Publishing Text Datasets
Data publishing refers to publishing a dataset in a specific format as a published dataset for subsequent model training operations.
Text datasets can be published in the following formats:
- Standard format: original format supported by the data project function.
The following is an example of the standard format, where context and target are key-value pairs.
{"context": "Hello, please introduce yourself.","target": "I am a Pangu model."} - Pangu format: To train a Pangu model, publish the dataset in Pangu format. To adapt to the data specifications of different Pangu models, you are advised to set Format Configuration to Pangu Format - Non-Thinking Chain or Pangu Format - Thinking Chain for dataset of the following types: text - single-turn Q&A, single-turn Q&A (with a system persona), multi-turn Q&A, multi-turn Q&A (with a system persona), DPO, and DPO (with a system persona) must be published in Pangu format (non-CoT).
The following is an example of the Pangu format (non-CoT), where context and target are key-value pairs. Different from the standard format, context is an array.
{"context": "Hello, please introduce yourself.","target": "I am a Pangu model."} - The following is an example of the Pangu format (CoT), where context, target, and thinking are key-value pairs. Compared with the Pangu Format - Non-Thinking Chain, the Pangu Format - Thinking Chain has an additional thinking key-value pair. The value of thinking is an array.
{"context":["Hello, please introduce yourself."],"target":"I am a Pangu model.","thinking":["OK. The user asks me to introduce myself. First, I need to specify the user's identity and usage scenario."]}
Creating a Text Dataset Publishing Task
To create a text dataset publishing task, perform the following steps:
- Log in to ModelArts Studio Large Model Deveopment Platform. In the My Spaces area, click the required workspace.
Figure 1 My Spaces
- In the navigation pane, choose Data Engineering > Data Publishing > Publish Task. On the displayed page, click Create Data Publish Task in the upper right corner.
- On the Create Data Publish Task page, filter datasets by dataset modality, for example, TEXT.
Figure 2 Filtering text datasets
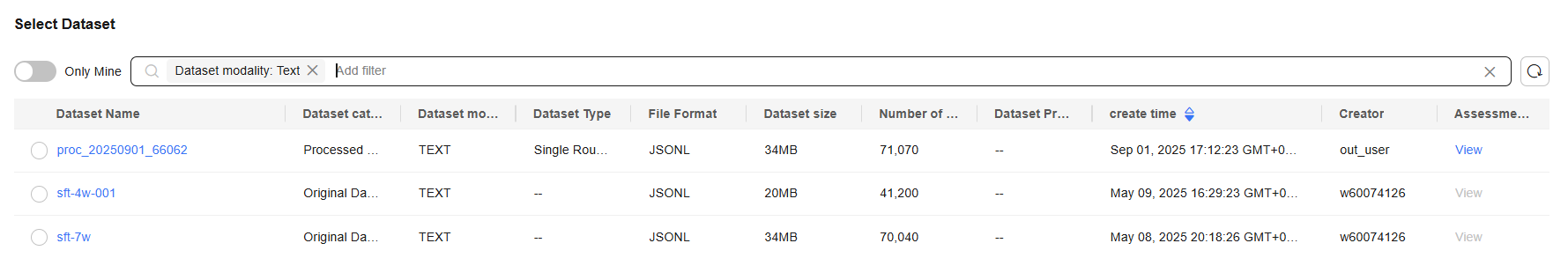
- Select a dataset and click Next.
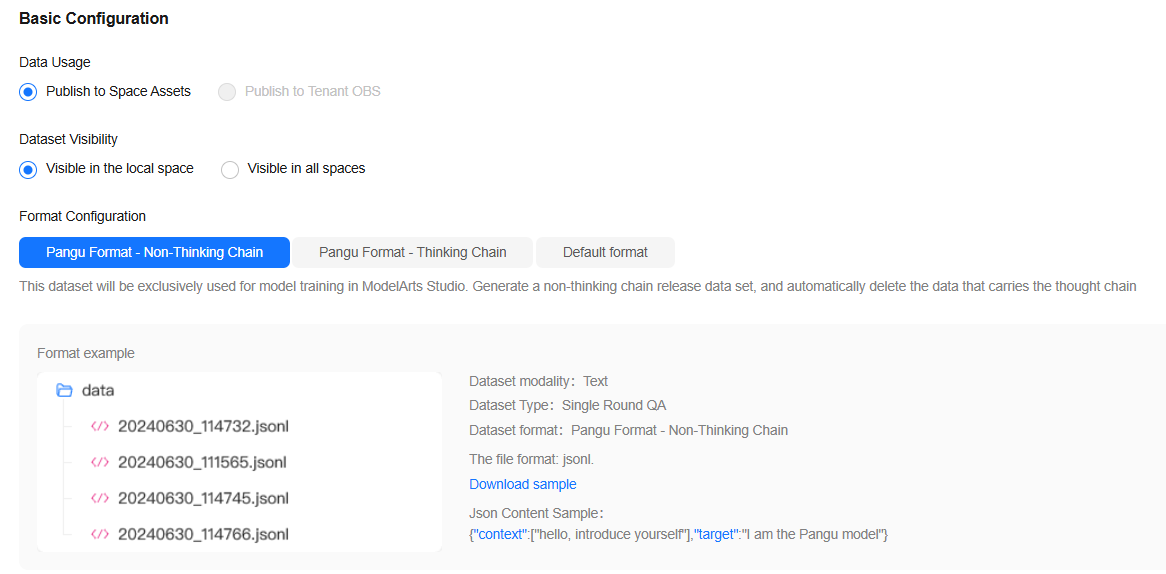
- In the Basic Configuration area, select the data usage, dataset visibility, and application scenario, as shown in Figure 3.
Data engineering supports the interconnection with Pangu models. To ensure that these datasets can be properly trained by these large models, the platform supports the publishing of datasets in different formats.
Currently, the standard and Pangu formats are supported.- Standard format: original format supported by the data project function. Datasets in this format can be published to assets but are not visible to downstream model development. It is used when Application Scenario is set to Other.
- Pangu format: dataset format defined for Pangu models. The dataset will be used in model development on ModelArts Studio. To adapt to data specifications of different Pangu models, you need to select Pangu Format - Non-Thinking Chain or Pangu Format - Thinking Chain for Format Configuration when configuring the dataset format. This format is used when Application Scenario is set to STUDIO Model Training.
- When the published dataset is used to train a Pangu model, set Format Configuration to Pangu format.
- When the published text dataset is of the following types, set Format Configuration to Pangu Format - Non-Thinking Chain or Pangu Format - Thinking Chain.
- Text - Single-turn Q&A
- Single-turn Q&A (with a system persona)
- Multi-turn Q&A
- Multi-turn Q&A (with a system persona)
- DPO
- DPO (with a system persona)
- When the text dataset to be published is a pre-trained dataset, set Format Configuration to Pangu format.
- If the dataset is published in Pangu Format - Non-Thinking Chain, the data that meets Pangu Format - Non-Thinking Chain will be deleted. If the dataset is published in Pangu Format - Thinking Chain, the data that meets Pangu Format - Non-Thinking Chain will be deleted.
- Enter the dataset name and description, set extended information, and click OK.
The extended information automatically retains the attributes of the selected dataset. After the dataset is published in Pangu Format - Thinking Chain, the backend automatically adds the reasoner tag to the simple_tag tag of the extended information. The model filters the dataset based on the tag.
Figure 4 Generating a published dataset
-
(Optional) If the dataset to be published as a pre-trained dataset, click Next to set resources after setting the extended information. Then, click OK to publish the dataset.Figure 5 Resource Allocation
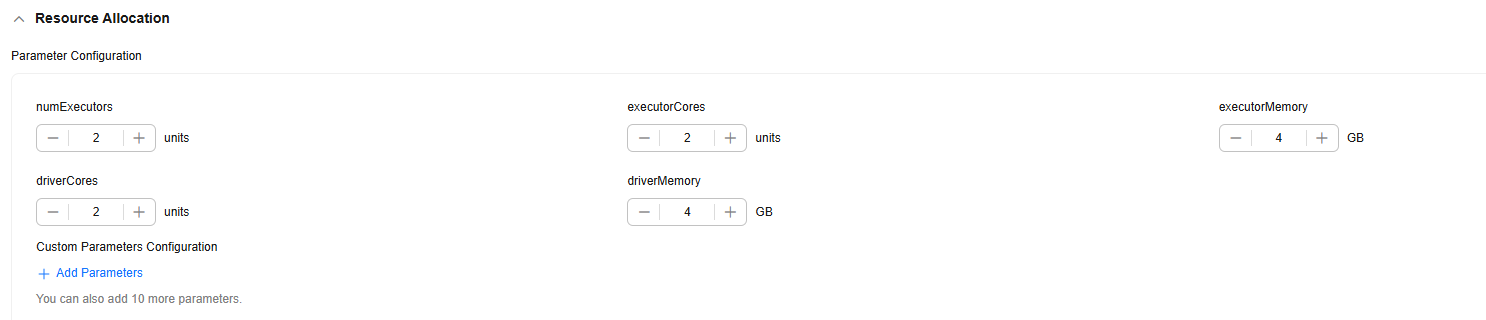
Table 1 describes the parameters.
Table 1 Parameter configuration Parameter
Description
numExecutors
Number of executors. The default value is 2. An executor is a process running on a worker node. It executes tasks and returns the calculation result to the driver. One core in an executor can run one task at the same time. Therefore, more tasks can be processed at the same time if you increase the number of the executors. You can add executors (if they are available) to process more tasks concurrently and improve efficiency.
numExecutors x executorMemory must be greater than or equal to 4 and less than or equal to 16.
executorCores
Number of CPU kernels used by each executor process. The default value is 2. Multiple cores in an executor can run multiple tasks at the same time, which increases the task concurrency. However, because all cores share the memory of an executor, you need to balance the memory and the number of cores.
numExecutors x executorMemory must be greater than or equal to 4 and less than or equal to 16. The ratio of executorCores to executorMemory must be in the range of 1:2 to 1:4.
executorMemory
Memory size used by each Executor process. The default value is 4. The executor memory is used for job execution and communication. You can increase the memory for a job that requires a great number of resources, and run small jobs concurrently with a smaller memory.
The ratio of executorCores to executorMemory must be in the range of 1:2 to 1:4.
driverCores
Number of CPU kernels used by each driver process. The default value is 2. The driver schedules jobs and communicates with executors.
The ratio of driverCores to driverMemory must be in the range of 1:2 to 1:4.
driverMemory
Memory used by the driver process. The default value is 4. The driver schedules jobs and communicates with executors. Add driver memory when the number and parallelism level of the tasks increases.
The ratio of driverCores to driverMemory must be in the range of 1:2 to 1:4.
- If the task status is Succeeded, the data publishing task is successfully executed. You can choose Data Engineering > Data Publishing > Datasets in the navigation pane and click the Published Dataset tab to view the published dataset.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot