Configuring SQL Throttling
Scenarios
SQL throttling allows you to create rules to control concurrent execution of SQL statements by specifying SQL type, keywords, and maximum concurrency. To maintain better performance at high concurrency, SQL statements that meet the specified SQL type and keyword and exceed the maximum concurrency will not be executed. You can check how many times SQL statements are intercepted by throttling rules.
You can also identify SQL statements that consume the most resources based on the execution duration or number of executions and then create throttling rules for these SQL statements.
Supported Versions
- 2.0.28.40 > kernel version ≥ 2.0.28.15 (Throttling rules for SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements are supported.)
- Kernel version ≥ 2.0.29.1 (Throttling rules for SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements are supported.)
- Kernel version ≥ 2.0.54.240600 (Throttling rules for SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT statements are supported.)
For details about how to check the kernel version, see How Can I Check the Version of a TaurusDB Instance?
Constraints
|
Scenario |
Constraint |
|---|---|
|
Adding a SQL throttling rule |
|
|
Matching a SQL throttling rule |
|
|
Recommended rule |
|
|
Historical SQL throttling rules |
|
|
Scenarios not subject to SQL throttling |
|
|
Impact of throttling rules |
|
Adding a Throttling Rule
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose DBA Assistant > Historical Diagnosis.
- Click SQL Explorer and then SQL Throttling.
- On the displayed page, toggle on Enable SQL Throttling.
- Click Add Rule. In the displayed dialog box, specify SQL Type, Keyword, and Max. Concurrent Requests.
Figure 1 Adding a SQL throttling rule
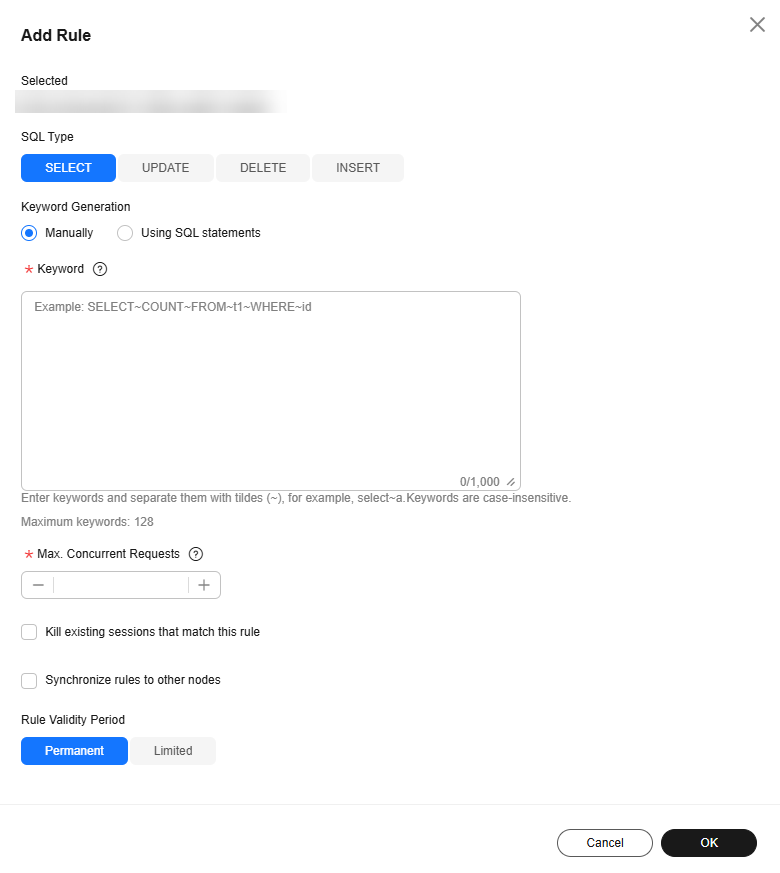
Table 2 Parameter description Parameter
Description
SQL Type
There are four options: SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT.
Keyword
A maximum of 128 keywords (case-insensitive) are supported. You can specify keywords in either of the following ways:
- Manually: Take select~a as an example. select and a are two keywords contained in a SQL throttling rule. The keywords are separated by a tilde (~). In this example, the rule restricts the execution of only the SQL statements containing keywords select and a.
- Using SQL statements: You can enter a SQL statement and then click Generate Keyword. The generated keywords are for reference only. Exercise caution when using them.
SQL statements match the keywords from first to last. For example, if one rule contains the keyword a~and~b, the statement *** a>1 and b>2 can match the keyword, but *** b>2 and a>1 cannot.
Empty characters before and after each keyword will be ignored, for example, spaces, '\n', '\r', and '\t'.
Max. Concurrent Requests
If the number of concurrent SQL statements matching the keyword exceeds this limit, the SQL statements will not be executed. The value ranges from 0 to 1000000000.
Kill existing sessions that match this rule
If this option is selected, all sessions generated by users subject to this SQL throttling rule will be killed.
Synchronize rules to other nodes
If this option is selected, new throttling rules will be synchronized to other nodes of a given instance.
Setting the validity period for a throttling rule
The validity period of a rule is the specific timeframe during which the rule is in effect.
- Permanent: The new SQL throttling rule takes effect permanently.
- Limited: You need to specify the expiration time for the SQL throttling rule. The validity period starts when the request to add the rule is submitted. The expiration time may be delayed for a maximum of 1 minute.
The expiration time can be a maximum of two weeks later than the current time.
You can click Historical SQL Throttling Rules on the right to view the expired SQL throttling rules.
- Confirm the settings and click OK.
- In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
Recommended Rule
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose DBA Assistant > Historical Diagnosis.
- Click SQL Explorer and then SQL Throttling.
- Click Recommended Rule.
- In the displayed dialog box, set the query criteria. You can filter top SQL statements by Avg. Duration or Executions.
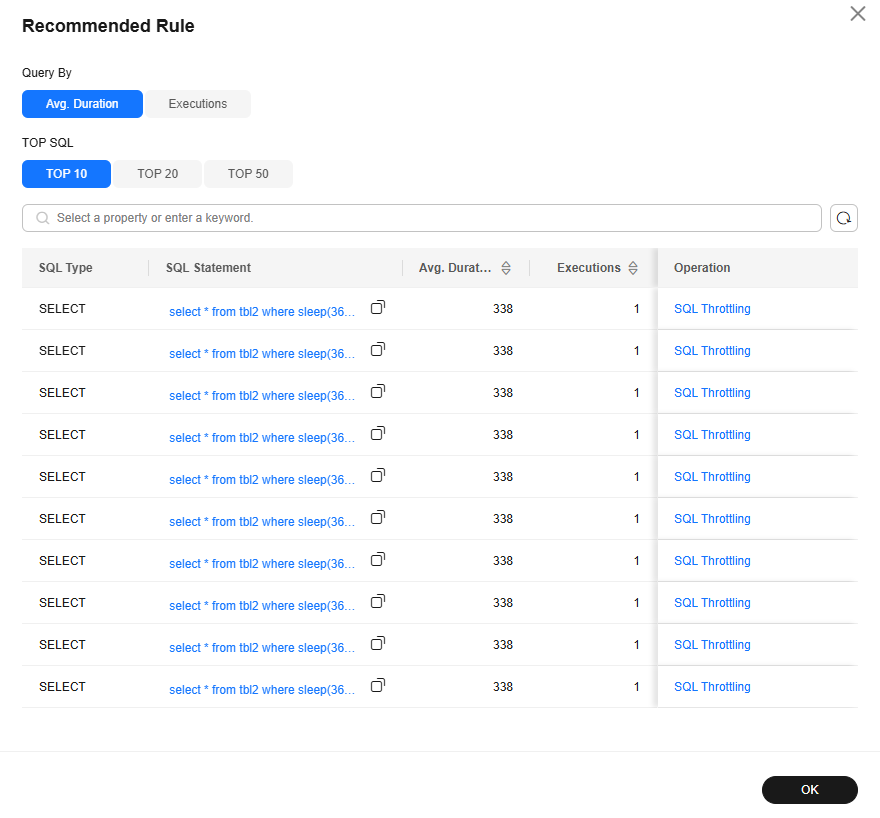
- Click OK.
- To throttle a high-load SQL statement, click SQL Throttling in the Operation column. In the displayed dialog box, add a SQL throttling rule. For more information, see Adding a Throttling Rule.
Deleting a Throttling Rule
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose DBA Assistant > Historical Diagnosis.
- Click SQL Explorer and then SQL Throttling.
- Locate a SQL throttling rule and click Delete in the Operation column.
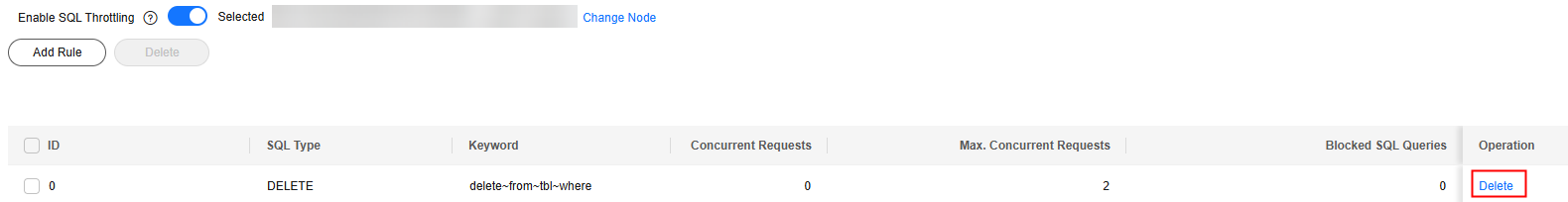
Alternatively, select one or more throttling rules and click Delete above the list.
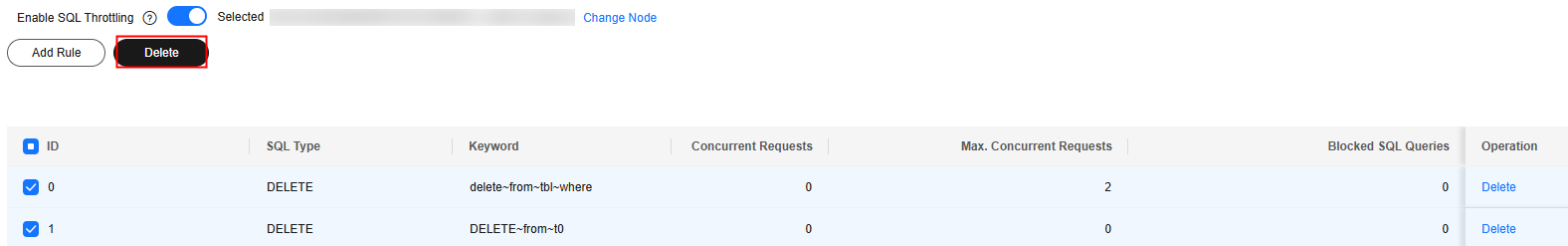
- In the displayed dialog box, confirm the throttling rules to be deleted. If you select Synchronize rules to other nodes, the throttling rules of other nodes of a given instance will also be deleted. Click OK.
Figure 2 Deleting a throttling rule
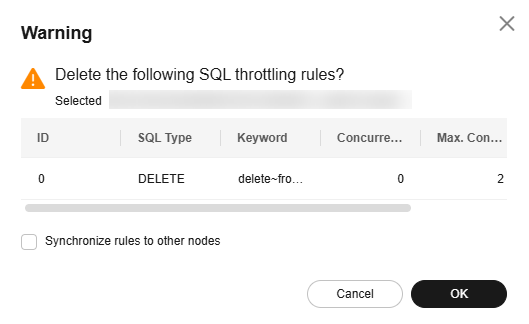
- (Optional) Click Historical SQL Throttling Rules to view the deleted and expired throttling rules.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





