Enabling and Configuring Access Control Attributes
Scenarios
To perform ABAC in an identity source, you need to enable access control in IAM Identity Center and add user attributes that need to be used in permission set policies to control user access to resources. The user attributes that can be added include basic information, contact information, work-related information, and address information. For details about the user attributes that support ABAC, see Supported User Attributes.
For example, if you want to use the username to assign their access to resources in the organization, you can add the username attribute on the Access Control Attributes tab for ABAC. Then, you can add a custom identity policy to the permission set in IAM Identity Center. This policy grants access permissions to a user only when their username matches the tag value you assigned to the organizational resources. For details about ABAC-related custom policies, see Creating Permissions Policies for ABAC.
The differences between performing ABAC on IAM Identity Center and on external identity providers are as follows:
- IAM Identity Center: You need to add the attributes for performing ABAC on the Access Control Attributes tab of IAM Identity Center.
- External identity provider: You can add the attributes in either of the following ways.
- Add the ABAC attributes in the external identity provider. You can configure an external identity provider to send attributes through SAML assertions. In this case, IAM Identity Center obtains the attribute keys and attribute values passed from the external identity provider for policy evaluation. For details, see the external identity provider documentation.
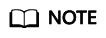
Attributes passed through SAML assertions are invisible on the Access Control Attributes tab of IAM Identity Center. You must learn about them in advance and add them to access control rules when creating permissions policies.
- Configure ABAC attributes on the Access Control Attributes tab of IAM Identity Center. If the ABAC attributes configured in IAM Identity Center are the same as those configured in the external identity provider, the former is preferentially used for access control decisions.
- Add the ABAC attributes in the external identity provider. You can configure an external identity provider to send attributes through SAML assertions. In this case, IAM Identity Center obtains the attribute keys and attribute values passed from the external identity provider for policy evaluation. For details, see the external identity provider documentation.
This section only describes the operations performed on the IAM Identity Center console. For the operations performed on the external identity provider, see their documentation.
Enabling Access Control Attributes
- Log in to the Huawei Cloud management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Management & Governance > IAM Identity Center.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Management & Governance > IAM Identity Center. - Choose Settings in the navigation pane.
- Click Enable on the Access Control Attributes tab.
Figure 1 Enabling access control attributes
Configuring Access Control Attributes
After access control attributes are enabled, you need to add attribute keys and attribute values for access control. A maximum of 20 attributes can be added.
- Log in to the Huawei Cloud management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Management & Governance > IAM Identity Center.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Management & Governance > IAM Identity Center. - Choose Settings in the navigation pane.
- Click Add on the Access Control Attributes tab.
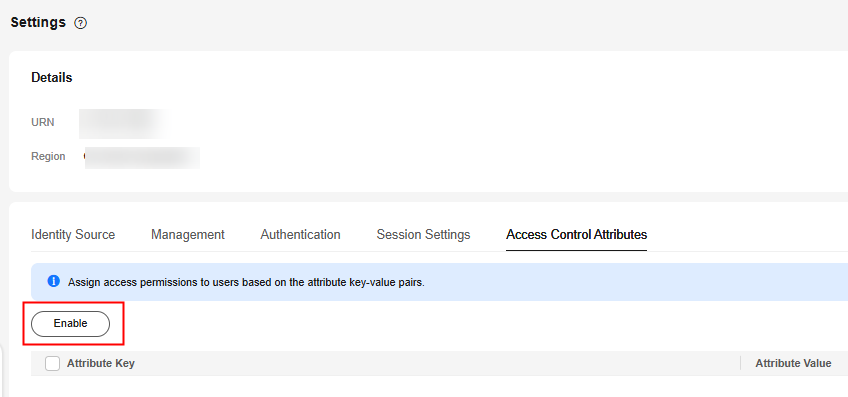
- In the displayed dialog box, add attribute keys and attribute values of the user for access control.
- Attribute Key: specifies the name of a user attribute and can be used in permissions policies. Only a single value is supported.
You can enter any name, which will be used when you define custom identity policies in the permission set. For example, if you set the attribute key to User_A, the PrincipalTag condition key in the custom identity policy must also be set to User_A, that is, g:ResourceTag/tag-key": "${g:PrincipalTag/User_A}.
- Attribute Value: specifies the type of a user attribute. You can select a user attribute type from the drop-down list box.
For example, if you select ${user:name}, then the username is used for access control. During authorization, the username must match the resource tag value. For details about the supported user attributes, see Supported User Attributes.
Figure 2 Adding access control attributes
- Attribute Key: specifies the name of a user attribute and can be used in permissions policies. Only a single value is supported.
- After the configuration is complete, click OK.
Now that you have enabled and configured access control attributes, you need to create custom identity policies of ABAC in the permission set by referring to Creating Permissions Policies for ABAC.
Editing or Deleting Access Control Attributes
After the access control attributes are added, you can modify or delete them at any time as required.
- Log in to the Huawei Cloud management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Management & Governance > IAM Identity Center.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Management & Governance > IAM Identity Center. - Choose Settings in the navigation pane.
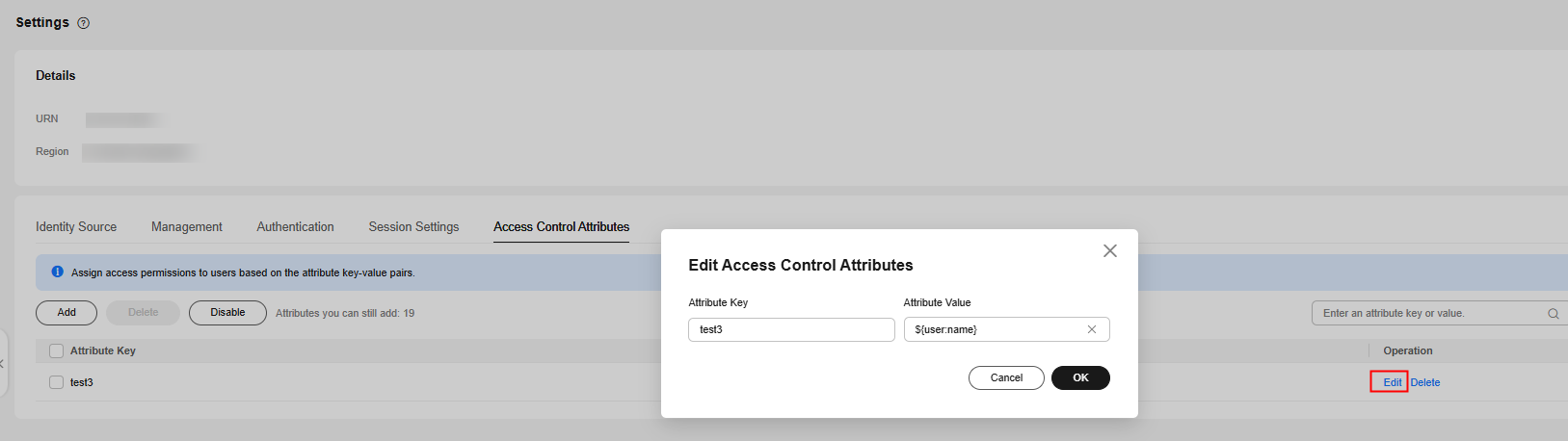
- On the Access Control Attributes tab, click Edit in the Operation column of the list.
- In the displayed dialog box, modify the attribute key or value and click OK.
Figure 3 Editing access control attributes
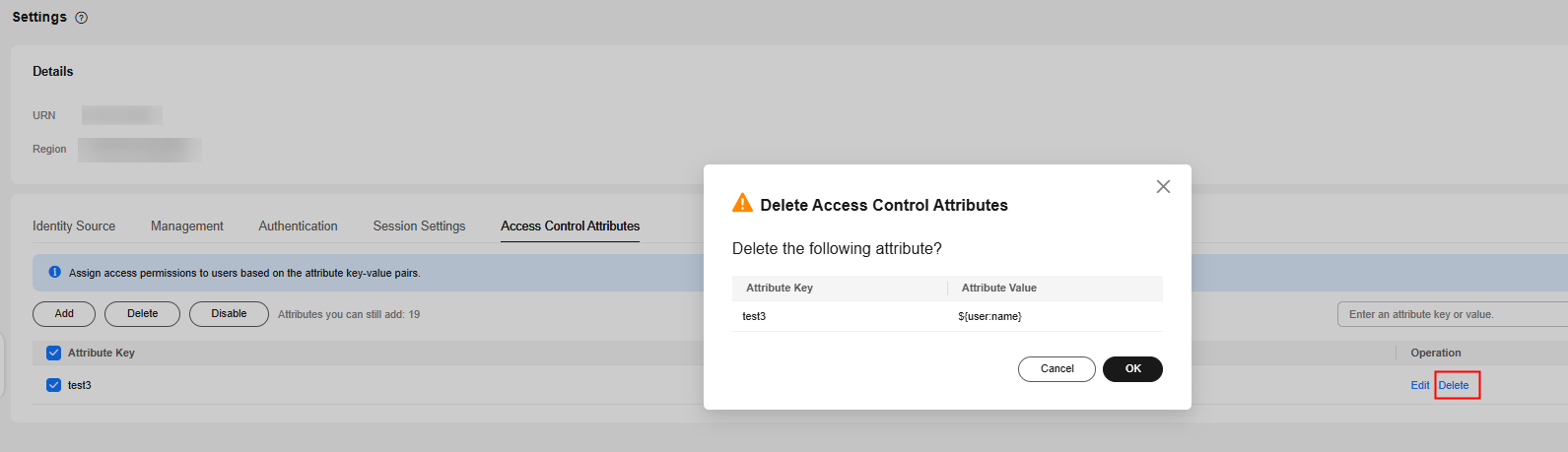
- Click Delete in the Operation column of the row that contains the target access control attribute. In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
Figure 4 Deleting an access control attribute
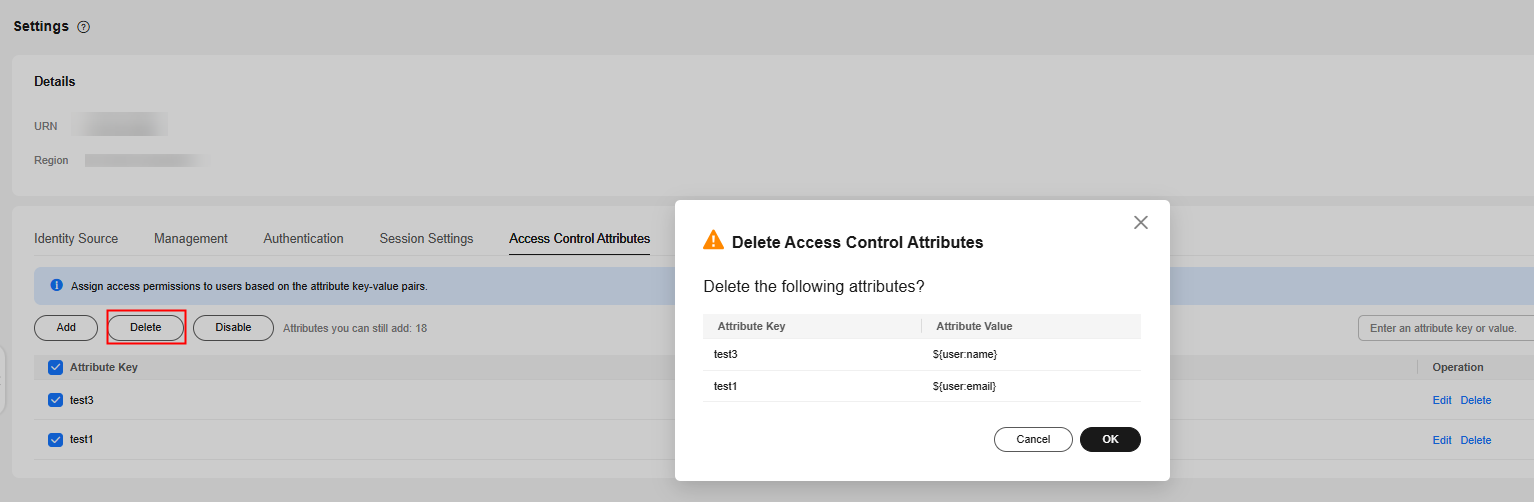
- Select multiple access control attributes to be deleted from the list and click Delete above the list. In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
Figure 5 Batch deleting access control attributes
Disabling Access Control Attributes
If you no longer need to use the ABAC function, you can disable it at any time. This operation will delete all configured attributes and cannot be restored. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
- Log in to the Huawei Cloud management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Management & Governance > IAM Identity Center.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Management & Governance > IAM Identity Center. - Choose Settings in the navigation pane.
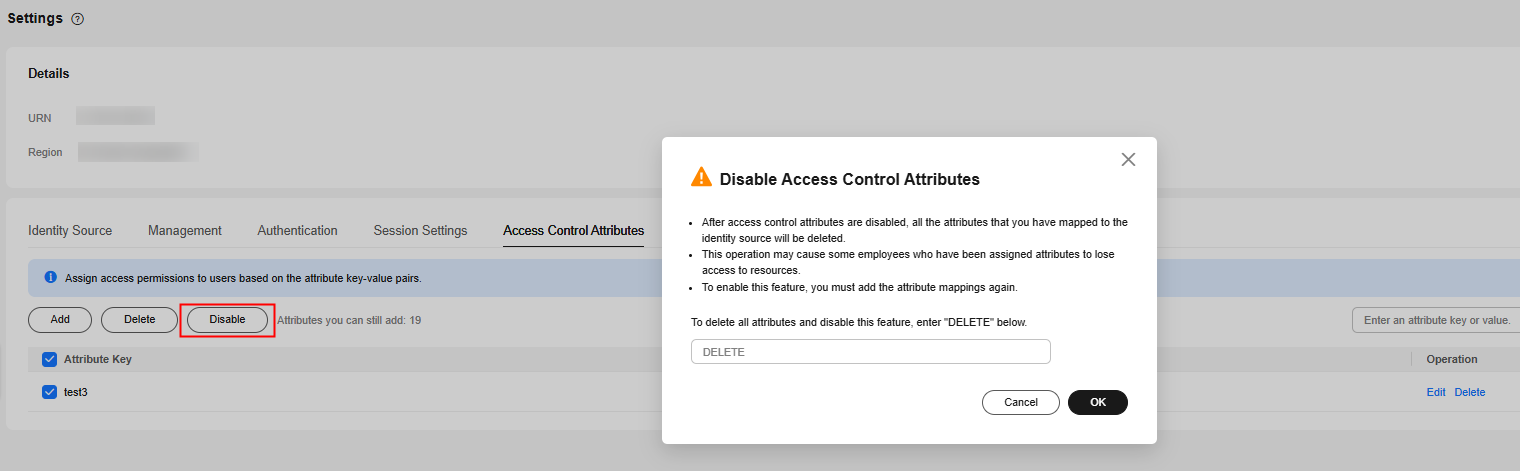
- On the Access Control Attributes tab, click Disable.
- In the displayed dialog box, read the information carefully. After confirmation, enter DELETE and click OK.
Figure 6 Disabling access control attributes
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





