Configuring a Scheduling Policy of a Component Instance
Based on features of components deployed using CCE, ServiceStage divides application components into the minimum deployment instances. The application scheduler monitors application instance information in real time. When detecting that a new pod needs to be scheduled, the application scheduler calculates all remaining resources (compute, network resources, and middleware) in the cluster to obtain the most appropriate scheduling target node.
ServiceStage supports multiple scheduling algorithms, including affinity scheduling between applications and AZs, between applications and nodes, and between applications.
You can freely combine these policies to meet your requirements.
Affinity
If an application is not containerized, multiple components of the application may run on the same virtual machine, and processes communicate with each other.
However, during containerization splitting, containers are usually split by process. For example, service processes are stored in a container, monitoring log processing or local data is stored in another container, and there is an independent life cycle. If closely related container processes run on distant nodes, routing between them will be costly and slow.
Affinity: Containers are scheduled onto the nearest node. This makes routing paths between containers as short as possible, which in turn reduces network overhead.
Anti-affinity: Instances of the same application are spread across different nodes to achieve higher availability. Once a node is down, instances on other nodes are not affected.
- Application-AZ Affinity and Anti-Affinity
- Affinity with AZs: Application components can be deployed in specific AZs.
- Non-affinity with AZs: Application components cannot be deployed in specific AZs.
- Application-Node Affinity and Anti-Affinity
- Affinity with Nodes: Application components can be deployed on specific nodes.
- Non-affinity with Nodes: Application components cannot be deployed on specific nodes.
- Application Affinity
It determines whether application components are deployed on the same node or different nodes.
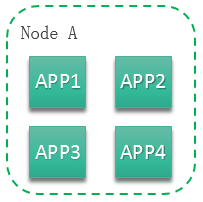
- Affinity with Applications: Application components are deployed on the same node. You can deploy application components based on service requirements. The nearest route between application components is used to reduce network consumption. For example, Figure 1 shows affinity deployment, in which all applications are deployed on the same node.
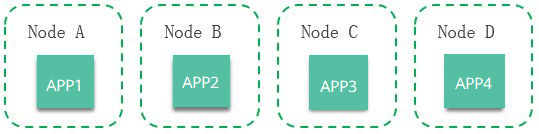
- Anti-affinity with Applications: Different applications or multiple instances of the same application component are deployed on different nodes. Anti-affinity deployment for multiple instances of the same application reduces the impact of system breakdowns. Anti-affinity deployment for applications can prevent interference between the applications.
As shown in Figure 2, four applications are deployed on four different nodes. The four applications are deployed in anti-affinity mode.
Precautions
When setting application component-node affinity and application component-application component affinity, ensure that the affinity relationships are not mutually exclusive; otherwise, application deployment will fail. For example, application deployment will fail when the following conditions are met:
- Anti-affinity is configured for two application components APP 1 and APP 2. For example, APP 1 is deployed on node A and APP 2 is deployed on node B.
- When APP 3 is deployed on node C and goes online, affinity is configured between APP 3 and APP 2. As a result, affinity relationships are mutually exclusive, and APP 3 fails to be deployed.
Procedure
- Choose Advanced Settings > Deployment Configuration.
- On the Scheduling Policies tab page, set the component instance scheduling policy by referring to the following table.
Purpose
Procedure
Setting application component-AZ affinity
- Click Add Affinity Object.
- Set the object type to AZ, and select the desired AZ.
- Click OK.
Setting application component-AZ anti-affinity
- Click Add Anti-affinity Object.
- Set the object type to AZ, and select the desired AZ.
- Click OK.
Setting application component-node affinity
- Click Add Affinity Object.
- Set the object type to Node, and select the desired node.
- Click OK.
Setting application component-node non-affinity
- Click Add Anti-affinity Object.
- Set the object type to Node, and select the desired node.
- Click OK.
Setting application component-application component affinity
- Click Add Affinity Object.
- Set the object type to Component, and select the desired application components.
- Click OK.
The selected application components are deployed on the same node.
Setting application component-application component anti-affinity
- Click Add Anti-affinity Object.
- Set the object type to Component, and select the desired application components.
- Click OK.
The selected application components are deployed on different nodes.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot