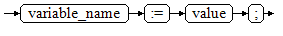Assignment Statements
Variable Syntax
Figure 1 shows the syntax diagram for assigning a value to a variable.
The above syntax diagram is explained as follows:
- variable_name: specifies the name of a variable.
- value can be a value or an expression. The type of value must be compatible with the type of variable_name.
Variable Value Assignment Example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
gaussdb=# DECLARE emp_id INTEGER := 7788; -- Assignment BEGIN emp_id := 5; -- Assignment DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(emp_id); emp_id := 5*7784; DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(emp_id); END; / -- The result is as follows: 5 38920 ANONYMOUS BLOCK EXECUTE |
INTO/BULK COLLECT INTO
INTO and BULK COLLECT INTO store values returned by statements in a stored procedure to variables. BULK COLLECT INTO allows some or all returned values to be temporarily stored in an array.
Example
gaussdb=# DROP TABLE IF EXISTS customers; NOTICE: table "customers" does not exist, skipping DROP TABLE gaussdb=# CREATE TABLE customers(id int,name varchar); CREATE TABLE gaussdb=# INSERT INTO customers VALUES(1,'ab'); gaussdb=# DECLARE my_id integer; BEGIN select id into my_id from customers limit 1; -- Assign a value. END; / ANONYMOUS BLOCK EXECUTE gaussdb=# DECLARE type id_list is varray(6) of customers.id%type; id_arr id_list; BEGIN select id bulk collect into id_arr from customers order by id DESC limit 20; -- Assign values in batches. END; / ANONYMOUS BLOCK EXECUTE

- BULK COLLECT INTO can only assign values to arrays or collections in batches. The array type uses LIMIT properly to prevent performance deterioration caused by excessive operations on data.
- For array variables, elements in parentheses () are preferentially identified as index sets. Therefore, expressions with parentheses cannot be written after array variables. For example, select (1+3) into va(5) cannot be written as select into va(5) (1+3) or select into va[5] (1+3).
- BULK COLLECT INTO can be used only in the ORA-compatible database.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot