Buying a GeminiDB Redis Cluster Instance
There are three GeminiDB Redis instance types: proxy cluster, Redis Cluster, and primary/standby.
This section describes how to buy a proxy cluster GeminiDB Redis instance on the GeminiDB console.
|
DB Instance Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Proxy cluster |
In a sharded cluster, a proxy cluster GeminiDB Redis instance is connected through proxies to a standalone Redis instance, Redis Sentinel, and Redis Cluster. The proxy cluster instance has strong horizontal scaling capabilities and can handle millions of QPS and dozens of terabytes of data. |
|
Redis Cluster |
With the native Redis Cluster architecture, a Redis Cluster GeminiDB Redis instance is directly connected to Redis Cluster. It can greatly reduce latency while improving performance. |
- Performance-enhanced proxy cluster instances are in OBT. To create them, choose Service Tickets > Create Service Ticket in the upper right corner of the console.
- Each tenant can create a maximum of 50 GeminiDB Redis instances by default. To request a higher quota, choose Service Tickets > Create Service Ticket in the upper right corner of the console and contact the customer service.
Billing
- Pay-per-use instances are billed based on how long they have been used. For details, see Pay-per-use Billing.
- Yearly/Monthly instances are billed based on your subscription period. For details, see Yearly/Monthly Billing.
Prerequisites
- You have created a Huawei Cloud account.
Procedure
- Log in to the GeminiDB console.
- On the Instances page, click Buy DB Instance.
- On the displayed page, specify a billing mode and instance specifications and click Next.
- Basic settings
Figure 1 Basic settings
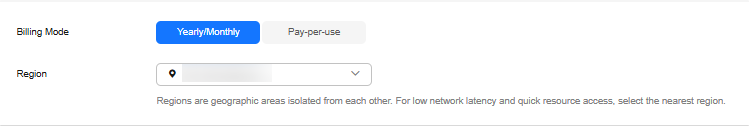
Table 1 Basic settings Parameter
Description
Billing Mode
Select Yearly/Monthly or Pay-per-use.
- Yearly/Monthly
- Specify Required Duration. The system deducts fees from your account based on the service price.
- If you do not need such an instance any longer after it expires, change the billing mode to pay-per-use. For details, see Changing a Yearly/Monthly Instance to Pay-per-Use.
NOTE:
- Yearly/Monthly instances cannot be deleted directly. If such an instance is no longer required, unsubscribe from it. For details, see How Do I Unsubscribe from a Yearly/Monthly Instance?.
- Pay-per-use
- You do not need to set Validity Period because you are billed based on how long you have actually used your instance.
- To use an instance for a long time, change its billing mode to yearly/monthly to reduce costs. For details, see Changing a Pay-per-Use Instance to Yearly/Monthly.
Region
Region where a tenant is located
NOTE:To reduce network latency, select a region nearest from which you will access the instance. Instances deployed in different regions cannot communicate with each other over a private network. After you buy an instance, you cannot change its region.
- Yearly/Monthly
- Resource configuration
Figure 2 Resource configuration
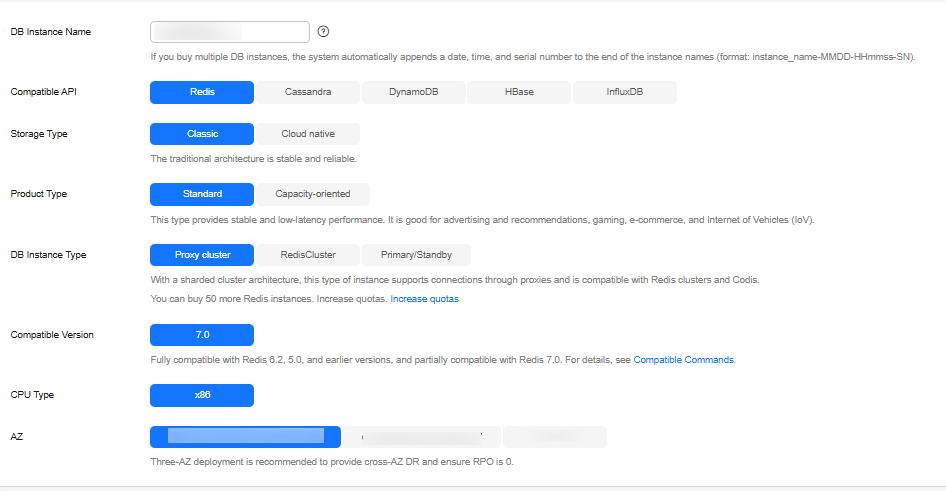
Table 2 Basic information Parameter
Description
DB Instance Name
The instance name:
- Can be the same as an existing instance name.
- Can contain 4 to 64 characters and must start with a letter. It is case-sensitive and allows only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
You can change the name of an instance after it is created. For details, see Modifying a GeminiDB Redis Instance Name.
Compatible API
Select Redis.
NOTE:GeminiDB is compatible with mainstream NoSQL databases, including Redis, DynamoDB, Cassandra, HBase, InfluxDB, and MongoDB. You can select GeminiDB APIs by following How Do I Select an API?
Storage Type
Select Classic or Cloud native.
- Classic: classic architecture with decoupled storage and compute
- Cloud native: more flexible, new-gen version with support for more AZs
NOTE:
- Cloud native storage is only available to cluster instances.
- Classic and cloud native are different deployment modes. Cloud native supports more AZs. If both classic and cloud native are supported, you can select any of them.
Product Type
Classic storage is available to standard and capacity-oriented instances. Cloud native storage is available to capacity-oriented and performance-enhanced instances.
- Standard: Stable and low-latency performance is provided for common scenarios such as advertising and recommendation, gaming, e-commerce, and Internet of Vehicles (IoV).
- Capacity-oriented: Large-capacity key-value storage is suitable for average performance requirements and expectations of low costs.
- Performance-enhanced instances provide high I/O performance and can handle up to millions of QPS per shard, with low latency.
NOTE:Performance-enhanced instances are in OBT. To create them, choose Service Tickets > Create Service Ticket in the upper right corner of the console.
DB Instance Type
Select Proxy cluster or RedisCluster.
- In a sharded cluster, a proxy cluster GeminiDB Redis instance is connected through proxies to a standalone Redis instance, Redis Sentinel, and Redis Cluster. The proxy cluster instance has strong horizontal scaling capabilities and can handle millions of QPS and dozens of terabytes of data.
- With the native Redis Cluster architecture, a Redis Cluster GeminiDB Redis instance is directly connected to Redis Cluster. It can greatly reduce latency while improving performance.
- A primary/standby instance is compatible with a standalone Redis node and Redis Sentinel. This instance type is used when hashtags are unavailable.
Compatible Version
7.0, 6.2 (including 6.2.X), 5.0, and earlier versions
CPU Type
x86
x86 CPUs use the Complex Instruction Set Computing (CISC) instruction set. Each instruction can be used to execute low-level hardware operations. Executing these instructions is complex and time-consuming.
AZ
Availability zone where the instance is created. An AZ is a part of a region with its own independent power supplies and networks. AZs are physically isolated but can communicate with each other over a private network.
Instances can be deployed in a single AZ or three AZs.
- If low network latency is required, deploy your instance in one AZ.
- If disaster recovery is required, select three AZs, and nodes of your instance will be evenly distributed across the three AZs.
- Instance configuration
Figure 3 Storage and specifications (standard)
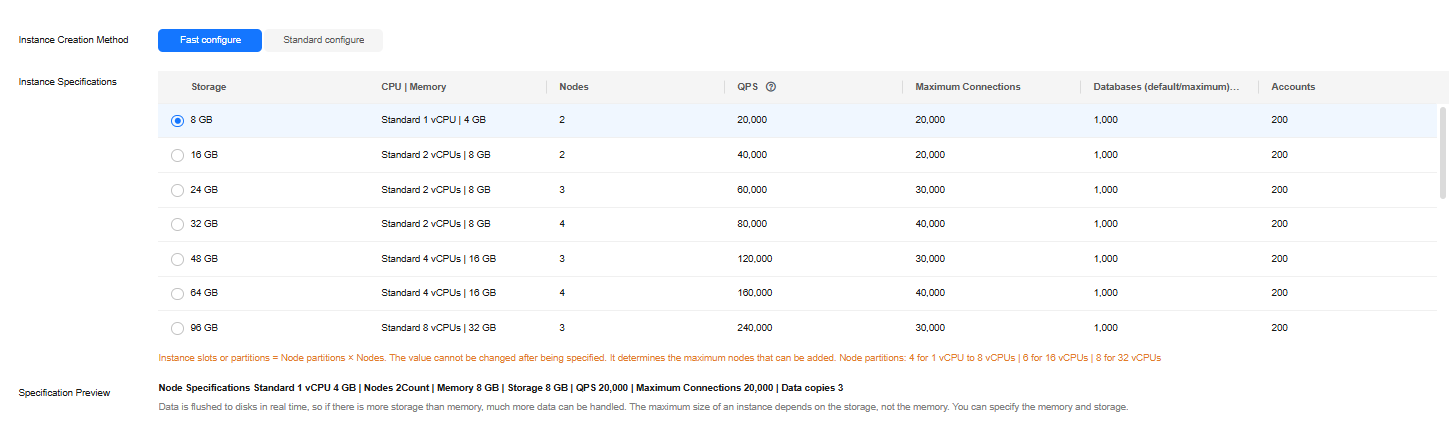 Figure 4 Storage and specifications (cloud native)
Figure 4 Storage and specifications (cloud native)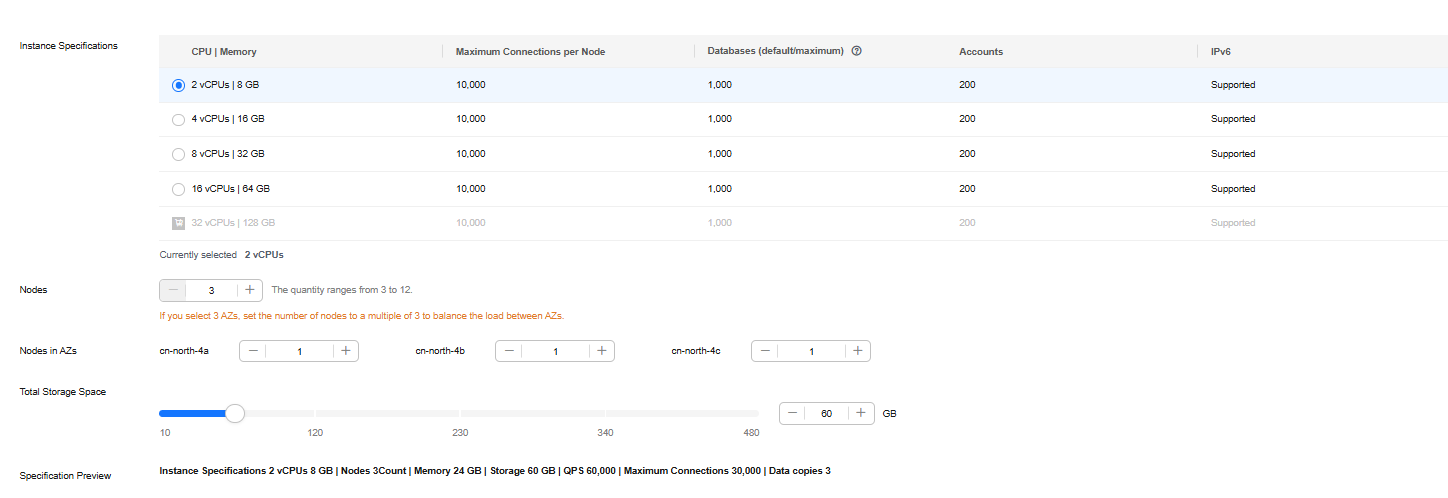
Table 3 Specifications and storage Parameter
Description
Instance Creation Method
You can select Fast configure or Standard configure for instances with classic storage.
- Fast configure: Select the recommended node specifications, quantity, and storage.
NOTE:- Instance specifications with the memory of 8 GB and 16 GB are available only in single AZs. The console shows available specifications.
- The QPS is only for reference.
- Standard configure: Specify instance flavor, node specifications, node quantity, and storage.
Instance Specifications
You need to specify instance specifications after selecting Fast configure for Instance Creation Method.
Higher CPU specifications provide better performance. Select specifications as needed.
For details, see Instance Specifications.
Specification Type
You need to select a specification type after selecting Standard configure for Instance Creation Method.
- Standard: The default and recommended CPU-to-memory ratio is 1:4, which balances low latency demands with high concurrency requirements.
- Enhanced: The CPU-to-memory ratio is 1:8, which boosts the access hit rate while reducing latency.
Node Specifications
You need to select node specifications after selecting Standard configure for Instance Creation Method and Classic for Storage Type.
For details, see Instance Specifications.
Nodes
You need to specify the node quantity after selecting Standard configure for Instance Creation Method.
Number of required nodes. After an instance is created, you can add nodes.
If the number of nodes exceeds the upper limit, you can choose Service Tickets > Create Service Ticket in the upper right corner of the console and contact the customer service.
Total Storage Space
You need to specify the storage space after selecting Standard configure for Instance Creation Method.
Higher CPU specifications provide better performance. Select specifications as needed.
For details, see Instance Specifications.
Specification Preview
After you select instance specifications, the system automatically shows details of the total capacity, node specifications, number of nodes, QPS benchmark, total number of connections, and number of data copies. This helps keep track of the selected instance specifications.
Auto Scale
You can determine whether to enable the function based on the site requirements.
- Trigger If Available Storage Drops To: If the storage usage exceeds the specified value, autoscaling will be triggered. The value can be 60%, 65%, 70%, 75%, 80%, 85%, and 90%.
- Increase By: percentage that your instance storage will be scaled up at. The value can be 10%, 15%, or 20%.
NOTE:Autoscaling is in OBT. To use this function, you can choose Service Tickets > Create Service Ticket in the upper right corner of the console and contact the customer service.
Static Data Encryption
You can determine whether to encrypt static data.
- Disable: Data is not encrypted.
- Enable: If you select this option, your data will be encrypted on disks and stored in ciphertext after you create an instance. When you download encrypted objects, the ciphertext will be decrypted into plaintext and then sent to you. Disk encryption can improve data security and may have slight impacts on database writes and reads.
Key Name: Select an existing key or create one.
NOTE:- This function is now in OBT. To use it, choose Service Tickets > Create Service Ticket in the upper right corner of the console and contact the customer service.
- An agency will be created after static data encryption is enabled.
- After an instance is created, the static data encryption status and the key cannot be changed.
- The key cannot be disabled, deleted, or frozen when it is in use. Otherwise, the database becomes unavailable.
- For details about how to create a key, see "Creating a Key" in Data Encryption Workshop User Guide.
Figure 5 Network settings
Table 4 Network settings Parameter
Description
VPC
Virtual private network where your instances are located. A VPC isolates networks for different services. You can select an existing VPC or create a VPC.
For details about how to create a VPC, see "Creating a VPC" in Virtual Private Cloud User Guide.
You can also use VPCs and subnets shared by other accounts.
VPC owners can share the subnets in a VPC with one or multiple accounts through Resource Access Manager (RAM), which ensures cost efficiency of network resources.
For more information about VPC subnet sharing, see VPC Sharing in Virtual Private Cloud User Guide.
If there are no VPCs available, the system allocates resources to you by default.
NOTE:- After a GeminiDB Redis instance is created, its VPC cannot be changed.
- If you want to connect to a GeminiDB Redis instance through an ECS over an internal network, the GeminiDB Redis instance and the ECS must be in the same VPC. If they are not in the same VPC, you can create a VPC peering connection to enable access.
Subnet
A subnet where your instance is created. The subnet provides dedicated and isolated networks, improving network security.
NOTE:An IPv6 subnet cannot be associated with your instance. Select an IPv4 subnet.
Security Group
A security group controls access between GeminiDB Redis instances and other services. Ensure that the security group you selected allows your client to access the instance.
If no security group is available, the system creates one for you.
Database Port
Database port number.
You can specify a port number based on your requirements. The port number ranges from 1024 to 65535 except 2180, 2887, 3887, 6377, 6378, 6380, 8018, 8079, 8091, 8479, 8484, 8999, 12017, 12333, and 50069.
If you do not specify a port number, port 6379 is used by default.
Access Control
Select Skip or Configure.
- Skip: Access is restricted based on the VPC access policy by default.
- Configure:Specify how access is controlled. Three options are available:
- All IP addresses: All IP addresses can access the instance.
- Whitelist: Only IP addresses in a group can access the instance.
- Blacklist: IP addresses in a group cannot access the instance.
NOTE:Redis Cluster GeminiDB Redis instances do not support access control.
Figure 6 Setting a password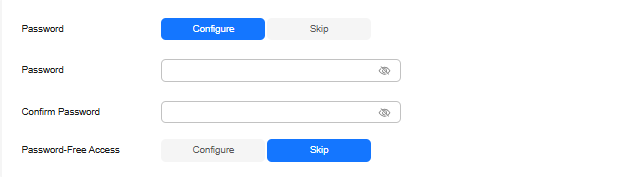
Table 5 Setting a password Parameter
Description
Setting a password
Select Skip or Configure.
- Skip: Set the database password after creating an instance.
- Configure: Set the database password when creating an instance.
NOTE:You cannot set a password after creating a Redis Cluster GeminiDB Redis instance.
Password
Password of database administrator rwuser:
- Must be 8 to 32 characters long.
- Can contain at least two types of the following characters: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters ~!@#%^*-_=+?
- For security reasons, set a strong password. The system will verify the password strength.
Keep your password secure. The system cannot retrieve it if it is lost.
Confirm Password
Enter the database password again.
Password-Free Access
Set password-free access to an instance. You can select Skip or Configure.
- Skip: Set password-free access after the GeminiDB Redis instance is created. For details, see Enabling Password-Free Access.
- Configure: Specify a maximum of 30 CIDR blocks to allow password-free access.
NOTE:
Redis Cluster GeminiDB Redis instances do not support password-free access.
Figure 7 Enterprise project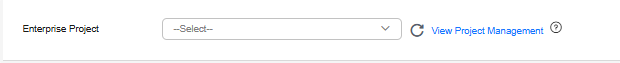
Table 6 Enterprise project Parameter
Description
Enterprise Project
This parameter is provided for enterprise users.
An enterprise project groups cloud resources, so you can manage resources and members by project. The default project is default.
Select an enterprise project from the drop-down list. For more information about enterprise projects, see Enterprise Management User Guide.
- Required duration and quantity
Figure 8 Required duration and quantity
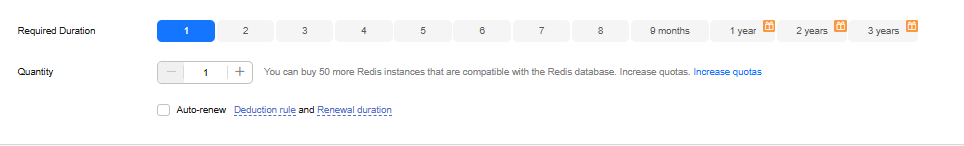
Table 7 Required duration Parameter
Description
Required Duration
The length of your subscription if you select Yearly/Monthly billing. Subscription lengths range from one month to three years.
Quantity
You can buy GeminiDB Redis instances in batches. The value ranges from 1 (default) to 50.
Auto-renew
- By default, this option is not selected.
- If you select this option, the instance is automatically renewed based on the subscription duration.
- More configurations
Figure 9 More configurations

Table 8 More configurations Parameter
Description
SSL
A security protocol. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates set up encrypted connections between clients and servers, preventing data from being tampered with or stolen during transmission.
You can enable SSL to improve data security. After an instance is created, you can connect to it using SSL.
NOTE:- If SSL is not enabled when you create an instance, you can enable it after the instance is created. For details, see Encrypting Data over SSL for a GeminiDB Redis Instance.
Rename High-risk Command
To prevent data loss, instance restart, and performance jitter caused by misoperations, you can rename high-risk commands of a GeminiDB Redis instance. For details, see Renaming Commands of a GeminiDB Redis Instance.
Parameter Template
You can use parameters in a parameter template to manage database API configurations. A database parameter template acts as a container for API configuration values that can be applied to one or more instances.
Each user can create up to 100 parameter templates. All types of instances in the same project can share the quota. For details, see Creating a Parameter Template.
Maintenance Window
Time range of change tasks that affect instances, such as specifications change and patch installation
- Skip
- Configure
Tags
This setting is optional. Adding tags helps you better identify and manage your instances. A maximum of 20 tags can be added for each instance.
If your organization has configured a tag policy for your GeminiDB Redis instance, you need to add a tag to the instance based on the tag policy. If the tag does not comply with the tag policy, the instance may fail to be created. Contact the organization administrator to learn details about the tag policy.
A tag consists of a tag key and a tag value.
- A tag key is mandatory if the instance will be tagged.
Each tag key is unique for each instance. It can contain 1 to 128 characters, cannot start with _sys_, and cannot start or end with a space. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: -_@.:/+=
- A tag value is optional if the instance will be tagged.
The value can contain a maximum of 255 characters. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: _.-:+=@/
After an instance is created, you can view its tag details on the Tags tab. In addition, you can add, modify, and delete tags of an existing instance. For details, see Tag Management.
- Basic settings
- On the displayed page, confirm instance details.
- Yearly/Monthly
- To modify the configurations, click Previous.
- If no modification is required, read and agree to the service agreement, click Pay Now, and complete the payment.
- Pay-per-use
- To modify the configurations, click Previous.
- If no modification is required, read and agree to the service agreement and click Submit.
- Yearly/Monthly
- On the Instances page, view and manage the created instance.
The instance creation process takes about 5 to 15 minutes. After the creation is complete, the status changes to Available.
You can click
 in the upper right corner of the page to refresh the instance status.
in the upper right corner of the page to refresh the instance status.
Follow-up Operations
- After creating an instance, you can add a description to it. For details, see Modifying a GeminiDB Redis Instance Name.
- The default database port is 6379. You can change it after creating an instance. To ensure data and instance security, change the database port immediately after creating the instance. For details, see Changing the Port of a GeminiDB Redis Instance.
FAQs
- How Do I Select Proper Node Specifications and Node Quantity When Purchasing a GeminiDB Redis Instance?
- Is a Primary/Standby or Cluster Deployment Mode Preferred for GeminiDB Redis Instances with Several GB of Storage Space?
- What Should I Do If the DAS Console Cannot Be Redirected After I Click Log In in the Operation Column in the Instance List or Click Log In on the Basic Information Page?
- Can I Change the VPC of a GeminiDB Redis Instance?
Related APIs
|
API |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Creates an instance. |
|
|
Deletes an instance. |
|
|
Queries instances and details based on specified conditions. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





