What Are the Differences Between EIPs, Private IP Addresses, and Virtual IP Addresses?
Different types of IP addresses have different functions.
|
IP Address Type |
Description |
Example Value |
|---|---|---|
|
Private IP address |
Private IP addresses come with your ECSs and belong to the VPC subnets of the ECSs. They are used for private communication on the cloud. |
|
|
Virtual IP address |
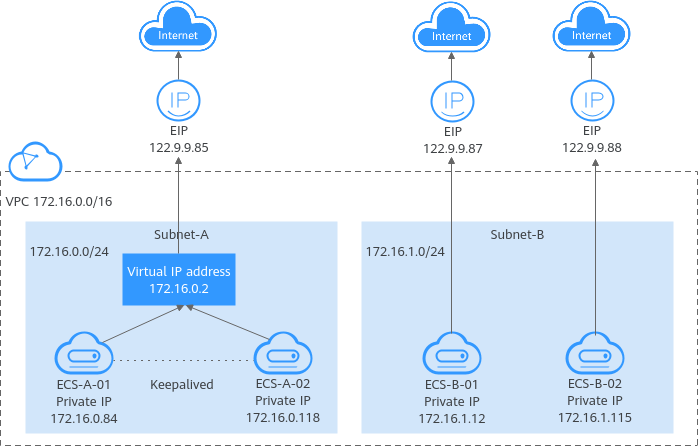
A virtual IP address is a private IP address independently assigned from a VPC subnet. It can be released when no longer needed. You can:
For more information about virtual IP addresses, see Virtual IP Address Overview. For details about how to set up a high availability cluster, see Using a Virtual IP Address and Keepalived to Set Up a High-Availability Web Cluster. |
Bind virtual IP address (172.16.0.2) both ECS-A-01 and ECS-A-02. The active/standby switchover of ECS-A-01 and ECS-A-02 can be implemented by using Keepalived. |
|
EIP |
EIPs allow cloud resources to access the Internet. They can be flexibly bound to or unbound from instances.
For more information, see EIP Overview. |
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





