Adding a Protected Directory
WTP monitors website directories in real time, backs up files, and restores tampered files using the backup, protecting websites from Trojans, illegal links, and tampering.
Constraints and Limitations
- Only the servers that are protected by the HSS WTP edition support the operations described in this section.
- The constraints on protected directories are as follows:
- For Linux,
- A server can have up to 50 protected directories.
- The complete path of a protected directory cannot exceed 256 characters.
- The folder levels of a protected directory cannot exceed 100.
- The total folders in protected directories cannot exceed 900,000.
- For Windows,
- A server can have up to 50 protected directories.
- The complete path of a protected directory cannot exceed 256 characters.
- For Linux,
- The constraints on local backup paths are as follows:
- Local backup is supported only in Linux.
- The local backup path must be valid, or web tamper protection will not take effect.
- The local backup path cannot overlap with the added protected directory.
- The available capacity of the disk where the local backup path is located is greater than the size of all protected directories.
Adding a Protected Directory
- Log in to the management console.
- In the upper left corner of the page, select a region, click
 , and choose Security & Compliance > HSS.
, and choose Security & Compliance > HSS. - Choose Server Protection > Web Tamper Protection. Click Configure Protection in the Operation column.
If your servers are managed by enterprise projects, you can select an enterprise project to view or operate the asset and scan information.
Figure 1 Entering the page of protection settings
- Click Settings under Protected Directory Settings.
Figure 2 Page for setting a protected directory

- You can add a maximum of 50 protected directories.
- Click Add. In the Add Protected Directory dialog box, set required parameters. For details, see Table 1.
Figure 3 Adding a protected directory

Table 1 Parameters for adding a protected directory Parameter
Description
Example Value
Protected Directory
Directory to be protected.
- Only one protected directory can be added. The directory length cannot exceed 256 characters.
- Do not add an OS directory as a protected directory.
- After a directory is added, the files and folders in the protected directory are read-only and cannot be modified directly.
- Linux: /etc/lesuo
- Windows: d:\web
Excluded Subdirectory
Subdirectories that do not need to be protected in the protected directory, such as temporary file directories.
A maximum of 10 subdirectories can be added. Separate multiple subdirectories with semicolons (;). Each subdirectory can contain a maximum of 256 characters.
- Linux: lesuo/test
- Windows: web\test
Excluded File Types
Types of files that do not need to be protected in the protected directory, such as log files.
- The file type can contain only letters and numbers. A maximum of 10 file types can be added. Each file type can contain a maximum of 10 characters. Multiple file types are separated by semicolons (;).
- To record the running status of the server in real time, exclude the log files in the protected directory. You can grant high read and write permissions for log files to prevent attackers from viewing or tampering with the log files.
log;pid;text
Local Backup Path
Set this parameter if your server runs the Linux OS.
Set a local backup path for files in protected directories. After WTP is enabled, files in the protected directory are automatically backed up to the local backup path.
The backup rules are described as follows:
- The local backup path must be valid and cannot overlap with the protected directory path.
- Excluded subdirectories and types of files are not backed up.
- Generally, the backup completes within 10 minutes. The actual duration depends on the size of files in the protected directory.
- If WTP detects that a file in a protected directory is tampered with, it immediately uses the backup file on the local server to restore the file.
/etc/backup
Excluded File Path
Set this parameter if your server runs the Linux OS.
Files that do not need to be protected in the protected directory.
A maximum of 50 paths can be added. Separate multiple paths with semicolons (;). Each path can contain a maximum of 256 characters.
lesuo/data;lesuo/list
- Click OK.
If you need to modify files in the protected directory, stop protection for the protected directory first. After the files are modified, resume protection for the directory in a timely manner.
- Click Add. In the Add Protected Directory dialog box, set required parameters. For details, see Table 1.
- Enable remote backup.
By default, HSS backs up the files from the protected directories (excluding specified subdirectories and file types) to the local backup directory you specified when adding protected directories. To protect the local backup files from tampering, you must enable the remote backup function.
For details about how to add a remote backup server, see Configuring Remote Backup.
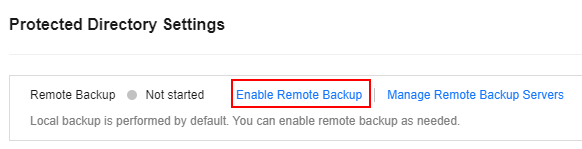
- On the Protected Directory Settings page, click Enable Remote Backup.
Figure 4 Enabling remote backup
- Select a backup server from the drop-down list box.
- Click OK.
- On the Protected Directory Settings page, click Enable Remote Backup.
Related Operations
- Export a protected directory: If you have configured a large number of protected directories, you can click
 on the protected directory configuration page to export the configurations of all protected directories to your local PC.
on the protected directory configuration page to export the configurations of all protected directories to your local PC. - Suspend protection: You can suspend WTP for a directory if needed. It is recommended that you resume WTP in a timely manner to prevent the files in the directory from being tampered with.
- Edit a protected directory: You can modify the added protected directory as needed.
- Delete a protected directory: You can delete the directories that do not need to be protected.

- After you suspend protection for a protected directory, delete it, or modify its path, files in the directory will no longer be protected. Before performing these operations, ensure you have taken other measures to protect the files.
- After you suspend protection for a protected directory, delete it, or modify its path, if you find your files missing in the directory, search for them in the local or remote backup path.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





