UCS Permissions
UCS permissions management allows you to grant permissions to IAM users and user groups under your tenant accounts. UCS combines the advantages of IAM and Kubernetes RBAC to provide a variety of authorization methods, including IAM fine-grained and token authorization and cluster-, fleet-, cluster namespace–, and fleet namespace–level authorization.
UCS allows you to manage permissions on related resources at a finer granularity, for example, to control the access of employees in different departments to cloud resources.
This section describes the UCS permissions management mechanism and related concepts. If your account has met your service requirements, you can skip the configurations in this section.

Permissions management applies to single clusters and fleets with cluster federation enabled. To use permissions management, enable cluster federation for your fleet.
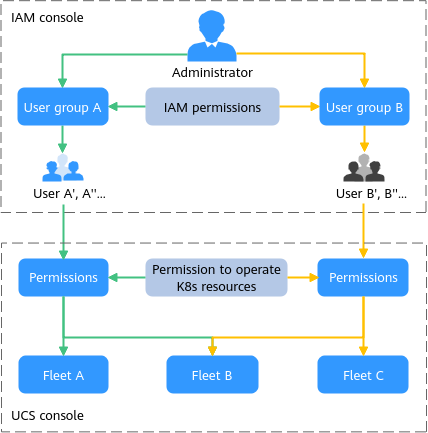
UCS Permissions Management
UCS permissions management involves UCS resource permissions and Kubernetes resource permissions in a cluster.
- UCS resource permissions are based on IAM system-defined policies and include cluster-level permissions and fleet-level permissions.
- Kubernetes resource permissions in a cluster are based on Kubernetes RBAC and include cluster namespace-level permissions and fleet namespace-level permissions.
UCS permissions are described as follows:
- Cluster-level permissions: You can grant cluster-level permissions to allow some user groups to perform operations on clusters (such as registering and deregistering clusters and managing cluster add-ons) and allow some user groups to only view clusters.
- Fleet-level permissions: You can grant fleet-level permissions to allow some user groups to perform operations on fleets (such as creating and deleting fleets, adding clusters to fleets, and deleting clusters from fleets) and allow some user groups to only view fleets.
UCS resource permissions involve UCS non-fleet APIs and Kubernetes APIs and support fine-grained IAM policies and enterprise project management. Fleet-level permissions are configured for flee-related resources (such as fleets and federations), and cluster-level permissions are configured for cluster-related resources (such as clusters and nodes). You must also configure namespace-level permissions to perform operations on fleet resources and Kubernetes resources (such as workloads, Services, and routes). Fleet-level permissions and cluster-level permissions are independent of each other.
- Cluster namespace-level permissions: You can regulate users' or user groups' access to Kubernetes resources (such as workloads, jobs, Services, and other native Kubernetes resources) based on their Kubernetes RBAC roles.
- Fleet namespace-level permissions: You can regulate users' or user groups' access to fleet resources (such as workloads, Services, MCI, distribution policies, and other native fleet resources) based on their fleet RBAC roles.
Kubernetes resource permissions in a cluster involve UCS Kubernetes APIs and are enhanced based on the Kubernetes RBAC capabilities. These permissions can be granted to IAM users or user groups for authentication and authorization, but are independent of fine-grained IAM policies.
In general, you can configure UCS permissions in two scenarios. The first is creating and managing clusters and fleets, as well as their related resources, such as nodes. The second is using Kubernetes resources in a cluster and fleet resources, such as workloads and Services.
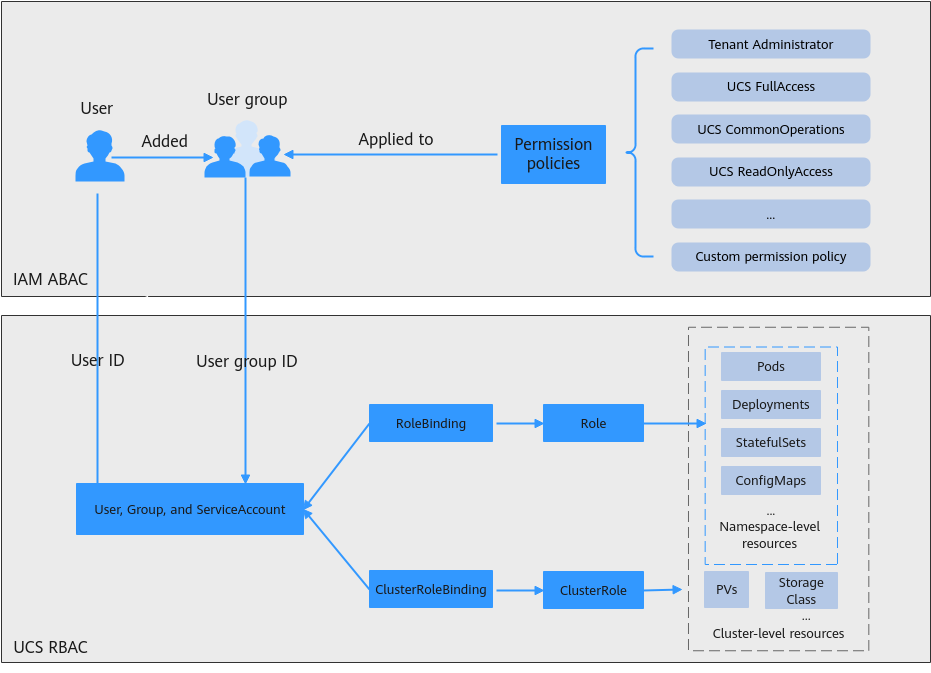
Figure 2 Illustration on UCS permissions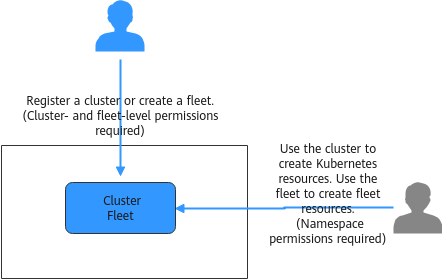
UCS Resource Permissions (IAM-based) and Kubernetes Resource Permissions in a Cluster (Kubernetes RBAC-based)
Users with different UCS resource permissions have different Kubernetes resource permissions in a cluster. Table 1 describes the Kubernetes resource permissions in a cluster for different users.
|
User Type |
UCS Resource Permissions |
Kubernetes Resource Permissions in a Cluster |
|---|---|---|
|
Users with the Tenant Administrator or UCS FullAccess permissions |
Operation permissions for Clusters, Fleets, Add-ons, Policy Center, Configuration Management, Traffic Distribution, Service Meshes, and Container Intelligent Analysis |
All namespace permissions
NOTE:
UCS FullAccess does not have the RBAC permissions of CCE clusters. You need to go to the Permissions page to grant permissions for CCE clusters. |
|
Users with the UCS CommonOperations permissions |
Read-only permissions for Clusters, Fleets, Traffic Distribution, Add-ons, Policy Center, and Configuration Management |
RBAC authorization |
|
IAM users with the UCS ReadOnlyAccess permissions |
Read-only permissions on UCS resources |
RBAC authorization |
|
IAM users with the UCS CIAOperations permissions |
Operation permissions for Container Intelligent Analysis instances on UCS |
RBAC authorization |
|
IAM users with the Tenant Guest permissions |
Read-only permissions on UCS resources |
RBAC authorization |
Permissions management flow
The following figure shows the permissions management flow of a new IAM user.
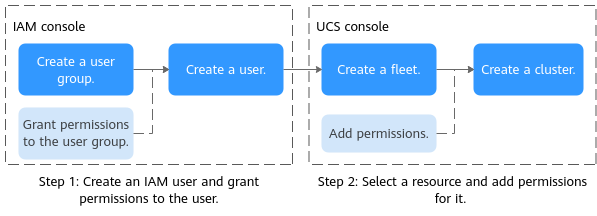
Basic Concepts
Figure 4 shows the relationships between the following basic concepts:
- User: You can use your administrator account to create IAM users and grant permissions on specific resources. Each IAM user has their own identity credentials (password and access keys) and uses cloud resources based on granted permissions.
- User group: You can use user groups to grant permissions to IAM users. IAM users added to a user group automatically obtain the permissions granted to the group. For example, after the administrator grants the UCS FullAccess permissions to a user group, users in the user group have the administrator permissions of UCS. If a user is added to multiple user groups, the user inherits the permissions granted to all these groups.
- Namespace: A namespace is a collection of resources and objects. You can create multiple namespaces in the same cluster. Data is isolated by namespace so that multiple namespaces can share the services of the same cluster without any interference with each other. For example, you can deploy workloads in a development environment into one namespace, and deploy workloads in a testing environment into another namespace.
- Permission types: The UCS administrator defines the scope of operations performed by one or more users on Kubernetes resources in a cluster. There are several common permission types on UCS, including Administrator, O&M, Developer, and Viewer. You can also create custom permissions. For details, see Adding Resource Permissions (on the Console).
- Fleet: A fleet contains multiple clusters. An administrator can use fleets to classify associated clusters. An administrator can also use a fleet for the unified management of multiple clusters, including permissions management, security policy configuration, configuration management, and multi-cluster orchestration.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot