Migrating Data to TaurusDB Enterprise Edition (OBT)
Scenarios
You can easily migrate data from RDS for MySQL instances to pay-per-use TaurusDB Enterprise Edition instances on the console. There is no need to create a DRS task. IP addresses remain unchanged and data can be transparently migrated with just a few clicks.
Source: RDS for MySQL
Destination: TaurusDB Enterprise Edition
Advantages
- No data is lost during the migration, and incremental migration is supported.
- Online live migration is supported. There is only one brief interruption during the workload migration step, lasting less than one minute.
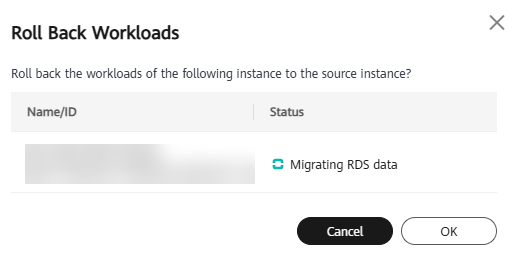
- Online migration rollback is supported. After the workload migration, you can also roll back the workloads to the status before the migration.
- You can retain the original database connection address and switch applications to TaurusDB Enterprise Edition without modifying any connection configuration.
- TaurusDB Enterprise Edition instances are free during the migration. After the migration is complete, billing automatically starts.
Versions and Storage
There are no constraints on the cloud disk type of the source instance. The following table lists the supported source and destination versions.
|
Source Instance Type |
Supported Source Version |
Supported Destination Version |
|---|---|---|
|
RDS for MySQL |
RDS for MySQL (5.7) |
TaurusDB Enterprise Edition |
|
RDS for MySQL (8.0) |
Constraints
- This function is in the OBT phase. To use it, submit a service ticket.
- To use this function, you must have the DRS Administrator privilege of DRS and the TaurusDB FullAccess privilege of TaurusDB.
- This function only supports the migration from RDS for MySQL to TaurusDB Enterprise Edition.
- The system will only switch your application's connection address from the RDS for MySQL primary node to the TaurusDB primary node.
- This function is not available to RDS for MySQL instances with an EIP bound, with database proxy enabled, or with TDE enabled.
Procedure
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot