Using Global Accelerator to Accelerate Communications Between Cloud and On-Premises Servers and Implement Multi-active DR
Overview
Application scenario: Suppose you have a web server deployed in your on-premises data center in the Chinese mainland and you want to deploy your services in one or more regions on Huawei Cloud for multi-active DR.
Solution architecture: To achieve multi-active DR, you can deploy your services both in on-premises data center and on the cloud (CN South-Guangzhou region). And also you can use Global Accelerator to speed up access while keeping services highly reliable.

Resource and Cost Planning
|
Resource |
Description |
Quantity |
Price |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Global accelerator |
You are charged based on how long each global accelerator is retained in your account. The smallest billing unit is one hour. Partial hours are counted as full hours. Global accelerator price = Unit price x Required duration |
1 |
For details, see Global Accelerator Pricing Details. |
|
Data transfer |
You are charged for either the inbound or outbound traffic, in GB, whichever direction has more traffic. Data transfer price = Unit price x Traffic used |
Per actual use |
|
|
Record sets added to the public zone |
Add an A record set with Line set to Default and Value set to the anycast IP address of the global accelerator. |
1 |
Free |
Flowchart

Step 1: Buy a Global Accelerator
To use Global Accelerator for faster access, you first need to create a global accelerator.
- Log in to the Global Accelerator console.
- On the Global Accelerator page, click Buy Global Accelerator.
Figure 1 Creating a global accelerator
- Configure the parameters. For details, see Table 2.
Figure 2 Creating a global accelerator

Table 2 Parameters for configuring a global accelerator Parameter
Description
Name
Name of the global accelerator you want to create.
Only letters, digits, and hyphens are allowed.
You can enter up to 64 characters.
Enterprise Project
An enterprise project you would like to use to centrally manage your Global Accelerator resources.
You can use an existing enterprise project or create one.
Applicability
Where the global accelerator will be used.
There are two options: Outside the Chinese mainland or Chinese mainland. Outside the Chinese mainland is selected by default.
Chinese mainland is recommended for this practice.
IP Address Type
The type of the IP address used by the global accelerator.
If you select Chinese mainland for Applicability, you can select IPv4 or IPv4+IPv6.
Default value: IPv4.
Tags
An identifier of the global accelerator. Each tag consists of a key and a value. You can add 20 tags for a global accelerator.
NOTE:If a predefined tag has been created in TMS, you can select the corresponding tag key and value.
For details about predefined tags, see Predefined Tag Overview.
If you have configured tag policies for Global Accelerator, you need to add tags to your accelerators based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, global accelerators may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
Description
Supplementary information about the global accelerator.
A maximum of 255 characters are allowed.
- Click Next.
Step 2: Add a Listener to the Global Accelerator
Add a listener to the global accelerator to route requests across endpoints based on the client affinity you set.

|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
Listener name. Only letters, digits, and hyphens are allowed. You can enter up to 64 characters. |
|
Protocol |
The protocol used by the listener to receive requests from clients. The protocol can be TCP or UDP. |
|
Port |
The ports or port ranges used by the listener to receive requests from clients. The port number ranges from 1 to 65535. You can enter one or more ports or port ranges separated by commas (,). Example: 1-10,11-50,51,52-200 |
|
Client Affinity |
How requests are routed. There are two options: None: The listener routes requests evenly among the endpoints in the endpoint group. Source IP address (only for TCP and UDP listeners): The source IP address of each request is calculated using the consistent hashing algorithm to obtain a unique hash key, and all the endpoints are numbered and mapped to the hash keys. Requests from the same IP address are forwarded to the same endpoint for processing. |
|
Tags |
An identifier of the listener. Each tag consists of a key and a value. You can add up to 20 tags to a listener.
NOTE:
If a predefined tag has been created in TMS, you can select the corresponding tag key and value. For details about predefined tags, see Predefined Tag Overview. If you have configured tag policies for Global Accelerator, you need to add tags to listeners based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, listeners may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies. |
|
Description |
Supplementary information about the listener. A maximum of 255 characters are allowed. |
Step 3: Associate Two Endpoints Group with the Listener
Associate two endpoint groups with the listener, one in CN East-Shanghai1 and the other in CN South-Guangzhou. For details, see Table 4.
|
Item |
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Endpoint group |
Name |
Name of the endpoint group. Each listener can be associated with only one endpoint group in a given region. Only letters, digits, and hyphens are allowed. You can enter up to 64 characters. |
|
Region |
Region where the endpoint group is used. Add one endpoint group in CN East-Shanghai1 and one in CN South-Guangzhou. |
|
|
Description |
Supplementary information about the endpoint group. A maximum of 255 characters are allowed. |
|
|
Traffic Dial |
The percentage of traffic directed to each endpoint group. If you increase the traffic dial, more requests will be distributed to this endpoint group. The value ranges from 0 to 100. If you set the traffic dial to 0, no requests will be distributed to this endpoint group. Set the traffic dial of both endpoint groups to 100.
NOTE:
If a listener has multiple endpoint groups, traffic will be first distributed to the endpoint group with the lowest latency and then to other endpoint groups based on the traffic dial value you set. |
|
|
Endpoint |
A single point of contact for clients. Global Accelerator distributes incoming traffic across healthy endpoints. Add the public IP address of your web server to the endpoint group in CN East-Shanghai1 and the EIP to the endpoint group in CN South-Guangzhou. |
|
|
Health Check |
Health Check |
Whether to enable health check. If you disable health check, requests may be forwarded to unhealthy endpoints. |
|
Protocol |
The health check protocol can be TCP or UDP. Default value: TCP. |
|
|
Port |
The port used for health check. The port number ranges from 1 to 65535. |
|
|
Advanced Settings |
||
|
Interval (s) |
The maximum time between two consecutive health checks, in seconds. The interval ranges from 1 to 60. |
|
|
Timeout (s) |
The maximum time required for waiting for a response to a health check request, in seconds. The timeout ranges from 1 to 60. |
|
|
Maximum Retries |
The maximum number of health check retries allowed. The value ranges from 1 to 10. |
|
Step 4: Add a Record Set
Add an A record set to map your domain name to the anycast IP address of the global accelerator.
This section uses Huawei Cloud DNS as an example.
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- On the Public Zones page, click the target domain name.
The Record Sets page is displayed.
- In the upper right corner of the page, click Add Record Set.
- On Add Record Set page, add an A record set as instructed by Table 5.
Figure 4 Adding an A record set
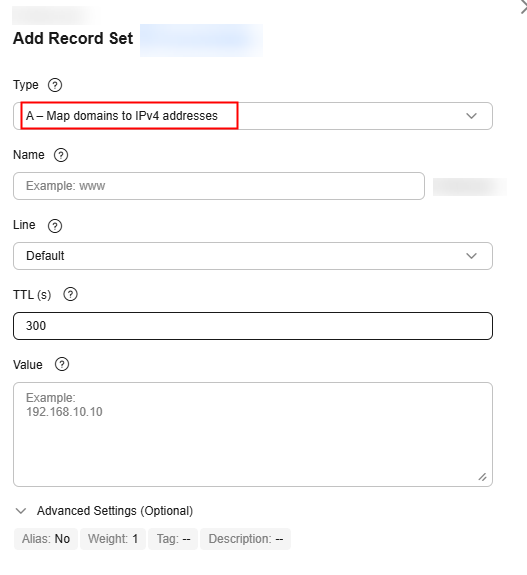
Table 5 Parameters for configuring an A record set Parameter
Description
Type
Record set type
An A record set is selected here.
Name
Prefix of the domain name to be resolved.
Retain the default value for this practice.
Line
Resolution line. The DNS server will return the IP address of the specified line, depending on where end users come from.
Set the value to Default.
TTL (s)
Cache duration of the record set on a local DNS server, in seconds.
The value ranges from 1 to 2147483647, and the default value is 300.
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value.
Retain the default value for this practice.
Value
IPv4 addresses mapped to the domain name.
Set the value to the anycast IP address of the global accelerator.
Alias
Whether to associate the record set with a cloud resource.
Retain the default value for this practice.
Alias Target
The cloud resource that you want to associate with the record set.
This parameter is available only when Alias is enabled.
Retain the default value for this practice.
Weight
(Optional) Weight of a record set.
The value ranges from 0 to 1000, and the default value is 1.
Retain the default value for this practice.
Tag
(Optional) Identifier of a record set. Each tag contains a key and a value. You can add a maximum of 10 tags to a record set.
Description
(Optional) Supplementary information about the record set.
You can enter a maximum of 255 characters.
- Click OK.
- Switch back to the Record Sets tab.
View the record set you have added and ensure that its status is Normal.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





