Using Global Accelerator for S2C VPN Acceleration
Overview
Application: Site-to-Cloud VPN (S2C VPN) establishes secure, reliable, and cost-effective encrypted connections between local networks, data centers, and cloud networks based on the IPsec protocol. However, S2C VPN has certain limitations:
- Cross-border VPN connections cannot be established between the Chinese mainland and other areas.
- The network quality is poor. There may be issues such as slow data rates, high latency, excessive jitter, and packet loss.
Global Accelerator can solve these problems. It provides you with a reliable, high-security, low-latency network for hybrid cloud deployment, cross-region VPC interconnection, multi-branch interconnection of enterprises, and more.
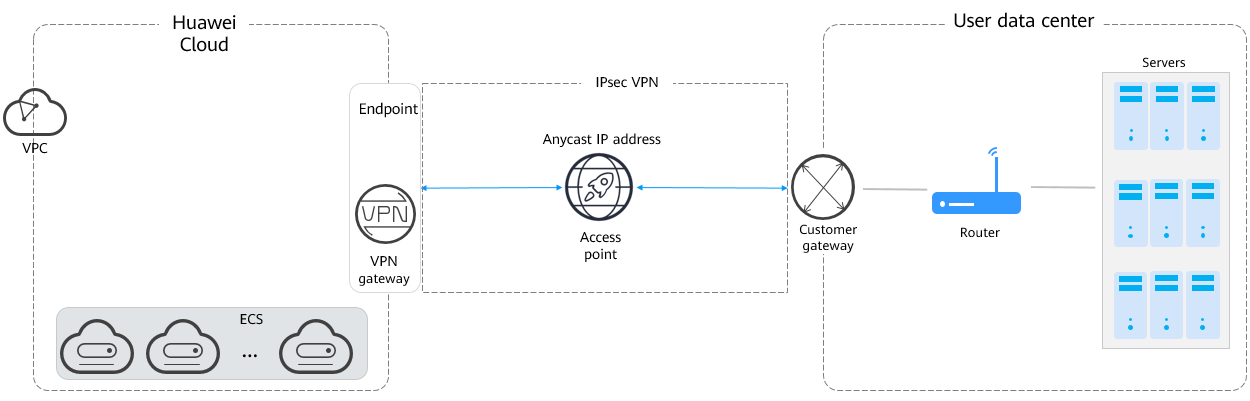
Solution architecture: Global Accelerator accelerates the IPsec VPN tunnel between a VPN gateway and a customer gateway. Figure 1 shows the solution architecture.
- The endpoint is set to the EIP of the VPN gateway. Global Accelerator uses this EIP to send traffic to the VPN gateway.
- An anycast IP address is used as the remote IP address of the customer gateway. The customer gateway uses this IP address to establish a VPN connection with the VPN gateway through Global Accelerator.
Constraints
- Huawei Cloud VPN IPsec tunnels use UDP, so you need to set the protocol to UDP when you configure a global accelerator listener.
- For EIP endpoints, Network Address Translation (NAT) is performed on data packets when they arrive at a global accelerator. So, the VPN gateway cannot identify the real IP address of the customer gateway. When configuring a VPN gateway, you need to enable access via a non-fixed IP address.
- This process described here only applies to the following S2C VPN gateway specifications: Professional 1 (non-fixed IP address) and Professional 2 (non-fixed IP address).
For details about S2C VPN specifications, see S2C VPN.
Resource and Cost Planning
|
Resource |
Description |
Quantity |
Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Global accelerator |
You are billed based on how long each global accelerator is retained in your account. The smallest billing unit is one hour. Partial hours are counted as full hours. Global accelerator price = Unit price × Required duration |
2
NOTE:
One S2C VPN gateway is associated with two EIPs. Each EIP requires one global accelerator. |
For details, see Global Accelerator Pricing Details. |
|
Data transmission |
You are billed by the GBs used by your global accelerators. You are charged for either the inbound or outbound traffic, whichever direction has more traffic. Data transmission price = Unit price × Traffic used |
Per actual use |
|
|
S2C VPN |
For a yearly/monthly Professional S2C VPN gateway, the maximum number of VPN connection groups and maximum bandwidth depend on the gateway specifications. |
1 |
For details, see VPN Pricing Details. |
Procedure
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Use the two EIPs as endpoints and configure a global accelerator for each of them. |
|
|
Create VPN connections. Use the purchased EIPs as the active EIP and active EIP 2 of the VPN gateway. |
|
|
After the basic VPN functions are usable, set the peer gateway IP address of the router in the user data center to the anycast IP address. |
|
|
Verify that the VPN connections are normal and the global accelerators are healthy. Confirm that the servers in your data center and the cloud servers in the VPC can ping each other. |
Step 1: Preparations
- Buy two EIPs. For details, see Assigning an EIP.
- If cross-border access is required between the VPN gateway and customer gateway, you need to apply for a cross-border permit. For details, see Cross-Border Permits Application.
Step 2: Buy Global Accelerators
- Log in to the Global Accelerator console.
- Click Buy Global Accelerator.
Select a region based on where the customer gateway is. The following uses a customer gateway outside the Chinese mainland as an example.Figure 2 Creating a global accelerator

- Configure the listener, endpoint groups, endpoints, health check, and other parameters.
- Listener: Set Protocol to UDP and Port Ranges to 500,4500.
- Endpoint Groups: Add an endpoint group based on the region where the VPN gateway is and add one of the purchased EIPs as an endpoint.
- Health Check: Enable health check. Set Protocol to UDP and Port to 500 or 4500.
- Click Next. Confirm the settings and complete the purchase.
- Repeat 2 to 4 to buy another global accelerator, with the other EIP used as an endpoint.
- Go back to the global accelerator list. Take note of the anycast IP addresses of the two EIPs in the IP Address column.
Step 3: Create VPN Connections
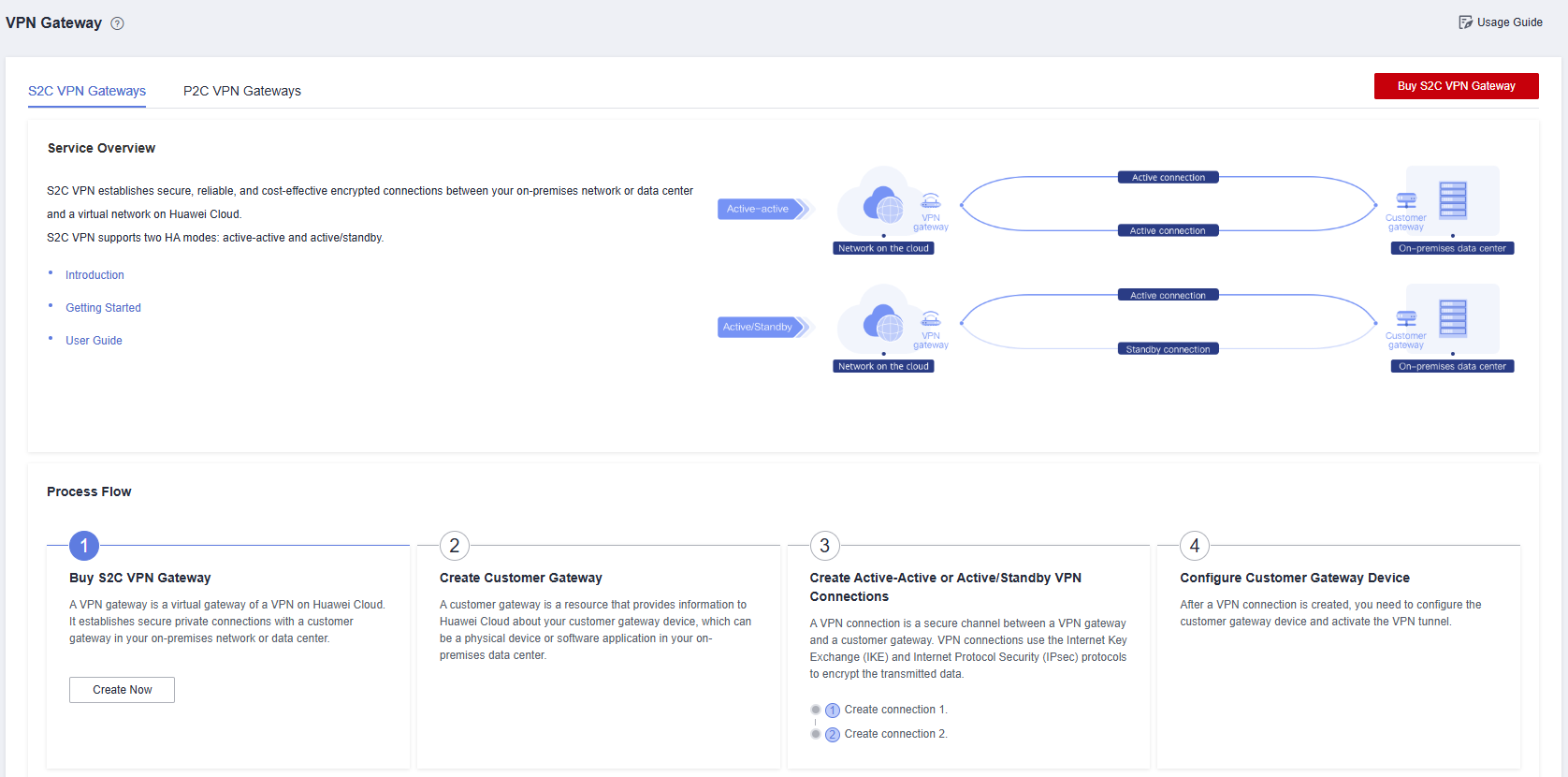
- Buy an S2C VPN gateway.
- Log in to the S2C VPN Gateway console.
- In the upper right corner, click Buy S2C VPN Gateway.
Figure 3 Buying an S2C VPN gateway
- Configure the VPN gateway parameters.
- Billing Mode: Select Yearly/Monthly.
- Specifications: Select Professional 1 or Professional 2 and enable access via a non-fixed IP address.
- EIP: Disable Shared Bandwidth. Select Use existing for Active EIP and Active EIP 2 and set them to the two purchased EIPs.
Figure 4 Configuring VPN gateway parameters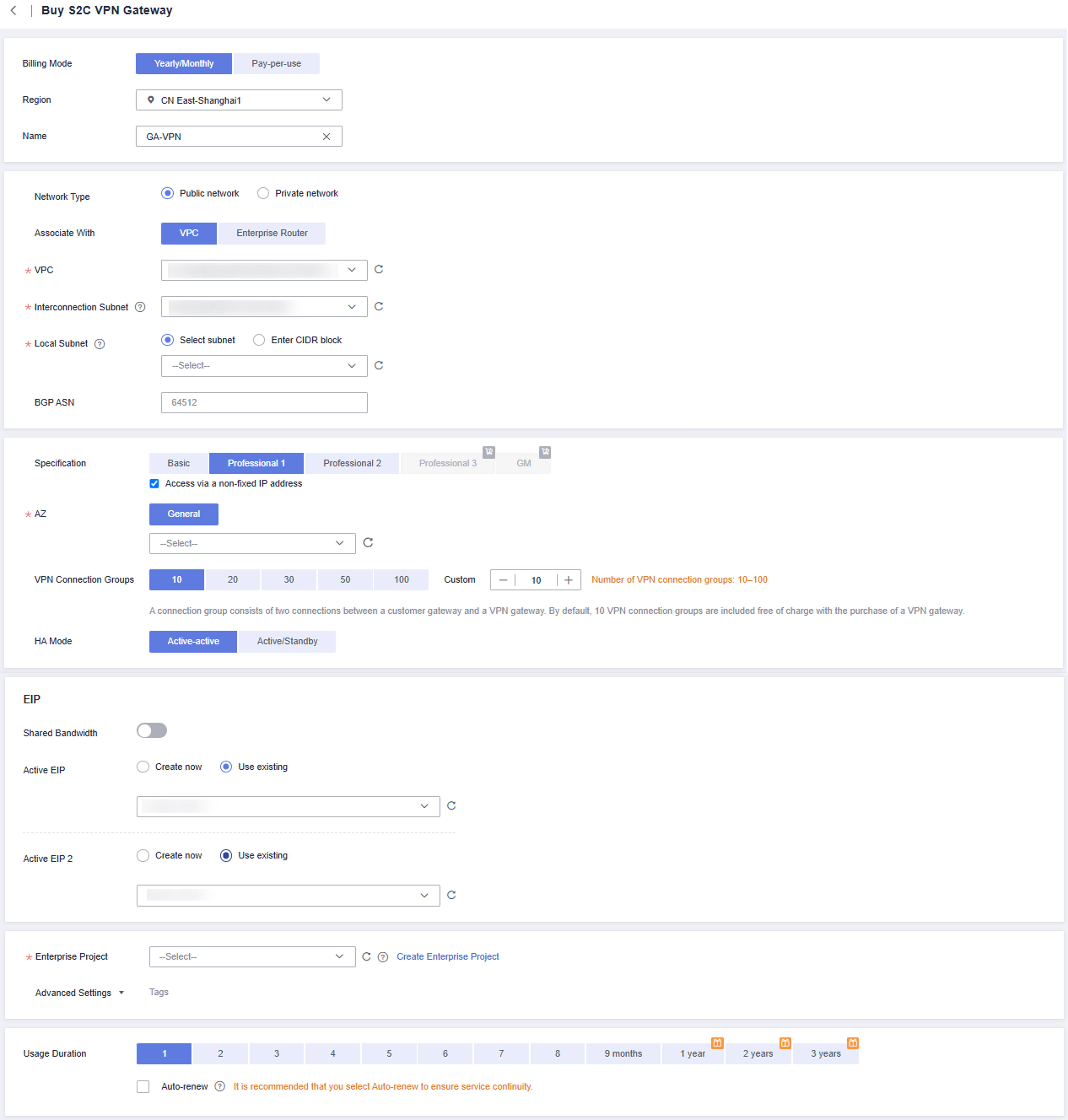
- Click Buy Now. Confirm the settings and pay for the bill.
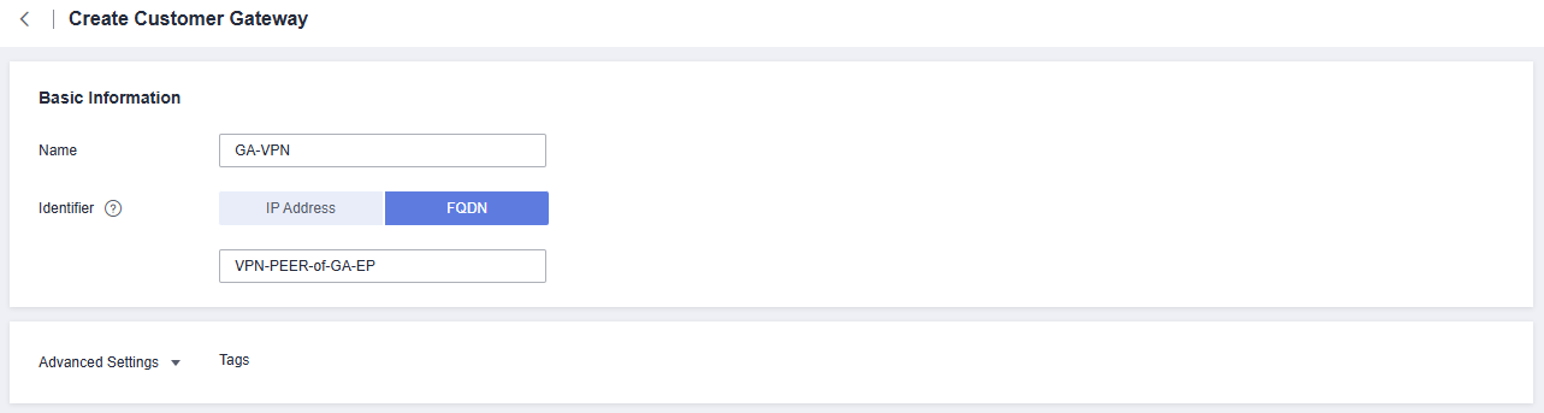
- Create a customer gateway.
- Log in to the Customer Gateway console.
- In the upper right corner, click Create Customer Gateway.
Figure 5 Creating a customer gateway
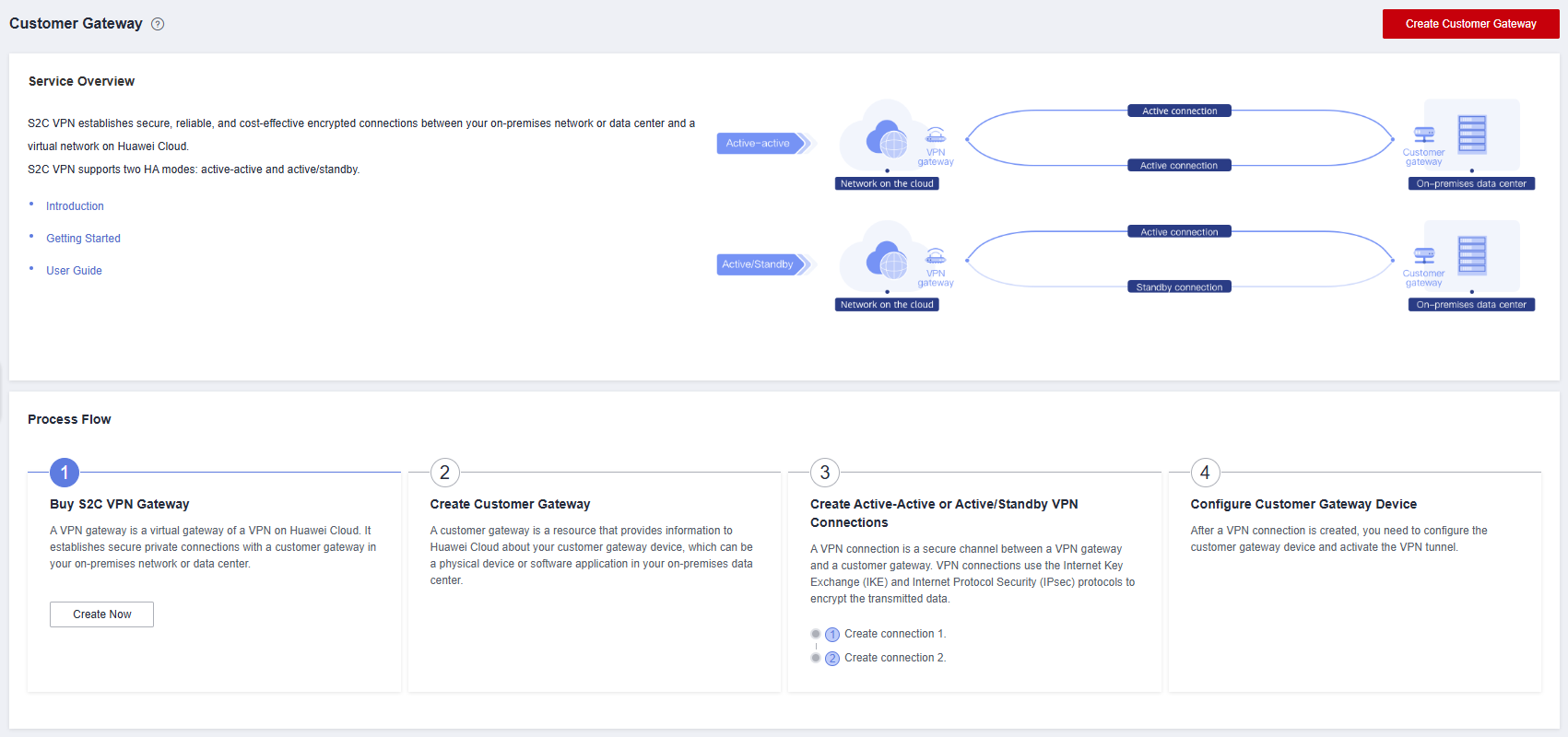
- Configure the customer gateway parameters.
- Create a VPN connection.
- Log in to the VPN Connection console.
- In the upper right corner, click Create VPN Connection.
Figure 7 Creating a VPN connection
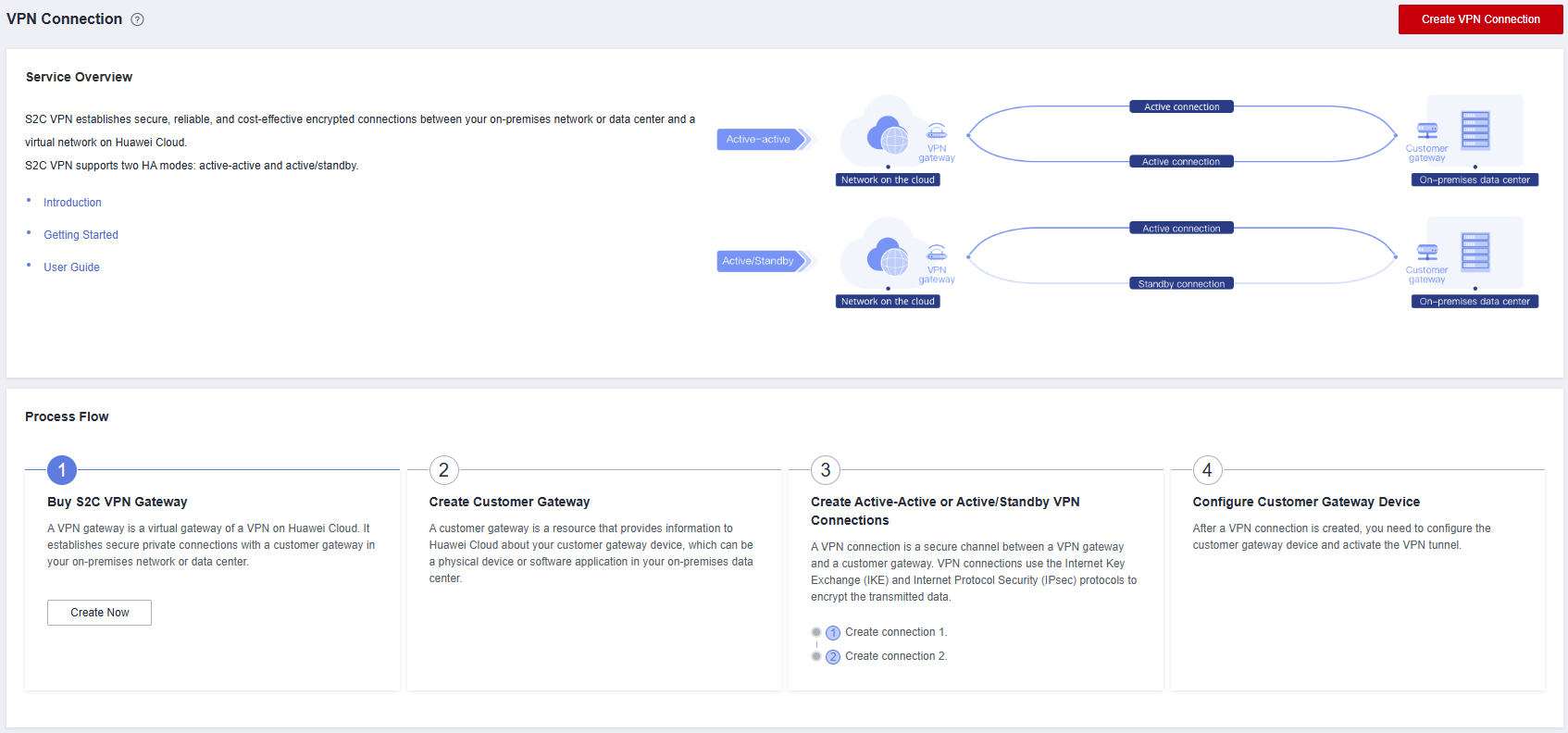
- Configure the VPN connection parameters.
- VPN Gateway: Select the VPN gateway created in 1.
- Gateway IP Address: Select either of the two EIPs associated with the VPN gateway.
- Customer Gateway: Select the customer gateway created in 2.
- VPN Type: Retain the default value Policy template.
Figure 8 Configuring VPN connection parameters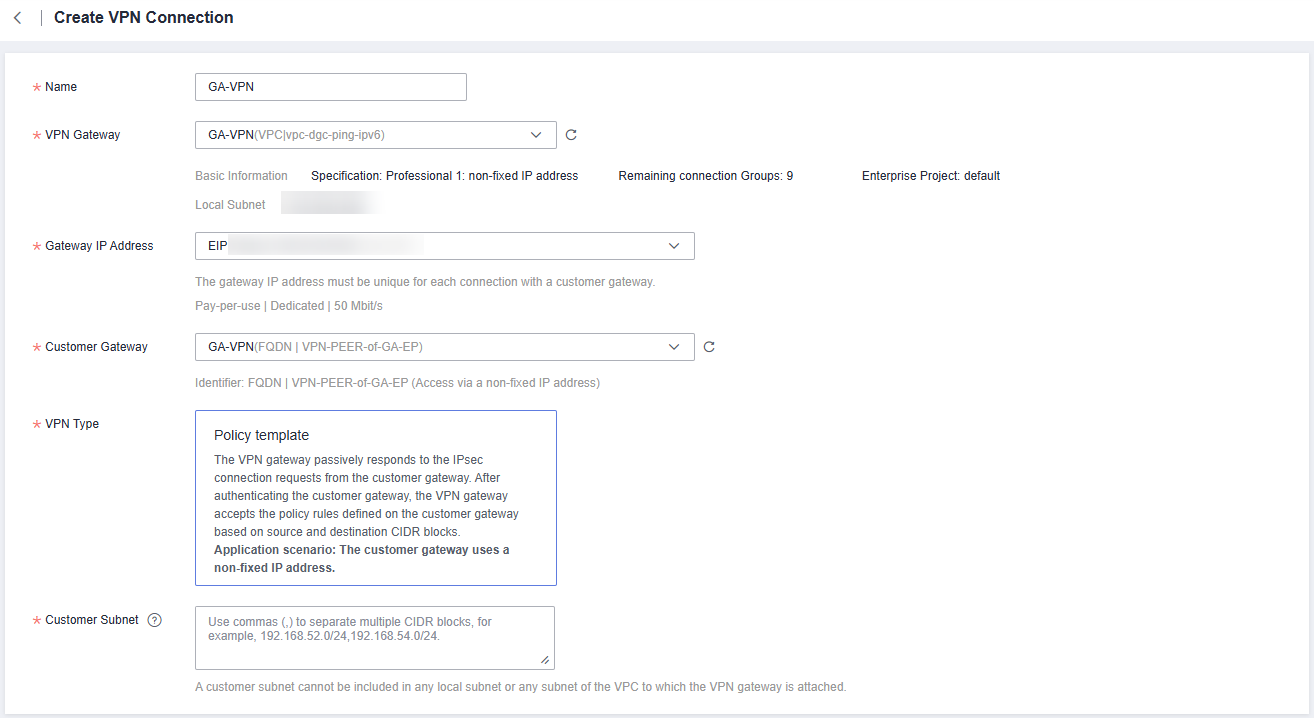
- Repeat the preceding steps to create a VPN connection for the other EIP associated with the VPN gateway.
Step 4: Configure the Customer Gateway Device
Compared with just using an S2C VPN, if you use an S2C VPN accelerated by Global Accelerator, there are a couple of items you need to note when configuring IPsec VPN on the customer gateway device:
- IKE: Set the local identifier type to FQDN and use the customer gateway identifier noted in 2 as the local identifier. Use the EIP of the S2C VPN gateway as the peer identifier and use the anycast IP address for this EIP as the peer gateway IP address.
- IPsec: Enable NAT traversal.
The settings depend on the customer gateway type. For details, see customer gateway operations in the Virtual Private Network Administrator Guide.
Step 5: Test the Network Connectivity
Test connectivity:
- Verify that the VPN connections are normal. For details, see Viewing a VPN Connection.
- Verify that the global accelerators are healthy. For details, see Viewing an Endpoint.
- Verify that servers in your data center and cloud servers in the VPC can ping each other.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot