IoT Device SDKs
Why Did the IoT Device SDK for C Fail to Be Started?
It is possible that the OpenSSL or Paho library files failed to be compiled or the export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./lib/ command was not used to load the library files. For details, see "Preparations" in IoT Device SDK (C) Development Guide.
Why Did the IoT Device SDK for Java Fail to Be Started?
It is because the JDK (1.8 or later) or Maven has not been installed.
Which Java SDK Demo Should I Refer to?
device_demo is recommended if you connect devices directly to the IoT platform and want to integrate the bootstrap (device provisioning) function, whereas gateway_demo is a better choice if you connect devices to the platform through common gateways or gateways that support generic protocols.
Which C SDK Demo Should I Refer to?
device demo is recommended if you connect devices directly to the IoT platform, whereas bootstrap_demo is recommended if you want to integrate the bootstrap function. gateway demo will be a better choice if you connect devices to the platform through common gateways or gateways that support generic protocols.
Why Was the Error Code 4 Returned When I Used the IoT Device SDK for C for Device Connection?
It is because the entered account name or password was incorrect. For details about the error codes returned upon connection failures, see the error code description in the MQTTAsyn.h file.
What Are the Differences Between the IoT Device SDK and IoT Device SDK Tiny?
IoT Device SDK Tiny is more lightweight than IoT Device SDK and suitable for devices with smaller memory and disk space and few child devices mounted. The dynamic link library is not used during compilation. The code provides the OS abstraction layer to adapt to different OSs, such as FreeRTOS, Linux, Nova OS, μC/OS-II, and OpenHarmony LiteOS-M. IoT Device SDK Tiny supports MQTT(S), LwM2M, and CoAP. It uses Mbed TLS for encryption, while IoT Device SDK C uses OpenSSL. For details, see Introduction to IoT Device SDKs.
Issues Related to IoT Device SDK C Tiny
- What Do I Do If "mqtt_imp_init: ###please implement mqtt by yourself####" Is Displayed in Logs?
Check whether the compilation architecture supports the __attribute__ ((weak)) function. If no, comment out all these functions. If link_tcpip_imp_init:###please implement this function by yourself#### is displayed, check whether the network layer adaptation is implemented.
- What Do I Do If the Task Execution Sequence Is Inconsistent with the Task Priority When Using the SDK?
By default, task priorities in the SDK range from 0 to 31 in descending order. You can adjust task priorities based on the OS.
- What Steps Are Included in the SDK Porting Process?
The porting process includes registering an OS with the OS abstraction layer (OSAL) and registering TCP/IP with the service abstraction layer (SAL). In addition, you can perform modular tailoring as required. For details, see Developer Guide.
- What Do I Do If Error Code 2 Is Returned When MQTT Is Used to Connect to Huawei Cloud?
The following figure shows the logs.
Figure 1 MQTT connection error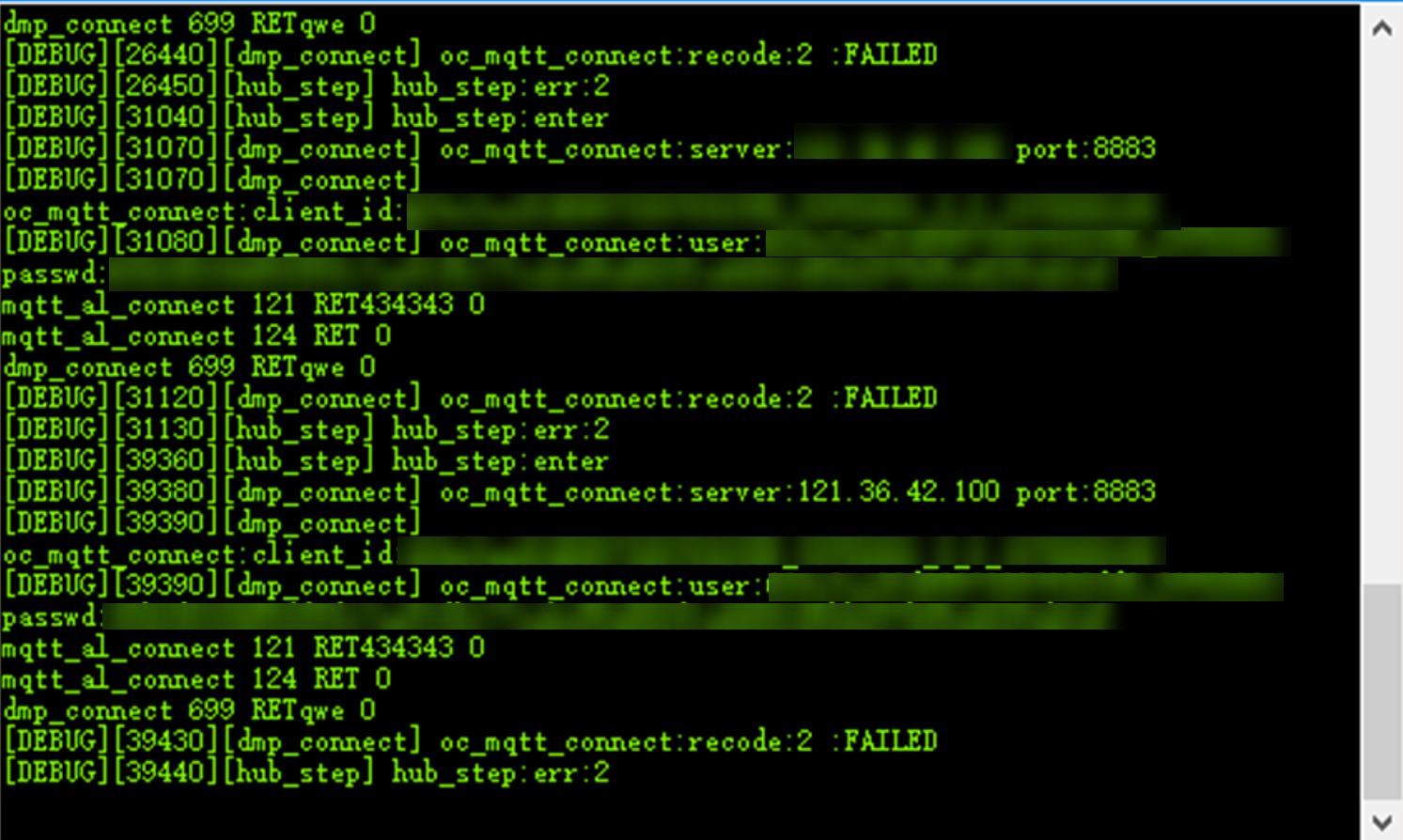
This is caused by a network error. Check whether your development board is connected to the network. If connected, check whether the IP address, domain name, and port number of the platform to be connected are correct. In the Linux environment, ping the platform address to check whether the address can be pinged.
- What Do I Do If a Device Does not Automatically Reconnect to Huawei Cloud After the Disconnected Network is Restored?
Figure 2 No reconnection
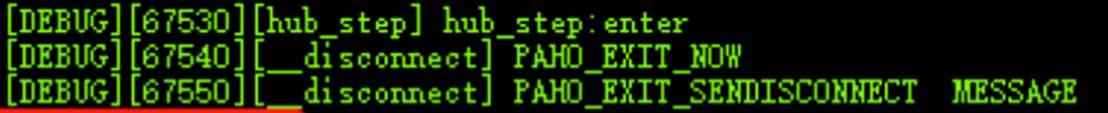
The log shows that Paho has exited and the device has been disconnected from the platform and goes offline. Change the sleep time in the __loop_entry() function in the network\mqtt\paho_mqtt\port\paho_mqtt_port.c file in the SDK directory from 1 ms to 100 ms (osal_task_sleep(100)). Then, check whether automatic reconnection is successful.
- What Do I Do If I Am Stuck in the Topic Subscription Process When MQTTS Is Used to Connect to Huawei Cloud?
Figure 3 Suspended topic subscription process
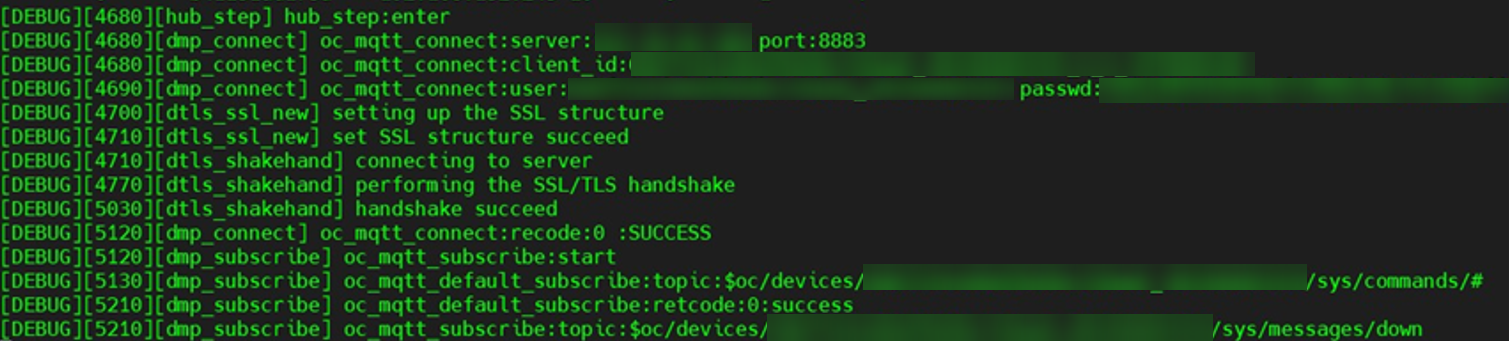
Change the value of CONFIG_PAHO_LOOPTIMEOUT in the iot_config.h file to 1000.
- What Do I Do If a Developer Board Successfully Connects to Huawei Cloud Using MQTT But Connection Fails When MQTTS Is Used?
The cause may be that the development board memory is insufficient. Check the remaining memory, which should be greater than 60 KB. For OpenHarmony L0 devices, call LOS_MemPoolSizeGet(m_aucSysMem0) to obtain the total memory and LOS_MemTotalUsedGet(m_aucSysMem0) to obtain the used memory. Then, you can get the remaining memory. If Shell is ported, you can run the free command to obtain the memory details.
- How Do I Interpret the Following Log Content Generated When MQTT Is Used to Connect to Huawei Cloud?
Figure 4 Normal MQTT connection setup
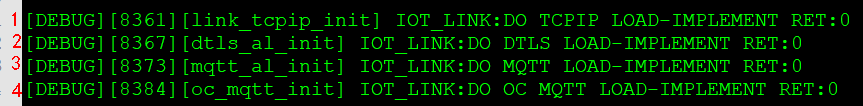
Lines 3 and 4 indicate that MQTT is used for connection. If MQTTS is used, line 2 will be displayed. If TCP/IP that adapts to SAL is used, line 1 will be displayed. If the corresponding log content is not displayed, find the macro of the initialization function of the corresponding function based on the link_main.c file, and then check whether the macro is enabled in iotlink_config.h.
- Why a Device Is Powered Off But Displayed as Online on IoTDA?
If a device does not proactively disconnect from IoTDA, the device disconnection time is related to the MQTT lifetime in the code, which is 1.5 times the heartbeat time. When establishing an MQTT connection, set the lifetime parameter.
- List of Devices with IoT Device SDK Tiny (Code Attached) Ported
See Porting Device List.
What Do I Do If the Error Message "Too many publishes in progress" Is Displayed When the IoT Device SDK (Java) Is used to Report Data?
There are too many concurrent messages. To solve this problem, increase the value of MAX_FLIGHT_COUNT in MqttConnection.java.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





