioned table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
CREATE TABLE test_range_row(a int, d int) DISTRIBUTE BY hash(a) PARTITION BY RANGE(d) ( PARTITION p1 values LESS THAN (60), PARTITION p2 values LESS THAN (75), PARTITION p3 values LESS THAN (90), PARTITION p4 VALUES LESS THAN (maxvalue) ); INSERT OVERWRITE INTO test_range_row PARTITION(p1) VALUES(55,51); INSERT OVERWRITE INTO test_range_row PARTITION(p3) VALUES(85,80); DELETE FROM test_range_row PARTITION(p1); |
1 2 |
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE test_ft(c1 text, c2 text, c3 text, c4 text) PARTITION BY (c1,c2,c3) AUTOMAPPED; |
1
|
INSERT OVERWRITE INTO test_ft PARTITION FOR(p1_1) VALUES(p1_1,2,3,4); |
1
|
INSERT OVERWRITE INTO test_ft PARTITION FOR(p1_2,p2_2) VALUES(p1_2,p2_2,3,4); |
Insert data into the level-3 (p1_3,p2_3,p3_3) partition.
1
|
INSERT OVERWRITE INTO test_ft PARTITION FOR(p1_3,p2_3,p3_3) VALUES(p1_3,p2_3,p3_3,4); |
Setting hive_compat_options to Avoid Interpreting Empty Strings as 0 in MySQL Compatibility Mode
In MySQL compatibility mode, DWS treats an empty string as 0 during data operations by default.
For example, importing data from Hive to DWS in finance can cause issues if an empty string is treated as 0. Since these values mean different things in finance, this mistake alters the data, reducing its accuracy and trustworthiness.
To ensure data integrity and consistency during data import, you can set the GUC parameter hive_compat_optionshive_compat_options to empty_str_to_null for conversion logic. When an empty string is inserted, the system converts the empty string to NULL.
Create a MySQL-compatible database.
1
|
CREATE DATABASE mysqldb DBCOMPATIBILITY 'MYSQL'; |
Reconnect to the new database mysqldb, run the following statements, and insert an empty string.
1 2 |
CREATE TABLE test1 (a int, b int); INSERT INTO test1 VALUES (1, ''); |
Query the data. The empty string is set to 0.
1
|
SELECT * FROM test1; |

Set the GUC parameter hive_compat_options to empty_str_to_null.
1
|
ALTER DATABASE mysqldb SET hive_compat_options TO empty_str_to_null; |
Insert data again.
1
|
INSERT INTO test1 VALUES (2, ''); |
Query the data. The empty string is automatically converted to NULL.
1
|
SELECT * FROM test1; |

FAQs
Optimization
- VALUES
When you insert data in batches using the INSERT statement, you are advised to combine multiple records into one statement to insert data, improving data loading performance. Example: INSERT INTO sections VALUES (30, 'Administration', 31, 1900),(40, 'Development', 35, 2000), (50, 'Development' , 60 , 2001);
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





