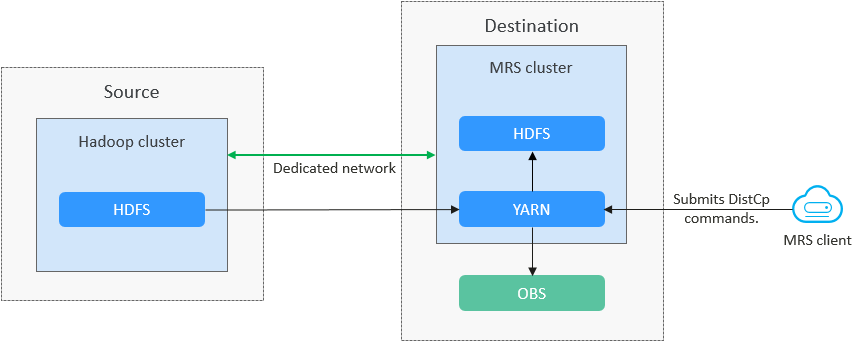
Migrating HDFS Data from a Self-Built Cluster to an MRS Cluster with DistCp
Scenarios
Distributed Copy (DistCp) is a distributed data replication tool provided by Hadoop. It is designed to efficiently transfer large volumes of data between HDFS clusters, between HDFS and the local file system, or even within the same cluster. DistCp leverages Hadoop's distributed computing capabilities and the parallel processing framework of MapReduce to enable highly efficient migration of large-scale data.
You can run the distcp command to migrate data stored in HDFS of a self-built Hadoop cluster to an MRS cluster.
Solution Architecture
Figure 1 shows the process for migrating data from a Hadoop cluster to an MRS cluster.
- Full data migration
- Create a snapshot for the directory to be migrated in the source Hadoop cluster.
- On the MRS cluster client, run the DistCp command for full data migration and set the destination path to OBS or HDFS.
- Incremental data migration
- Create a snapshot for the directory that requires incremental migration in the source Hadoop cluster.
- On the MRS cluster client, run the DistCp command with the -update -delete parameter added to perform incremental migration. Set the destination path to HDFS.
Data migration supports different networking types, such as the public network, VPN, and Direct Connect. Select a networking type as required to ensure that the source and destination networks can communicate with each other.
|
Migration Network Type |
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
|
Direct Connect |
|
|
|
VPN |
|
|
|
Public IP address |
|
|
Notes and Constraints
- If the migration destination is an OBS bucket, DistCp does not support incremental migration because OBS does not support snapshots.
- You need to learn about the customer's services and communicate with the customer to determine the migration time window. You are advised to perform the migration during off-peak hours.
Prerequisites
- You have created an MRS cluster that contains the Hadoop service.
- You have prepared an ECS execution node and installed the MRS cluster client on the node. The node and the MRS cluster are in the same VPC and security group.
- The source cluster, destination cluster, and the node where the MRS cluster client is installed can communicate with each other. (Direct Connect is recommended.)
Migrating All Data Using DistCp
- Install the MRS cluster client on the prepared ECS node.
For details about how to install the client, see Installing an MRS Cluster Client. For example, the client installation directory is /opt/client.
- Obtain the IP address and port number of the active HDFS NameNode in the source cluster.
The query method varies depending on the self-built clusters. You can contact the cluster administrator or log in to the cluster management page to query the information.
Figure 2 Checking the HDFS NameNode port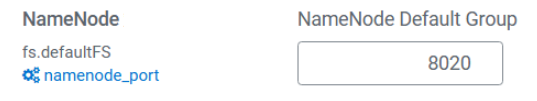
- Log in to MRS Manager of the destination cluster and check the IP address and port number of the active HDFS NameNode.
- Choose Cluster > Services > HDFS and click Instances. On the displayed page, view the IP address of the NameNode (hacluster,Active) instance in the instance list.
- Click Configurations, and search for and view the NameNode port parameter dfs.namenode.rpc.port.
- Obtain the HDFS file directory containing the data to be migrated from the source cluster.
For example, in this example, the directory to be migrated is /benchmarks/TestDFSIO/io_data.
- Configure user access to the source HDFS on the ECS execution node.
vim /etc/profile
Configure environment variables.
export HADOOP_USER_NAME=hdfs
Load the environment variables.
source /etc/peofile
- Create a snapshot for the specified HDFS directory in the source cluster. The snapshot is saved in /Snapshot directory/.snapshot.
- Enable the snapshot function for the specified directory in the source cluster.
hdfs dfsadmin -allowSnapshot Snapshot directorySource cluster directory format: hdfs://IP address of the active NameNode:Port/Directory
For example, run the following command:
hdfs dfsadmin -allowSnapshot hdfs://192.168.1.100:8020/benchmarks/TestDFSIO/io_data
- Create a snapshot.
hdfs dfs -createSnapshot Snapshot directory Snapshot file name
For example, run the following command:
hdfs dfs -createSnapshot hdfs://192.168.1.100:8020/benchmarks/TestDFSIO/io_data snapshot01
- Enable the snapshot function for the specified directory in the source cluster.
- Go to the MRS cluster client directory.
cd /opt/client
source bigdata_env
User authentication is required for MRS clusters with Kerberos authentication enabled.
kinit HDFS service user - Run the distcp command on the node where the MRS cluster client is installed to migrate data.
hadoop distcp -prbugpcxt Path for storing snapshots in the source cluster Data storage path in the destination cluster
For example, run the following command:
hadoop distcp -prbugpcxt hdfs://192.168.1.100:8020/benchmarks/TestDFSIO/io_data/.snapshot/snapshot01/* hdfs://192.168.1.200:8020/hdfs/
Wait until the MapReduce task is complete.
- After the full migration is complete, check whether the files are successfully migrated to the destination cluster.
hdfs dfs -ls HDFS file directoryFor example, all files in the source cluster are as follows.

All files in the destination cluster are as follows.

Migrating Incremental Data using DistCp
- Create a snapshot for the directory that requires incremental migration in the source cluster.
hdfs dfs -createSnapshot Snapshot directory Snapshot file name
For example, run the following command:
hdfs dfs -createSnapshot hdfs://192.168.1.100:8020/benchmarks/TestDFSIO/io_data snapshot02
- Run the distcp command on the node where the MRS cluster client is installed to migrate incremental data.
hadoop distcp -prbugpcxt Path for storing snapshots in the source cluster Data storage path in the destination cluster
For example, run the following command:
hadoop distcp -prbugpcxt -update -delete hdfs://192.168.1.100:8020/benchmarks/TestDFSIO/io_data/.snapshot/snapshot02/* hdfs://192.168.1.200:8020/hdfs
Wait until the MapReduce task is complete.
- After migration, check the number and size of files in the destination and compare them with the source to ensure consistency.
hdfs dfs -ls HDFS file directoryFor example, incremental files in the source cluster are as follows.

Incremental files in the destination cluster are as follows.
FAQs About Data Migration Using DistCp
- Version differences
If the Hadoop version of the source cluster matches the MRS cluster in major version (minor versions may differ), you can use the following command to synchronize service data from the source table to the MRS cluster:
hadoop distcp -prbugpcaxt hdfs://Active NameNode IP address:Port/Snapshot path Save path
If the Hadoop version of the source cluster is significantly different from the MRS cluster version, use WebHDFS or HFTP to replace HDFS to run the following commands:
hadoop distcp -prbugpcaxt webhdfs://Active NameNode IP address:Port/Snapshot path Save path
Or
hadoop distcp -prbugpcaxt hftp://Active NameNode IP address:Port/Snapshot path Save path
- Parameters of the DistCp commands
- -p[rbugpcaxt]: specifies the attributes of the retained data.
- IP address: IP address of the active NameNode in the source cluster.
- Port: The default open-source port for HDFS is 8020, and the port for WebHDFS and HFTP is 50070.
- If the source cluster provides a unified domain name for access, you can change Active NameNode IP address:Port to the domain name URL.
- DistCp permission control
When DistCp is used for migration, file or directory copy operations may fail due to insufficient permissions.
Ensure that the user executing the DistCp command has sufficient permissions to read from the source path and write to the destination path. You can use the -p option to preserve the permission information.
- Timeout interval change using the DistCp command
When you run the DistCp command, if some files being copied are particularly large, you are advised to increase the timeout settings for the MapReduce jobs that execute the copy tasks.
You can specify mapreduce.task.timeout in the DistCp command to increase the timeout interval.
For example, run the following command to change the timeout interval to 30 minutes:
hadoop distcp -Dmapreduce.task.timeout=1800000 hdfs://cluster1/source hdfs://cluster2/target
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot