Enabling Request Distribution Among Row Store and Column Store Nodes for Complex OLAP Queries
Scenarios
OLTP workloads involve both read and write requests in most cases. Write requests are processed by the primary node, and read requests are processed by read replicas or the primary node. OLAP workloads involve only read requests in most cases. Read requests are processed by HTAP nodes.
If your system handles both OLTP and OLAP workloads, you can use column-store indexes to distribute OLAP requests to HTAP nodes and OLTP requests to read replicas through a proxy address for optimal efficiency.
- Read replicas: process read requests based on row store. Row store nodes deliver higher performance when processing OLTP read requests.
- HTAP nodes: process read requests based on column store. HTAP nodes outperform read replicas when processing OLAP read requests (such as complex SQL and analytic SQL queries).
Request Distribution Methods
Automatic request distribution and manual request distribution are supported.
|
Method |
Description |
Constraint |
|---|---|---|
|
Automatic request distribution |
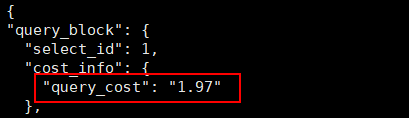
After this function is enabled, a proxy instance distributes requests based on the actual execution cost of a SQL statement to maximize the query performance. Criteria:
|
|
|
Manual request distribution |
If automatic distribution does not work as expected, you can use the HINT syntax to forcibly execute a row store or column store execution plan. |
- |
Constraints
Databases whose names contain Chinese characters cannot be synchronized. The destination database and task names cannot contain Chinese characters, and the destination database name must contain at least three characters.
Prerequisites
- Parameters have been configured for a TaurusDB instance according to the following table.
Table 2 Parameter description Parameter
Value
How to Modify
Description
binlog_expire_logs_seconds
86400
It is recommended that the binlog retention period be greater than one day. 86,400s = 60 (seconds) x 60 (minutes) x 24 (hours). This prevents incremental replication failures caused by a short binlog retention period.
rds_global_sql_log_bin
ON
To use this parameter, ensure that the kernel version of your TaurusDB instance is 2.0.45.230900 or later.
For details about how to check the kernel version, see How Can I Check the Version of a TaurusDB Instance?
- Databases and tables have been created for the TaurusDB instance.
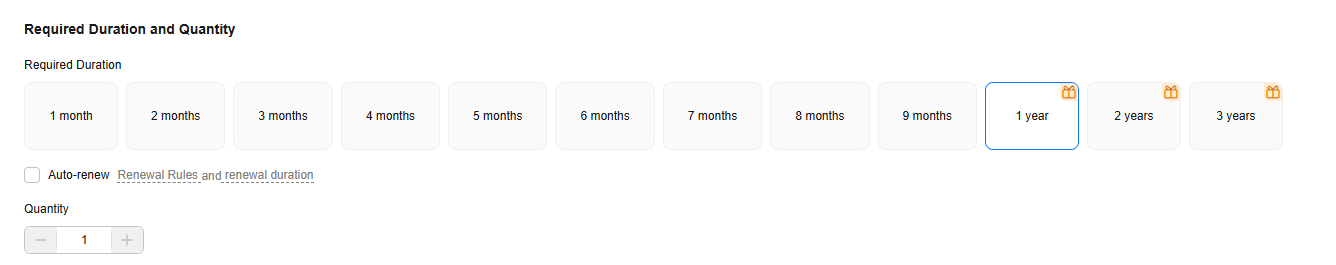
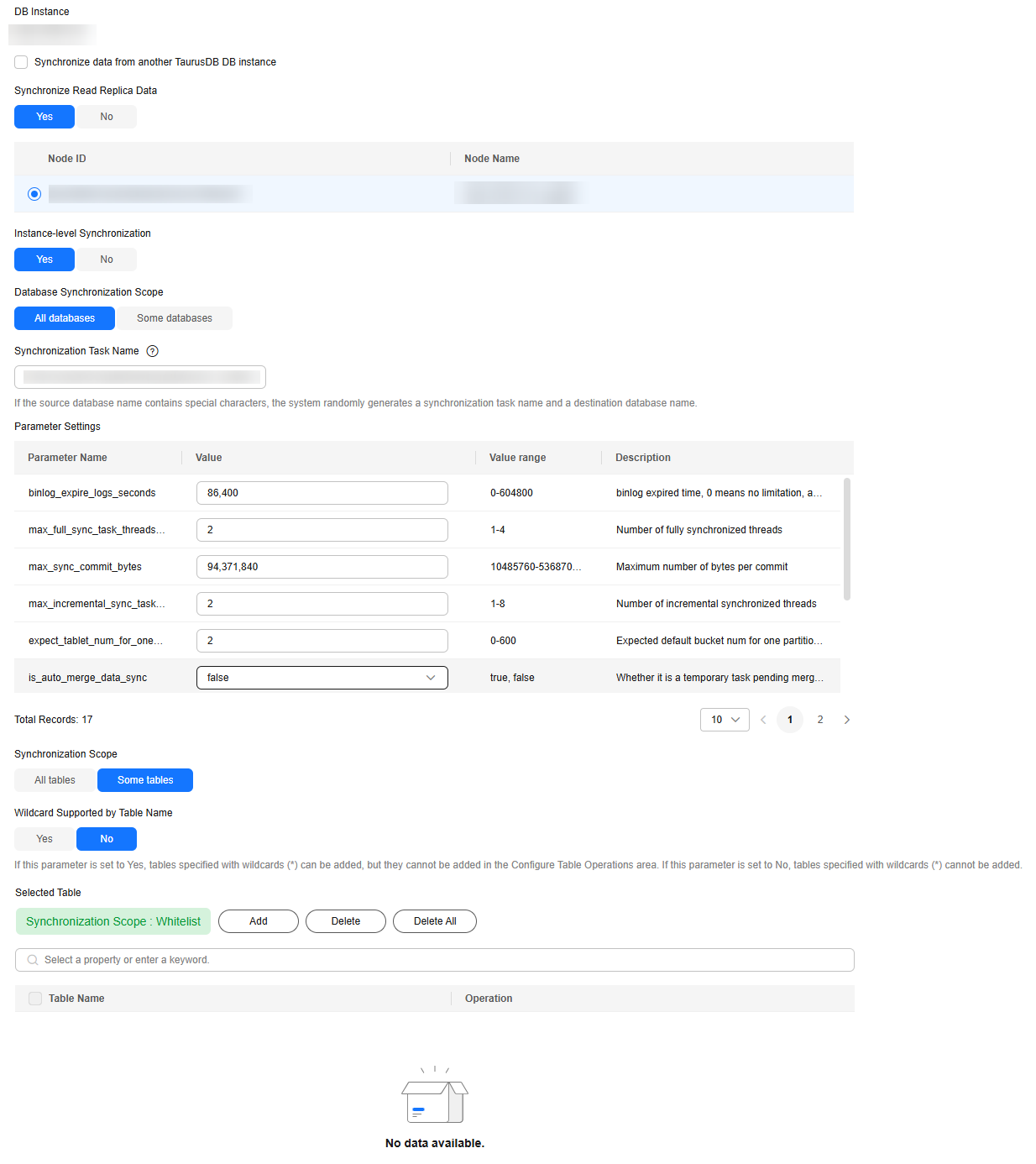
Procedure
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot