Overview
As enterprise data is migrated to the cloud, data security and privacy protection are facing increasingly severe challenges. The encrypted database will solve the privacy protection issues in the entire data lifecycle, covering network transmission, data storage, and data running status. Furthermore, the encrypted database can implement data privacy permission separation in a cloud scenario, that is, separate data owners from data administrators in terms of the read permission. The encrypted equality query is used to solve equality query issues of ciphertext data.
Encryption Model
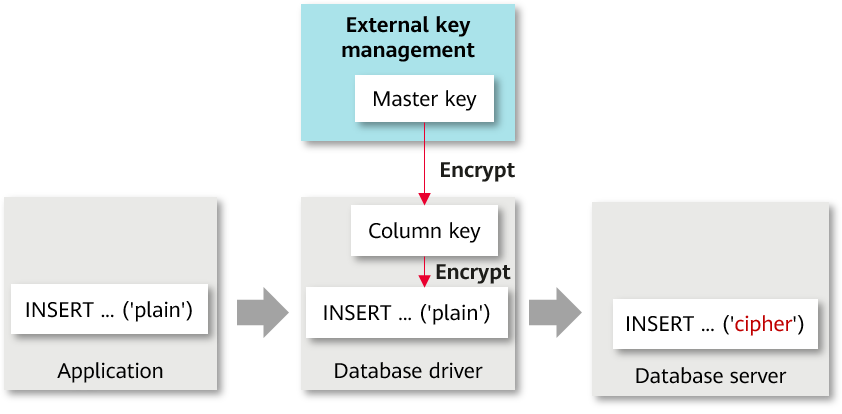
A fully-encrypted database uses a multi-level encryption model. The encryption model involves three objects: data, column key, and master key, which are described as follows:
- Data, including:
- Data contained in the SQL syntax. For example, the INSERT... VALUES ('data') syntax contains 'data'.
- Query result returned from the database server, for example, the query result returned after the SELECT syntax is executed.

An encrypted database encrypts data of encrypted columns in the SQL syntax in the driver and decrypts the query result of the encrypted columns returned from the database server.
- Column key: Data is encrypted by using column keys. The column keys are generated by the database driver or manually imported by users. The column key ciphertext is stored on the database server.
- Master key: Column keys are encrypted by using master keys. The master keys are generated and stored by an external key manager. The database driver automatically accesses the external key manager to encrypt and decrypt column keys.
Overall Process
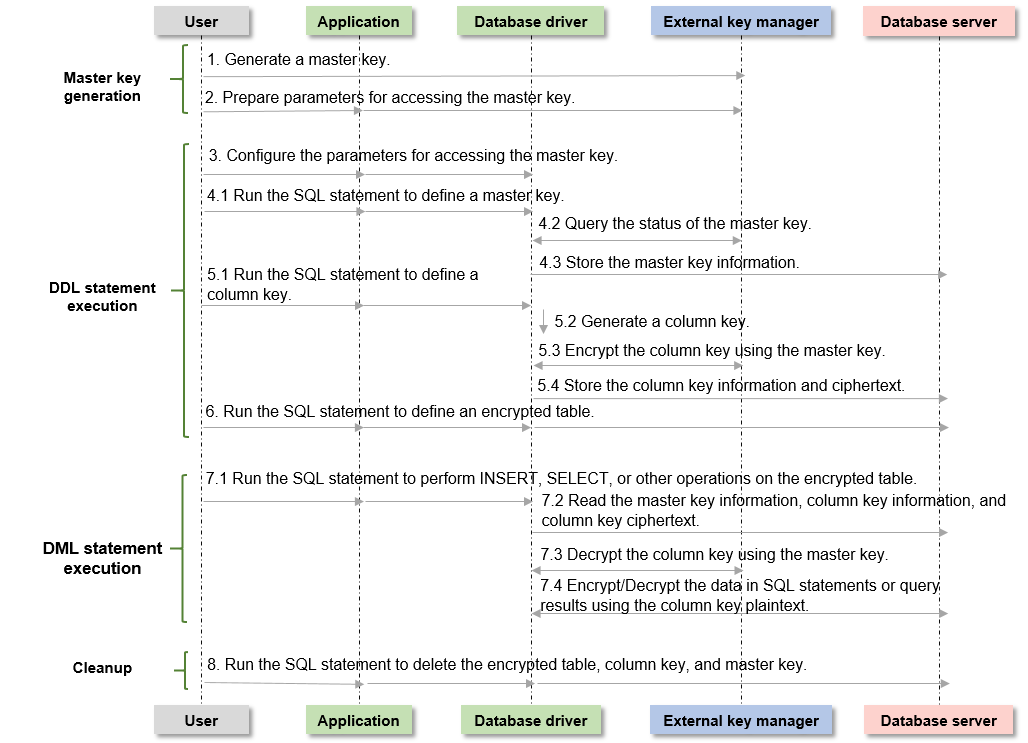
The process of using a fully-encrypted database consists of the following four phases. This section describes the overall process. Sections Using gsql to Operate an Encrypted Database and Using JDBC to Operate an Encrypted Database describe the detailed usage process.
1. Master key generation phase: First, you need to generate a master key in Huawei Cloud key management service. After the master key is generated, you need to prepare the parameters for accessing the master key.
2. DDL statement execution phase: In this phase, you can use the key syntax of the encrypted database to define the master key and column key in sequence, define the table, and specify a column in the table as an encrypted column. When defining the master key and column key, you need to access the master key generated in the previous phase.
3. DML statement execution phase: After an encrypted table is created, you can directly execute syntax including but not limited to INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE. The database driver automatically encrypts and decrypts data of the encrypted column based on the encryption definition in the previous phase.
4. Cleanup phase: Delete the encrypted table, column key, and master key in sequence.
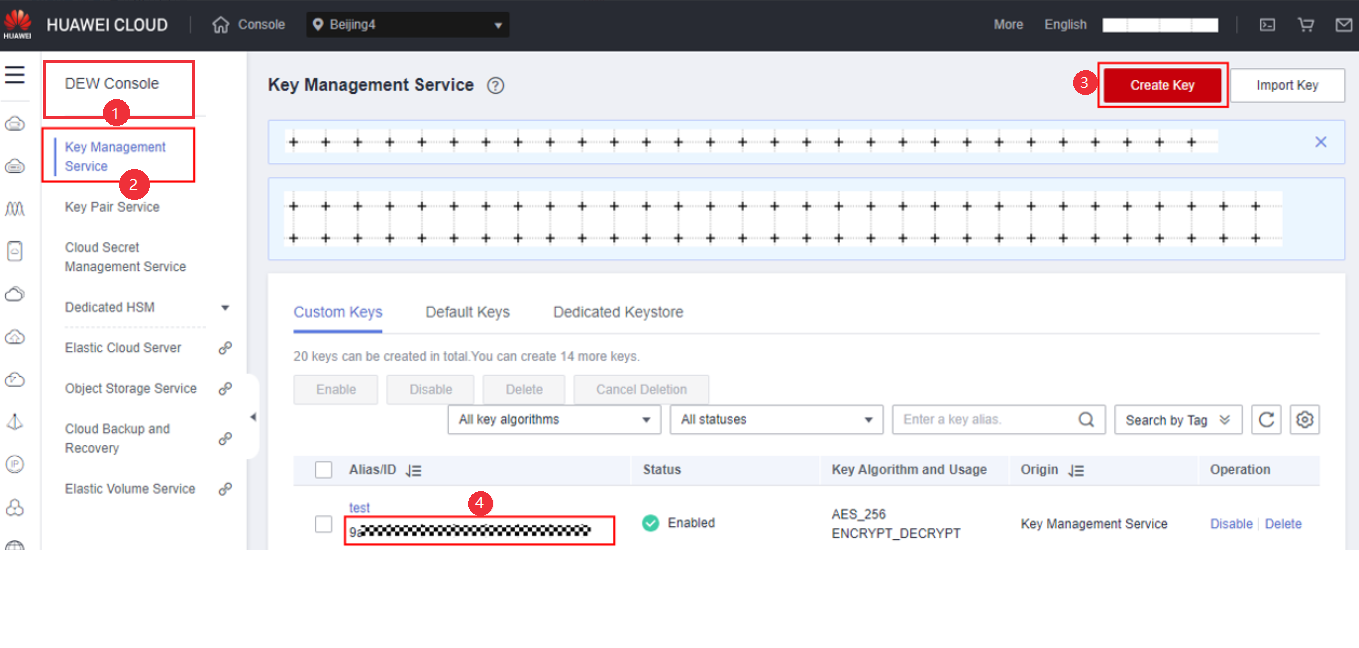
Master Key Generation Phase
When you use an encrypted database for the first time, you need to use an external key manager to generate at least one master key. The operation procedure is as follows:
- Huawei Cloud scenario
- Access the Huawei Cloud website, register an account, and log in.
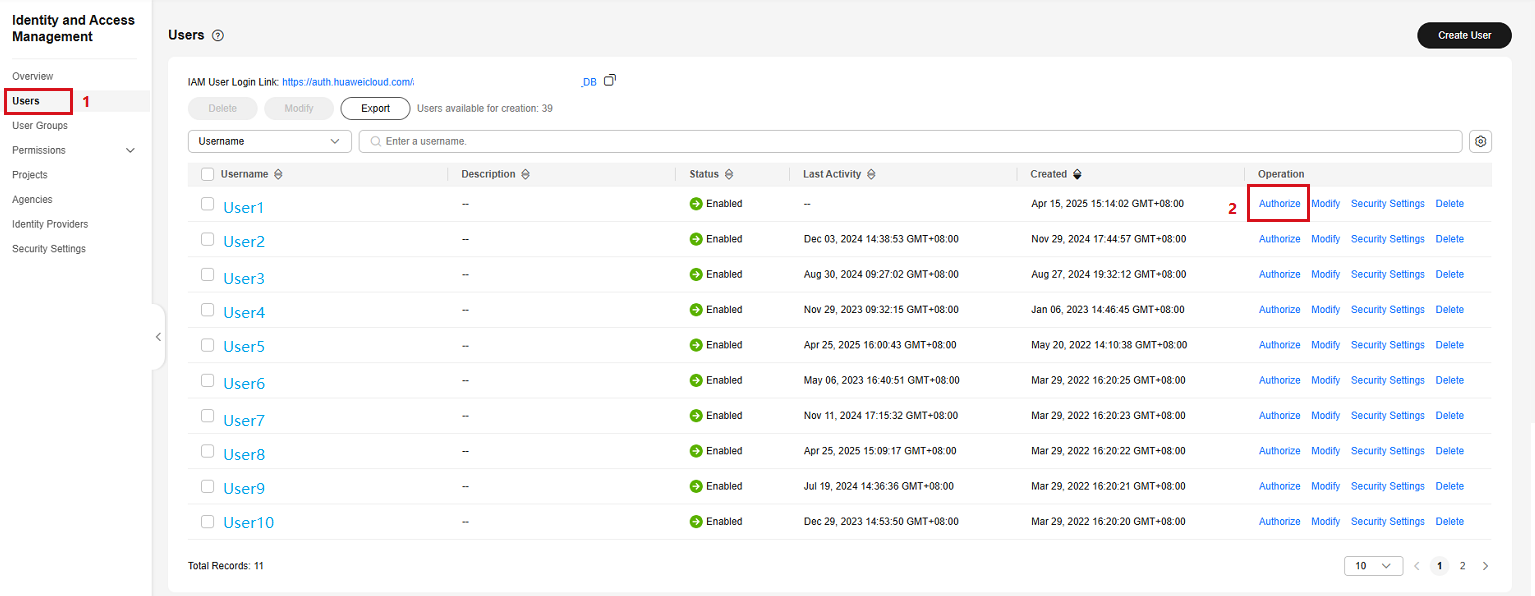
- Search for and access the IAM service. On the Users page, click Create User to create an IAM user, set a password for the user, associate the user with a user group, and grant the DEW permission to the user group.
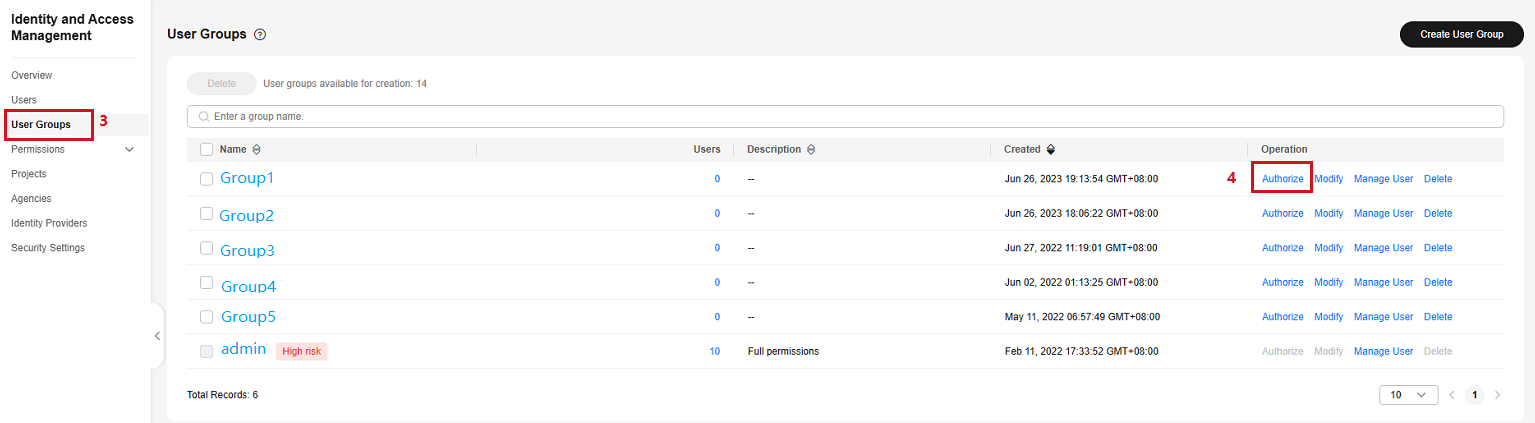
- Return to the login page, and select to log in as the IAM user created in the previous step to log in. The subsequent operations are all performed by the IAM user.
- Choose Key Management Service and click Create Key to create at least one key, that is, the master key.
- Remember the master key ID. Each master key has a key ID. When using encrypted data, you need to configure the master key ID. The database driver accesses the master key through the RESTful API.
After the master key is generated, you need to prepare parameters for the data driver to access the master key, such as the IAM username and project ID. Huawei Cloud supports two identity authentication modes. The number of parameters and parameter types required by the two authentication modes are different. You can select either of them. To obtain these parameters, perform the following steps:
- Method 1: AK/SK authentication
- AK and SK: Log in to the Huawei Cloud console, click the username in the upper right corner, and choose My Credentials. On the displayed page, click Access Keys. Click Create Access Key to create an AK/SK pair. After the creation is successful, you can download the AK and SK.
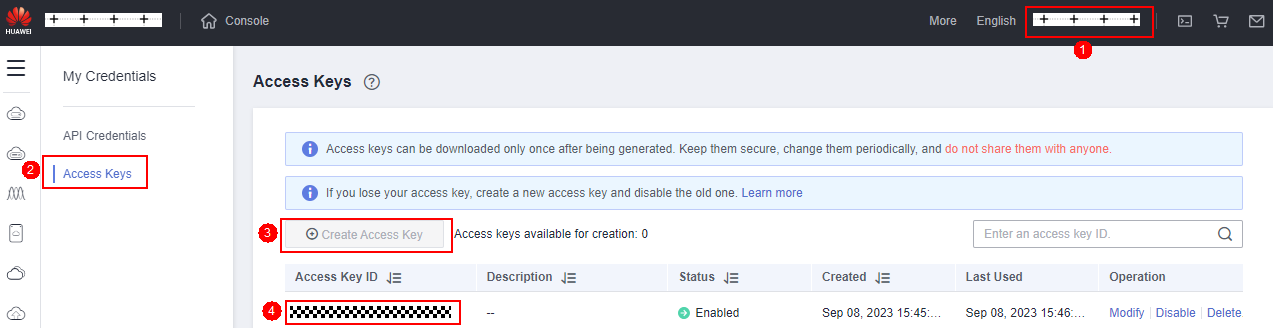
- Project ID: On the Huawei Cloud console, click the username in the upper right corner, and choose My Credentials. On the displayed page, click API Credentials to find the project ID.
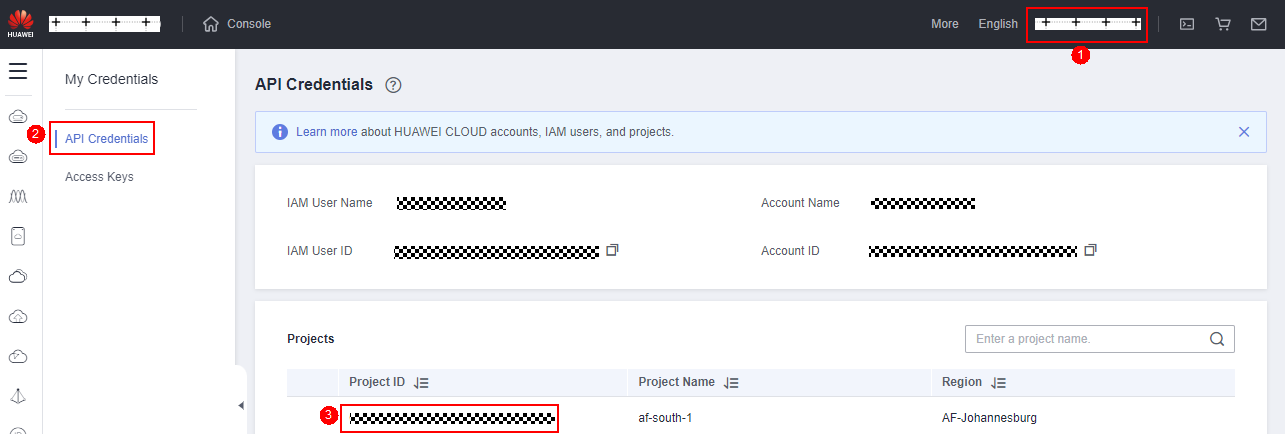
- KMS server address: https://kms.Project.myhuaweicloud.com/v1.0/Project ID/kms
- AK and SK: Log in to the Huawei Cloud console, click the username in the upper right corner, and choose My Credentials. On the displayed page, click Access Keys. Click Create Access Key to create an AK/SK pair. After the creation is successful, you can download the AK and SK.
- Method 2: Account and password authentication
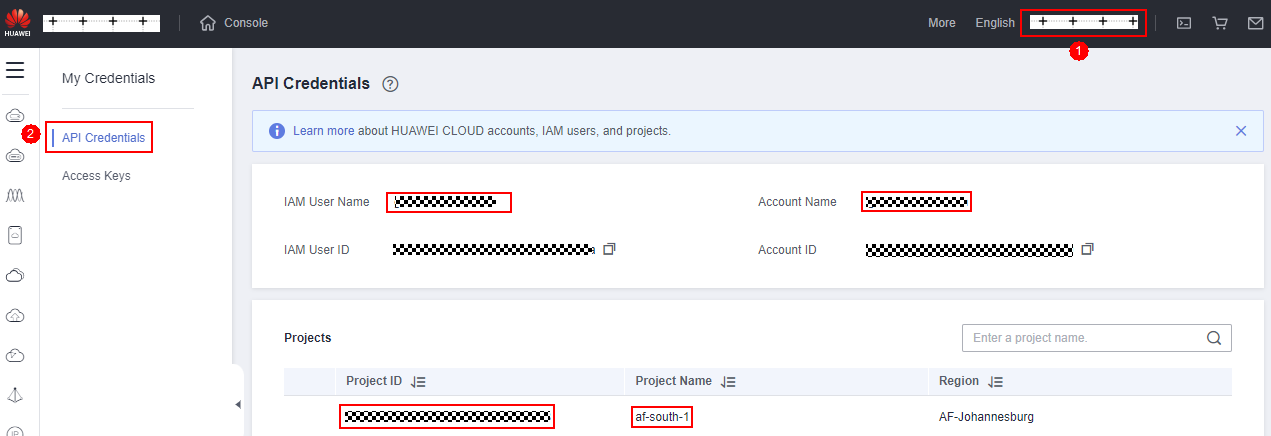
- IAM username, account name, project, and project ID: On the Huawei Cloud console, click the username in the upper right corner and choose My Credentials. On the displayed page, you can obtain the IAM username, account name, project, and project ID, as shown in the following figure.
- IAM server address: https://iam.Project.myhuaweicloud.com/v3/auth/tokens
- IAM user password: Enter the password of the IAM user.
- KMS server address: https://kms.Project.myhuaweicloud.com/v1.0/Project ID/kms
- IAM username, account name, project, and project ID: On the Huawei Cloud console, click the username in the upper right corner and choose My Credentials. On the displayed page, you can obtain the IAM username, account name, project, and project ID, as shown in the following figure.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot