Creating and Executing Verification Tasks
You can use the created source and target connections to create verification tasks.
For details about the supported big data components and verification methods, see Overview.
Precautions
- A pair of verification tasks for the source and the target must use the same verification method.
- If the data volume is large, a 99.5% success rate is considered normal.
- If the source and target HBase clusters use different security authentication modes, the verification tasks cannot be executed at the same time, or they will fail to be executed. This is because the authentication information must be handled differently in each cluster. The secured cluster requires authentication information to be loaded, whereas the non-secured cluster needs that information cleared.
- If the source Lindorm or HBase service is locked due to arrears, you can still create data connections and verification tasks, but data access and operations will be restricted, preventing verification tasks from being executed. Before starting data verification, ensure that the source big data service is active and your account balance is sufficient. If the service is locked, promptly pay the overdue amount to unlock it. Once the service is unlocked, you can run the data verification tasks again.
- The verification results of data migrated between Hive 2.x and Hive 3.x may be inaccurate. In Hive 2.x, when you query the fixed-length type CHAR (N) of data, if the actual data length does not meet the specified length N, Hive will pad the string with spaces to reach the required length. However, in Hive 3.x, this padding operation does not occur during queries. This may result in differences between different versions. To avoid this issue, you are advised to use Beeline to perform the verification.
- If you use Yarn to run verification tasks in the source and target MRS clusters, execute the verification tasks separately, and ensure that one task is completed before starting another.
- When you verify data consistency for clusters of MRS 3.3.0 or later, do not use cluster nodes as executors, or the verification will fail.
Constraints
- Before verifying data migrated from EMR Delta Lake to MRS Delta Lake, please note:
- If the source EMR cluster uses Spark 3.3.1, data verification is supported regardless of whether the source cluster contains metadata storage.
- If the source EMR cluster uses Spark 2.4.8, data verification is supported only when the source cluster contains metadata storage.
- Verification is not supported for HBase tables that only store cold data.
- A verification task must be completed within one day. If the task extends past midnight (00:00), the verification results may be inaccurate. Plan verification tasks carefully to avoid execution across days.
- Field verification is not supported if the source Alibaba Cloud cluster uses ClickHouse 21.8.15.7 and the target Huawei Cloud cluster uses ClickHouse 23.3.2.37. This is because the two versions process IPv4 and IPv6 data types and function calculation results differently.
- During the daily incremental verification, hourly incremental verification, and date-based verification for Hive, date partitions cannot be verified if their partition values do not follow the standard YYYY-MM-DD format.
- Content verification is supported for unsecured HBase clusters, regardless of whether the clusters are self-built or created using cloud services like EMR for HBase, MRS (HBase), and CloudTable (HBase).
Prerequisites
- A table group has been created, and tables to be verified have been added to the group. For details, see Creating a Table Group and Adding Tables to the Group.
- Connections to the source and the target have been created. For details, see Creating Connections
Procedure
- Sign in to the MgC console. In the navigation pane, under Project, select your big data migration project from the drop-down list.
- In the navigation pane, choose Migrate > Big Data Verification.
- In the Features area, click Task Management.
- Click Create Task in the upper right corner of the page.
- Select a big data component and verification method as needed and click Next.
- Configure task parameters based on the selected big data component and verification method.
The task parameters vary with the big data component.
- Parameters for creating a full verification task
- Parameters for creating a daily incremental verification task
- Parameters for creating an hourly incremental verification task
- Parameters for creating a date-based verification task
- Parameters for creating a selective verification task
Table 1 Parameters for creating a full verification task Area
Parameter
Configuration
Basic Info
Task Name
The default name is Component-Full-Verification-4 random characters (including letters and numbers). You can also customize a name.
Task Settings
Table Groups
Select the table groups that contain the tables to be verified.
Executor Connection
This parameter is available for Hive, Delta Lake, and Hudi.
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source executor connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target executor connection.
DLI Connection
If DLI is selected in the previous step, the task can only be created for the target. You need to select the created DLI connection.
Doris Connection
If Doris is selected in the previous step:
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source Doris connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target Doris connection.
HBase Connection
This parameter is available for HBase and CloudTable (HBase).
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source HBase connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target HBase or CloudTable (HBase) connection.
ClickHouse Connection
This parameter is available for ClickHouse, Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB for ClickHouse, and CloudTable (ClickHouse).
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source MRS ClickHouse or Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB for ClickHouse connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target MRS ClickHouse or CloudTable (ClickHouse) connection.
Metadata Connection (Optional)
This parameter is available for Delta Lake.
To improve processing efficiency, you can select metadata connections to the source Delta Lake cluster that the groups of tables to be verified belong to.
Execution Time
Specify when the task will be executed. After the task is activated, it will be automatically executed at the specified time every day.
NOTE:You are advised to run the verification during off-peak hours.
Advanced Options
- Concurrency: Specify the number of concurrent threads on an executor for the verification task. The default value is 3. The value ranges from 1 to 10.
CAUTION:
If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Hive cluster, set this parameter based on the source data volume and master node specifications. Consider the following rules:
- The total number of concurrent threads for verification tasks running simultaneously in the source cluster cannot exceed 70% of the total number of cores on the metadata node.
- The total resources allocated to verification tasks cannot exceed the resources of the execution queue. The total resources allocated to tasks can be calculated as follows:
Allocated memory = Number of executors × Memory on an executor × Concurrency
Allocated cores = Number of executors × Cores on an executor × Concurrency
For example, if the total source data size is 500 GB across 10,000 tables, including 8 large tables with 50 GB data and 100,000 partitions each, and the master node has 8 vCPUs and 32 GB of memory:
- According to rule 1, the maximum number of concurrent requests is 5, which is the rounded down value of 5.6 (0.7 × 8).
- According to rule 2, you need to select spark-sql in the Execution Command area and set the following parameters:

executor-memory = 4G
master = yarn
num-executors = 20
executor-cores = 2
driver-memory = 10G
- Max. SQL Statements per File: Each time the task is executed, files are created for storing the SQL statements generated for querying tables. You can control how many SQL statements can be stored in a single file. The default value is 10. The recommended value ranges from 1 to 50.
- Timeout (s): indicates the maximum time allowed for an SQL statement to end normally. The unit is second (s). The default value is 600. The value ranges from 600 to 7,200.
- Send SMN Notifications: Determine whether to use SMN to notify you of the task status in a timely manner through emails, SMS messages, or customized URLs.
NOTICE:
- Before enabling this function, you need to create a topic on the SMN console. For details, see Creating a Topic.
- Using this function may incur a small amount of fees, which are settled by SMN. For details, see SMN Billing.
Data Filtering
Non-partitioned Table Verification
Decide how to verify non-partitioned tables.
- Verify all: All non-partitioned tables are verified for consistency.
- Skip all: All non-partitioned tables are skipped during consistency verification.
- Filter by update time: Only non-partitioned tables whose update time falls within the specified time range are verified for consistency. The update time of a non-partitioned table may not be accurate if it contains non-inserted data, and the table may be excluded from verification.
Advanced Options
Max. Fields per SQL Statement: Limit how many fields can be queried by one SQL statement. Too many or few fields in a SQL statement results in low query efficiency. The default value is 500. The value ranges from 100 to 500.
OBS Bucket Check
-
- If you need to upload task logs and content verification results to an OBS bucket for management and analysis, configure an OBS bucket. After the bucket is configured, the task logs and content verification results will be automatically uploaded to the specified OBS bucket.
- If you do not need to upload the task logs and content verification results to OBS, select I confirm that I only need to view logs and data verification results on the MgC Agent and do not need to upload them to OBS.
Command Parameters
(available for Hive)
Security Authentication
If security authentication (for example, Kerberos authentication) is enabled for the big data cluster, select this option and configure the security authentication command. You must first manually upload the .keytab file that contains the authentication key to the executor.
- Keytab Path: Enter the path where the .keytab file is stored on the executor.
- Keytab Principal: Enter the principal of the .keytab file.
Execution Command
You can configure Beeline or Spark SQL command parameters to run SQL statements for consistency verification.
- Beeline: a command line tool used to interact with Hive.
- Spark SQL: a command line tool used to execute SQL statements to query and analyze data.
MaxCompute Parameters
(available for MaxCompute)
-
Add MaxCompute parameters as needed. For details, see MaxCompute Documentation.
Execution Settings
(available for DLI)
Parameter
Set the parameters as required. For details about the supported custom parameters, see Custom Parameters.
Execution Settings
(available for HBase)
Parameters
Add command line parameters as required.
Command Parameters (available for Delta Lake and Hudi)
Security Authentication (only available for target Delta Lake clusters)
If security authentication (for example, Kerberos authentication) is enabled for the big data cluster, select this option and configure the security authentication command. You must first manually upload the .keytab file that contains the authentication key to the executor.
- Keytab Path: Enter the path where the .keytab file is stored on the executor.
- Keytab Principal: Enter the principal of the .keytab file.
spark-sql
Spark SQL is a module used in Spark for structured data processing. In Spark applications, you can seamlessly use SQL statements or DataSet APIs to query structured data. For more information, see SparkSQL Principles. Retain the default settings.
spark-submit
This is a basic Spark shell command used to submit Spark applications. The command is as follows:
./bin/spark-submit \ --class <main-class> \ --master <master-url> \ ... # other options <application-jar> \ [application-arguments]
Parameter description:
- --class: indicates the name of the class of a Spark application.
- --master: indicates the master to which the Spark application links, such as Yarn-client and Yarn-cluster.
- application-jar: indicates the path of the JAR file of the Spark application.
- application-arguments: indicates the parameter required to submit the Spark application. (This parameter can be empty.)
The parameters that need to be added depend on the scenario:
- If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Delta Lake cluster that uses Spark 3, add the following parameter:
- Parameter: jars
- Value: '/opt/apps/DELTALAKE/deltalake-current/spark3-delta/delta-core_2.12-*.jar,/opt/apps/DELTALAKE/deltalake-current/spark3-delta/delta-storage-*.jar'
CAUTION:
Replace the parameter values with the actual environment directory and Delta Lake version.
- If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Delta Lake 2.1.0 cluster that uses Spark 2.4.8, add the following parameter:
- Parameter: mgc.delta.spark.version
- Value: 2
Table 2 Parameters for creating a daily incremental verification task Area
Parameter
Configuration
Basic Info
Task Name
The default name is Component-daily-incremental-verification-4 random characters (including letters and numbers). You can also customize a name.
Task Settings
Table Groups
Select the table groups that contain the tables to be verified.
Executor Connection
This parameter is available for Hive, Delta Lake, and Hudi.
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source executor connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target executor connection.
DLI Connection
If DLI is selected in the previous step, the task can only be created for the target. You need to select the created DLI connection.
Doris Connection
If Doris is selected in the previous step:
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source Doris connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target Doris connection.
HBase Connection
If HBase is selected in the previous step:
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source HBase connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target HBase or CloudTable (HBase) connection.
Metadata Connection (Optional)
This parameter is available for Hive and Delta Lake.
If you are creating a verification task for the target Hive cluster, select the metadata connection to this Hive cluster. The connection is used to check whether the partitions to be verified can be found in the target cluster.
To improve processing efficiency, you can select metadata connections to the source Delta Lake cluster that the groups of tables to be verified belong to.
Execution Time
Specify when the task will be executed. After the task is activated, it will be automatically executed at the specified time every day.
Advanced Options
- Concurrency: Specify the number of concurrent threads on an executor for the verification task. The default value is 3. The value ranges from 1 to 10.
CAUTION:
If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Hive cluster, set this parameter based on the source data volume and master node specifications. Consider the following rules:
- The total number of concurrent threads for verification tasks running simultaneously in the source cluster cannot exceed 70% of the total number of cores on the metadata node.
- The total resources allocated to verification tasks cannot exceed the resources of the execution queue. The total resources allocated to tasks can be calculated as follows:
Allocated memory = Number of executors × Memory on an executor × Concurrency
Allocated cores = Number of executors × Cores on an executor × Concurrency
For example, if the total source data size is 500 GB across 10,000 tables, including 8 large tables with 50 GB data and 100,000 partitions each, and the master node has 8 vCPUs and 32 GB of memory:
- According to rule 1, the maximum number of concurrent requests is 5, which is the rounded down value of 5.6 (0.7 × 8).
- According to rule 2, you need to select spark-sql in the Execution Command area and set the following parameters:

executor-memory = 4G
master = yarn
num-executors = 20
executor-cores = 2
driver-memory = 10G
- Max. SQL Statements per File: Each time the task is executed, files are created for storing the SQL statements generated for querying tables. You can control how many SQL statements can be stored in a single file. The default value is 10. The recommended value ranges from 1 to 50.
- Timeout (s): indicates the maximum time allowed for an SQL statement to end normally. The unit is second (s). The default value is 600. The value ranges from 600 to 7,200.
- Send SMN Notifications: Determine whether to use SMN to notify you of the task status in a timely manner through emails, SMS messages, or customized URLs.
NOTICE:
- Before enabling this function, you need to create a topic on the SMN console. For details, see Creating a Topic.
- Using this function may incur a small amount of fees, which are settled by SMN. For details, see SMN Billing.
Data Filtering
Incremental Scope
Select the time period in which the incremental data needs to be verified as consistent. By default, a 24-hour period is selected. T indicates the execution time of the task, and T-n indicates a time n × 24 hours before the execution time.
If you select Consecutive days, the system verifies consistency of the incremental data generated during these consecutive days.
Non-partitioned Table Verification
Decide how to verify non-partitioned tables.
- Verify all: All non-partitioned tables are verified for consistency.
- Skip all: All non-partitioned tables are skipped during consistency verification.
- Filter by update time: Only non-partitioned tables whose update time falls within the specified time range are verified for consistency. The update time of a non-partitioned table may not be accurate if it contains non-inserted data, and the table may be excluded from verification.
Advanced Options
- Partition Filtering: Determine to filter table partitions by creation time or update time.
- By update time: An update time indicates the timestamp a table partition was last modified or updated. Choose this option if you are concerned about the latest status or changes of data in a partition.
- By creation time: A creation time indicates the timestamp when a partition was created. Choose this option if you are concerned about the data generated from the time when the partition is created to a certain time point.
- Max. Partitions: Limit how many partitions in a table are verified. The default value is 3. The value ranges from 1 to 50.
For example, if this parameter is set to 3, the system verifies the consistency of only the first three partitions in the partition list in descending order.
- Max. Fields per SQL Statement: Limit how many fields can be queried by one SQL statement. Too many or few fields in a SQL statement results in low query efficiency. The default value 0 means no limit is set. The value ranges from 100 to 500.
OBS Bucket Check
-
- If you need to upload task logs and content verification results to an OBS bucket for management and analysis, configure an OBS bucket. After the bucket is configured, the task logs and content verification results will be automatically uploaded to the specified OBS bucket.
- If you do not need to upload the task logs and content verification results to OBS, select I confirm that I only need to view logs and data verification results on the MgC Agent and do not need to upload them to OBS.
Execution Script
(available for Hive)
Security Authentication
If security authentication (for example, Kerberos authentication) is enabled for the big data cluster, select this option and configure the security authentication command. You must first manually upload the .keytab file that contains the authentication key to the executor.
- Keytab Path: Enter the path where the .keytab file is stored on the executor.
- Keytab Principal: Enter the principal of the .keytab file.
Execution Command
You can configure Beeline or Spark SQL command parameters to run SQL statements for consistency verification.
- Beeline: a command line tool used to interact with Hive.
- Spark SQL: a command line tool used to execute SQL statements to query and analyze data.
MaxCompute Parameters
(available for MaxCompute)
-
Add MaxCompute parameters as needed. For details, see MaxCompute Documentation.
Execution Settings
(available for DLI)
Parameter
Set the parameters as required. For details about the supported custom parameters, see Custom Parameters.
Execution Settings
(available for HBase)
Parameter
Add command line parameters as required.
Command Parameters (available for Delta Lake and Hudi)
Security Authentication (only available for target Delta Lake clusters)
If security authentication (for example, Kerberos authentication) is enabled for the big data cluster, select this option and configure the security authentication command. You must first manually upload the .keytab file that contains the authentication key to the executor.
- Keytab Path: Enter the path where the .keytab file is stored on the executor.
- Keytab Principal: Enter the principal of the .keytab file.
spark-sql
Spark SQL is a module used in Spark for structured data processing. In Spark applications, you can seamlessly use SQL statements or DataSet APIs to query structured data. For more information, see SparkSQL Principles. Retain the default settings.
spark-submit
This is a basic Spark shell command used to submit Spark applications. The command is as follows:
./bin/spark-submit \ --class <main-class> \ --master <master-url> \ ... # other options <application-jar> \ [application-arguments]
Parameter description:
- --class: indicates the name of the class of a Spark application.
- --master: indicates the master to which the Spark application links, such as Yarn-client and Yarn-cluster.
- application-jar: indicates the path of the JAR file of the Spark application.
- application-arguments: indicates the parameter required to submit the Spark application. (This parameter can be empty.)
The parameters that need to be added depend on the scenario:
- If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Delta Lake cluster that uses Spark 3, add the following parameter:
- Parameter: jars
- Value: '/opt/apps/DELTALAKE/deltalake-current/spark3-delta/delta-core_2.12-*.jar,/opt/apps/DELTALAKE/deltalake-current/spark3-delta/delta-storage-*.jar'
CAUTION:
Replace the parameter values with the actual environment directory and Delta Lake version.
- If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Delta Lake 2.1.0 cluster that uses Spark 2.4.8, add the following parameter:
- Parameter: mgc.delta.spark.version
- Value: 2
Table 3 Parameters for creating an hourly incremental verification task Area
Parameter
Configuration
Basic Info
Task Name
The default name is Component-hourly incremental verification-4 random characters (including letters and numbers). You can also customize a name.
Task Settings
Table Groups
Select the table groups that contain the tables to be verified.
Executor Connection
This parameter is available for Hive, Delta Lake, and Hudi.
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source executor connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target executor connection.
DLI Connection
If DLI is selected in the previous step, the task can only be created for the target. You need to select the created DLI connection.
Doris Connection
If Doris is selected in the previous step:
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source Doris connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target Doris connection.
Metadata Connection (Optional)
This parameter is available for Hive and Delta Lake.
If you are creating a verification task for the target Hive cluster, select the metadata connection to this Hive cluster. The connections are used to check whether the partitions to be verified can be found in the target cluster.
To improve processing efficiency, you can select metadata connections to the source Delta Lake cluster that the groups of tables to be verified belong to.
Start Time
Specify when the task will be executed. After the task is activated, it will be automatically executed at the specified time every day.
Advanced Options
- Concurrency: Specify the number of concurrent threads on an executor for the verification task. The default value is 3. The value ranges from 1 to 10.
CAUTION:
If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Hive cluster, set this parameter based on the source data volume and master node specifications. Consider the following rules:
- The total number of concurrent threads for verification tasks running simultaneously in the source cluster cannot exceed 70% of the total number of cores on the metadata node.
- The total resources allocated to verification tasks cannot exceed the resources of the execution queue. The total resources allocated to tasks can be calculated as follows:
Allocated memory = Number of executors × Memory on an executor × Concurrency
Allocated cores = Number of executors × Cores on an executor × Concurrency
For example, if the total source data size is 500 GB across 10,000 tables, including 8 large tables with 50 GB data and 100,000 partitions each, and the master node has 8 vCPUs and 32 GB of memory:
- According to rule 1, the maximum number of concurrent requests is 5, which is the rounded down value of 5.6 (0.7 × 8).
- According to rule 2, you need to select spark-sql in the Execution Command area and set the following parameters:

executor-memory = 4G
master = yarn
num-executors = 20
executor-cores = 2
driver-memory = 10G
- Max. SQL Statements per File: Each time the task is executed, files are created for storing the SQL statements generated for querying tables. You can control how many SQL statements can be stored in a single file. The default value is 10. The recommended value ranges from 1 to 50.
- Timeout (s): indicates the maximum time allowed for an SQL statement to end normally. The unit is second (s). The default value is 600. The value ranges from 600 to 7,200.
- Send SMN Notifications: Determine whether to use SMN to notify you of the task status in a timely manner through emails, SMS messages, or customized URLs.
NOTICE:
- Before enabling this function, you need to create a topic on the SMN console. For details, see Creating a Topic.
- Using this function may incur a small amount of fees, which are settled by SMN. For details, see SMN Billing.
Data Filtering
Execution Interval
Control how frequently the task will be executed.
Non-partitioned Table Verification
Decide how to verify non-partitioned tables.
- Verify all: All non-partitioned tables are verified for consistency.
- Skip all: All non-partitioned tables are skipped during consistency verification.
- Filter by update time: Only non-partitioned tables whose update time falls within the specified time range are verified for consistency. The update time of a non-partitioned table may not be accurate if it contains non-inserted data, and the table may be excluded from verification.
Advanced Options
- Partition Filtering: Determine to filter table partitions by creation time or update time.
- By update time: An update time indicates the timestamp a table partition was last modified or updated. Choose this option if you are concerned about the latest status or changes of data in a partition.
- By creation time: A creation time indicates the timestamp when a partition was created. Choose this option if you are concerned about the data generated from the time when the partition is created to a certain time point.
- Max. Partitions: Limit how many partitions in a table are verified. The default value is 3. The value ranges from 1 to 50.
For example, if this parameter is set to 3, the system verifies the consistency of only the first three partitions that are sorted by ID in descending order.
- Max. Fields per SQL Statement: Limit how many fields can be queried by one SQL statement. Too many or few fields in a SQL statement results in low query efficiency. The default value 0 means no limit is set. The value ranges from 100 to 500.
OBS Bucket Check
-
- If you need to upload task logs and content verification results to an OBS bucket for management and analysis, configure an OBS bucket. After the bucket is configured, the task logs and content verification results will be automatically uploaded to the specified OBS bucket.
- If you do not need to upload the task logs and content verification results to OBS, select I confirm that I only need to view logs and data verification results on the MgC Agent and do not need to upload them to OBS.
Execution Script
(available for Hive)
Security Authentication
If security authentication (for example, Kerberos authentication) is enabled for the big data cluster, select this option and configure the security authentication command. You must first manually upload the .keytab file that contains the authentication key to the executor.
- Keytab Path: Enter the path where the .keytab file is stored on the executor.
- Keytab Principal: Enter the principal of the .keytab file.
Execution Command
You can configure Beeline or Spark SQL command parameters to run SQL statements for consistency verification.
- Beeline: a command line tool used to interact with Hive.
- Spark SQL: a command line tool used to execute SQL statements to query and analyze data.
MaxCompute Parameters
(available for MaxCompute)
-
Add MaxCompute parameters as needed. For details, see MaxCompute Documentation.
Execution Settings
(available for DLI)
Parameter
Set the parameters as required. For details about the supported custom parameters, see Custom Parameters.
Command Parameters (available for Delta Lake and Hudi)
Security Authentication (only available for target Delta Lake clusters)
If security authentication (for example, Kerberos authentication) is enabled for the big data cluster, select this option and configure the security authentication command. You must first manually upload the .keytab file that contains the authentication key to the executor.
- Keytab Path: Enter the path where the .keytab file is stored on the executor.
- Keytab Principal: Enter the principal of the .keytab file.
spark-sql
Spark SQL is a module used in Spark for structured data processing. In Spark applications, you can seamlessly use SQL statements or DataSet APIs to query structured data. For more information, see SparkSQL Principles. Retain the default settings.
spark-submit
This is a basic Spark shell command used to submit Spark applications. The command is as follows:
./bin/spark-submit \ --class <main-class> \ --master <master-url> \ ... # other options <application-jar> \ [application-arguments]
Parameter description:
- --class: indicates the name of the class of a Spark application.
- --master: indicates the master to which the Spark application links, such as Yarn-client and Yarn-cluster.
- application-jar: indicates the path of the JAR file of the Spark application.
- application-arguments: indicates the parameter required to submit the Spark application. (This parameter can be empty.)
The parameters that need to be added depend on the scenario:
- If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Delta Lake cluster that uses Spark 3, add the following parameter:
- Parameter: jars
- Value: '/opt/apps/DELTALAKE/deltalake-current/spark3-delta/delta-core_2.12-*.jar,/opt/apps/DELTALAKE/deltalake-current/spark3-delta/delta-storage-*.jar'
CAUTION:
Replace the parameter values with the actual environment directory and Delta Lake version.
- If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Delta Lake 2.1.0 cluster that uses Spark 2.4.8, add the following parameter:
- Parameter: mgc.delta.spark.version
- Value: 2
Table 4 Parameters for creating a date-based verification task Area
Parameter
Configuration
Basic Info
Task Name
The default name is Component-date-based-Verification-4 random characters (including letters and numbers). You can also customize a name.
Task Settings
Table Groups
Select the table groups that contain the tables to be verified.
Executor Connection
This parameter is available for Hive, Delta Lake, and Hudi.
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source executor connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target executor connection.
DLI Connection
If DLI is selected in the previous step, the task can only be created for the target. You need to select the created DLI connection.
Metadata Connection (Optional)
This parameter is available for Hive and Delta Lake.
If you are creating a verification task for the target Hive cluster, select the metadata connection to this Hive cluster. The connection is used to check whether the partitions to be verified can be found in the target cluster.
To improve processing efficiency, you can select metadata connections to the source Delta Lake cluster that the groups of tables to be verified belong to.
Execution Time
Specify when the task will be executed. After the task is activated, it will be automatically executed at the specified time every day.
Advanced Options
- Concurrency: Specify the number of concurrent threads on an executor for the verification task. The default value is 3. The value ranges from 1 to 10.
CAUTION:
If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Hive cluster, set this parameter based on the source data volume and master node specifications. Consider the following rules:
- The total number of concurrent threads for verification tasks running simultaneously in the source cluster cannot exceed 70% of the total number of cores on the metadata node.
- The total resources allocated to verification tasks cannot exceed the resources of the execution queue. The total resources allocated to tasks can be calculated as follows:
Allocated memory = Number of executors × Memory on an executor × Concurrency
Allocated cores = Number of executors × Cores on an executor × Concurrency
For example, if the total source data size is 500 GB across 10,000 tables, including 8 large tables with 50 GB data and 100,000 partitions each, and the master node has 8 vCPUs and 32 GB of memory:
- According to rule 1, the maximum number of concurrent requests is 5, which is the rounded down value of 5.6 (0.7 × 8).
- According to rule 2, you need to select spark-sql in the Execution Command area and set the following parameters:

executor-memory = 4G
master = yarn
num-executors = 20
executor-cores = 2
driver-memory = 10G
- Max. SQL Statements per File: Each time the task is executed, files are created for storing the SQL statements generated for querying tables. You can control how many SQL statements can be stored in a single file. The default value is 10. The recommended value ranges from 1 to 50.
- Timeout (s): indicates the maximum time allowed for an SQL statement to end normally. The unit is second (s). The default value is 600. The value ranges from 600 to 7,200.
- Send SMN Notifications: Determine whether to use SMN to notify you of the task status in a timely manner through emails, SMS messages, or customized URLs.
NOTICE:
- Before enabling this function, you need to create a topic on the SMN console. For details, see Creating a Topic.
- Using this function may incur a small amount of fees, which are settled by SMN. For details, see SMN Billing.
Data Filtering
Time Range
Select the time period in which the incremental data needs to be verified as consistent. By default, a 24-hour period is selected. T indicates the execution time of the task, and T-n indicates a time n × 24 hours before the execution time.
If you select Consecutive days, the system verifies consistency of the incremental data generated during these consecutive days.
Non-partitioned Table Verification
Decide how to verify non-partitioned tables.
- Verify all: All non-partitioned tables are verified for consistency.
- Skip all: All non-partitioned tables are skipped during consistency verification.
- Filter by update time: Only non-partitioned tables whose update time falls within the specified time range are verified for consistency. The update time of a non-partitioned table may not be accurate if it contains non-inserted data, and the table may be excluded from verification.
Advanced Options
Max. Fields per SQL Statement: Limit how many fields can be queried by one SQL statement. Too many or few fields in a SQL statement results in low query efficiency. The default value 0 means no limit is set. The value ranges from 100 to 500.
OBS Bucket Check
-
- If you need to upload task logs and content verification results to an OBS bucket for management and analysis, configure an OBS bucket. After the bucket is configured, the task logs and content verification results will be automatically uploaded to the specified OBS bucket.
- If you do not need to upload the task logs and content verification results to OBS, select I confirm that I only need to view logs and data verification results on the MgC Agent and do not need to upload them to OBS.
Execution Script
(available for Hive)
Security Authentication
If security authentication (for example, Kerberos authentication) is enabled for the big data cluster, select this option and configure the security authentication command. You must first manually upload the .keytab file that contains the authentication key to the executor.
- Keytab Path: Enter the path where the .keytab file is stored on the executor.
- Keytab Principal: Enter the principal of the .keytab file.
Execution Command
You can configure Beeline or Spark SQL command parameters to run SQL statements for consistency verification.
- Beeline: a command line tool used to interact with Hive.
- Spark SQL: a command line tool used to execute SQL statements to query and analyze data.
MaxCompute Parameters
(available for MaxCompute)
-
Add MaxCompute parameters as needed. For details, see MaxCompute Documentation.
Execution Settings
(available for DLI)
Parameter
Set the parameters as required. For details about the supported custom parameters, see Custom Parameters.
Command Parameters (available for Delta Lake and Hudi)
Security Authentication (only available for target Delta Lake clusters)
If security authentication (for example, Kerberos authentication) is enabled for the big data cluster, select this option and configure the security authentication command. You must first manually upload the .keytab file that contains the authentication key to the executor.
- Keytab Path: Enter the path where the .keytab file is stored on the executor.
- Keytab Principal: Enter the principal of the .keytab file.
spark-sql
Spark SQL is a module used in Spark for structured data processing. In Spark applications, you can seamlessly use SQL statements or DataSet APIs to query structured data. For more information, see SparkSQL Principles. Retain the default settings.
spark-submit
This is a basic Spark shell command used to submit Spark applications. The command is as follows:
./bin/spark-submit \ --class <main-class> \ --master <master-url> \ ... # other options <application-jar> \ [application-arguments]
Parameter description:
- --class: indicates the name of the class of a Spark application.
- --master: indicates the master to which the Spark application links, such as Yarn-client and Yarn-cluster.
- application-jar: indicates the path of the JAR file of the Spark application.
- application-arguments: indicates the parameter required to submit the Spark application. (This parameter can be empty.)
The parameters that need to be added depend on the scenario:
- If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Delta Lake cluster that uses Spark 3, add the following parameter:
- Parameter: jars
- Value: '/opt/apps/DELTALAKE/deltalake-current/spark3-delta/delta-core_2.12-*.jar,/opt/apps/DELTALAKE/deltalake-current/spark3-delta/delta-storage-*.jar'
CAUTION:
Replace the parameter values with the actual environment directory and Delta Lake version.
- If you are creating a verification task for an Alibaba Cloud EMR Delta Lake 2.1.0 cluster that uses Spark 2.4.8, add the following parameter:
- Parameter: mgc.delta.spark.version
- Value: 2
Table 5 Parameters for creating a selective verification task Area
Parameter
Configuration
Basic Info
Task Name
The default name is Component-selective-verification-4 random characters (including letters and numbers). You can also customize a name.
Task Settings
Table Groups
Select the table groups that contain the tables to be verified.
HBase Connection
This parameter is available for HBase and CloudTable (HBase).
- To create a verification task for the source, select the source HBase connection.
- To create a verification task for the target, select the target HBase or CloudTable (HBase) connection.
Advanced Options
- Concurrency: Specify the number of concurrent threads on an executor for the verification task. The default value is 3. The value ranges from 1 to 10.
- Timeout (s): indicates the maximum time allowed for an SQL statement to end normally. The unit is second (s). The default value is 600. The value ranges from 600 to 7,200.
- Send SMN Notifications: Determine whether to use SMN to notify you of the task status in a timely manner through emails, SMS messages, or customized URLs.
NOTICE:
- Before enabling this function, you need to create a topic on the SMN console. For details, see Creating a Topic.
- Using this function may incur a small amount of fees, which are settled by SMN. For details, see SMN Billing.
Data Filtering
Time Range
Select the time period in which the data needs to be verified as consistent.
OBS Bucket Check
-
- If you need to upload task logs and content verification results to an OBS bucket for management and analysis, configure an OBS bucket. After the bucket is configured, the task logs and content verification results will be automatically uploaded to the specified OBS bucket.
- If you do not need to upload the task logs and content verification results to OBS, select I confirm that I only need to view logs and data verification results on the MgC Agent and do not need to upload them to OBS.
Execution Settings
(available for HBase)
Parameter
Add command parameters based on the selected run mode and requirements.
- Click Save. After the creation is successful, the system automatically synchronizes the task settings to the MgC Agent. Then in the task list, you can view the created task and its settings synchronization status.
- After the settings synchronization is complete, execute the task using either of the following methods:
- Automatic execution: The task will be executed at the specified time automatically.
- In the task list, locate the task and click Activate in the Schedule Status column.
- In the displayed dialog box, click OK to activate the task.
- Manual execution: You can manually execute the task immediately.
- In the task list, locate the task and click Execute in the Operation column.
- In the displayed dialog box, click OK to execute the task immediately.
- Automatic execution: The task will be executed at the specified time automatically.
- Click View Executions in the Operation column. On the executions list page, you can:
- View the status, progress statistics, and execution start time and end time of each task execution.

If a task execution takes a long time or the page is incorrectly displayed, set the log level of the executor's Driver to ERROR.
- Upload the logs of a task execution to your OBS bucket for review and analysis by clicking Upload Log in the Operation column. Before uploading logs, you need to configure a log bucket on the MgC Agent console. For details, see Configuring a Log Bucket.
- Cancel a running execution or terminate an execution using the Cancel/Terminate button.
- If there are tables whose verification results are not obtained, obtain the results again by clicking Path in the Statistics column.
- View the status, progress statistics, and execution start time and end time of each task execution.
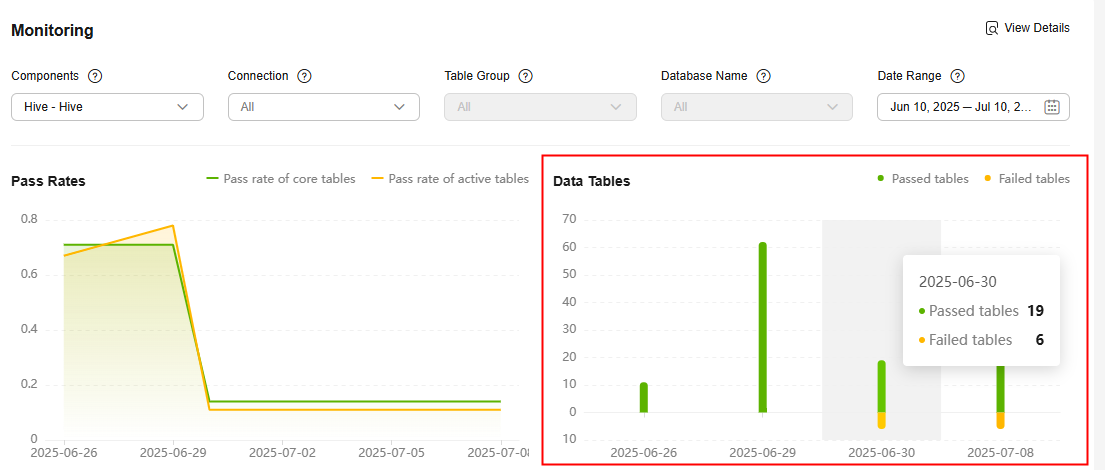
Monitoring
After the big data verification is complete, you can view the verification results in the Monitoring area on the Big Data Verification page. You can filter data by component type, connection, table group, database name, and verification date. Then you can see the corresponding verification pass rates, data table quantities, and the breakdown details.
Click View Details in the upper right corner of the Monitoring area. On the Verification Results page, view the detailed verification results of each data table. The verification batch displayed is the last execution batch in the selected date range. For any data table that fails the verification, click Analyze Cause in the Verification Result column to record the reason. For details, see Recording Inconsistency Causes.

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot