Help Center/
PanguLargeModels/
User Guide/
Using Data Engineering to Create a Dataset/
Processing Datasets/
Managing Processing Operators/
Custom Data Processing Operators/
Typical Operator Development Examples
Updated on 2025-11-20 GMT+08:00
Typical Operator Development Examples
Example 1: Audio Duration Filter Operator
Directory structure of the operator package:
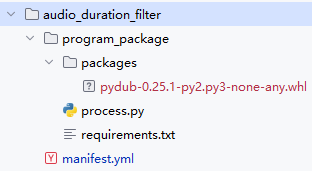
manifest.yml file content:
id: audio_duration_filtername: audio duration filteringdescription: Retains samples whose audio duration is within the specified access duration.author: "Huawei Cloud/EI"tags: language: - zh format: - wav - mp3 category: data filtering modal: - AUDIOruntime: cpu-arch: - ARM resources: - cpu: 4 memory: 8192 environment: PYTHON entrypoint: process.py auto-data-loading: truearguments: - key: duration_range name: retention duration (s) type: int between: true min: 0 tips: Retains audio files whose duration is within the specified access duration. required: true visible: true default: 5;3600
process.py file content:
import osimport numpy as npimport pandas as pdfrom pydub import AudioSegmentimport argparseimport logginglogging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)def get_audio_duration(file_path): try: audio = AudioSegment.from_file(file_path) duration = len (audio) / 1000 # Convert the value to seconds. except: duration = None return durationclass Process: def __init__(self, args: argparse.Namespace): logger.info(f'self.args is {args},type is {type(args)}') min_duration, max_duration = args.duration_range.split(';') self.min_duration = int(min_duration) if min_duration else 0 self.max_duration = int(max_duration) if max_duration else np.inf def __call__(self, df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame: duration_list = [] filter_list = [] for row in df.itertuples(): duration = get_audio_duration(row.file_path) duration_list.append(duration) filter_list.append(0) df['duration'] = duration_list # Filter files by duration. The value 0 indicates that files are reserved, and the value 1 indicates that files are filtered out. The filtering action is executed by the upper-layer operator framework. df['filter'] = np.where((df['duration'] >= self.min_duration) & (df['duration'] <= self.max_duration), 0, 1) return df
requirements.txt file content:
pydub
Example 2: Extracting JSON Objects from Text
Directory structure of the operator package:
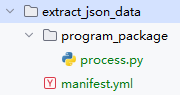
manifest.yml file content:
id: extract_json_dataname: Extract JSON Objects from Textdescription: Extracts a JSON object from a text.author: "Huawei Cloud/EI"version: 1.0.0tags: language: - zh format: - jsonl - txt - json category: Data conversion modal: - TEXT - OTHERruntime: cpu-arch: - ARM resources: - cpu: 4 memory: 8192 environment: PYTHON entrypoint: process.py auto-data-loading: false
process.py file content:
import osimport pandas as pdimport argparseimport jsonimport logginglogging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)from moxing.file import list_directory, copydef extract_json_data(input_file, output_file): """ Extracts JSON data from the input file and writes the data to the output file (JSONL format). :param input_file: input file name :param output_file: output file name """ with open(input_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as fin, \ open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as fout: for line in fin: line = line.strip() if not line: continue # Use a colon (:) to separate each line of data (at most once). parts = line.split(' : ', 1) if len(parts) < 2: print(f"Skip invalid lines: {line}") continue json_str = parts[1].strip() try: # Try to directly parse the JSON file. json_data = json.loads(json_str) except json.JSONDecodeError: try: # Replace common Chinese quotation marks and try again. fixed_str = json_str.replace('"', '"').replace('"', '"') json_data = json.loads(fixed_str) except: print (f"Parsing failed. Skip: {json_str}") continue # Write a valid JSON object to the output file (JSONL format). fout.write(json.dumps(json_data, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')class Process: def __init__(self, args): # Create a local directory for storing files downloaded from OBS. self.input_dir = r'input_dir' os.makedirs(self.input_dir, exist_ok=True) # Create a local directory to store the JSONL file generated by the operator. self.output_dir = r'output_dir' os.makedirs(self.output_dir, exist_ok=True) self.args = args logger.info(f'self.args is {self.args},type is {type(self.args)}') def __call__(self, input): input_obs_path = self.args.obs_input_path output_obs_path = self.args.obs_output_path file_name_list = list_directory(input_obs_path, recursive=False) file_path_dict = {file_name: os.path.join(input_obs_path, file_name) for file_name in file_name_list} # Data processing for file_name, obs_file_path in file_path_dict.items(): input_file = os.path.join(self.input_dir, file_name) output_file = os.path.join(self.output_dir, file_name) copy(obs_file_path, input_file) extract_json_data(input_file, output_file) copy(output_file, os.path.join(output_obs_path, file_name))
Parent topic: Custom Data Processing Operators
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
The system is busy. Please try again later.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





