RBAC Syntax of RBAC Policies
Policy Structure
An RBAC policy consists of a Version, a Statement, and Depends.

Policy Syntax
When selecting a policy for a user group, click  below the policy to view the details of the policy. The DWS Administrator policy is used as an example to describe the syntax of RBAC policies.
below the policy to view the details of the policy. The DWS Administrator policy is used as an example to describe the syntax of RBAC policies.
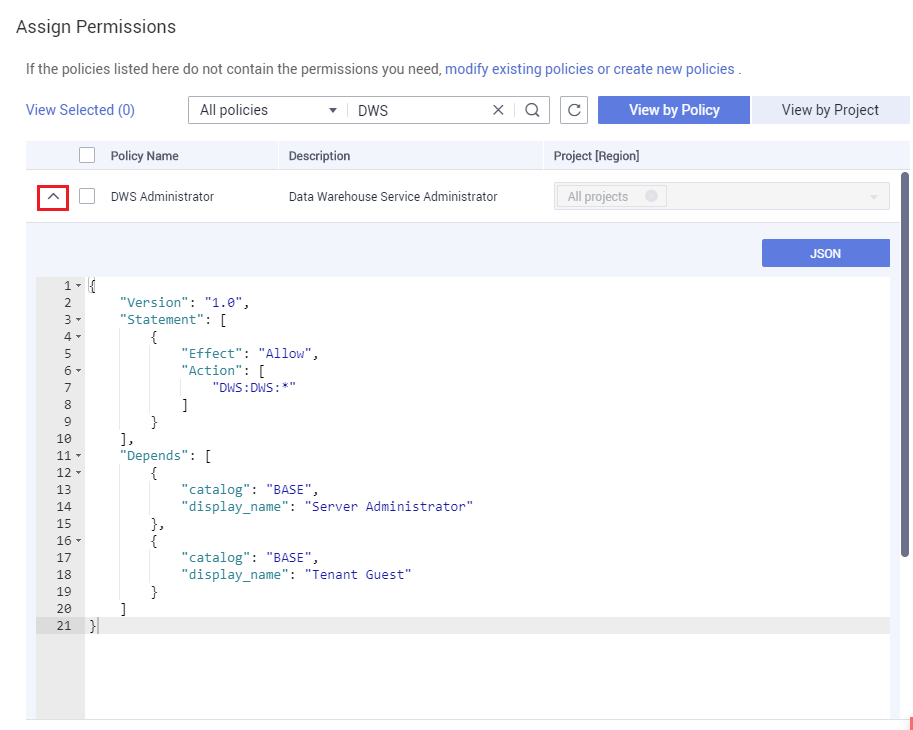
{
"Version": "1.0",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dws:dws:*"
]
}
],
"Depends": [
{
"catalog": "BASE",
"display_name": "Server Administrator"
},
{
"catalog": "BASE",
"display_name": "Tenant Guest"
}
]
}
|
Parameter |
Meaning |
Value |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Version |
Policy version |
The value is fixed to 1.0. |
|
|
Statement |
Action |
Operations to be performed on DWS |
Format: Service name:Resource type:Operation. dws:dws:*: Permissions for performing all operations on all resource types in DWS. dws indicates the service name. The asterisk (*) is a wildcard. |
|
Effect |
Whether the operation defined in an action is allowed |
|
|
|
Depends |
catalog |
Name of the service to which dependencies of a policy belong |
Service name Example: BASE |
|
display_name |
Name of a dependent policy |
Policy name Example: Server Administrator |
|
When using RBAC for authentication, pay attention to the Depends parameter and grant other dependent permissions at the same time.
For example, the DWS Administrator permission depends on the Server Administrator and Tenant Guest permissions. When granting the DWS Administrator permission to users, you also need to grant the two dependent permissions to the users.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





