Analyzing a Graph Using Temporal BFS
The temporal breadth-first search (BFS) algorithm searches for associated vertices using temporal message passing and temporal BFS techniques. It then generates the visit time of each algorithm and its distance from the source vertex.
The procedure is as follows:
- In the Temporal tab of the Graph Analysis area on the left of the graph editor page, click Temporal BFS, and set the parameters in the drop-down list.
- Set the start time, end time, and their properties. For details, see Setting a Timeline. To modify the parameters, click the text box or
 in the lower left corner.
in the lower left corner. - Start Vertex: ID of the start vertex
- k: Traversal depth, indicating the maximum number of vertices in a traversal. The value ranges from 1 to 100. The default value is 3.
- directed: Whether the traversal is performed along the directions of edges in the graph. The value can be true (default) or false.
- true: Traversal is performed along edge directions.
- false: Edge directions will not be considered in the traversal.
Figure 1 Temporal BFS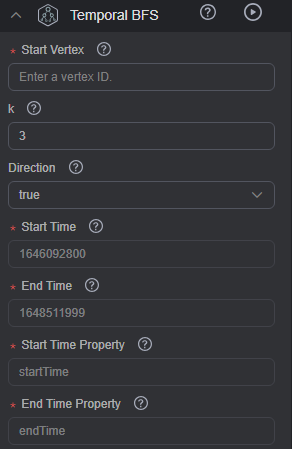
- Set the start time, end time, and their properties. For details, see Setting a Timeline. To modify the parameters, click the text box or
- Click
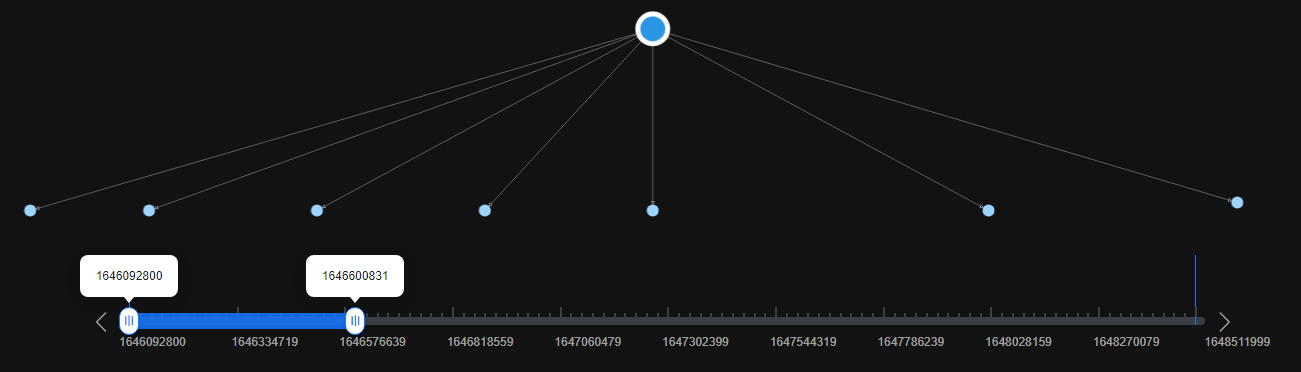
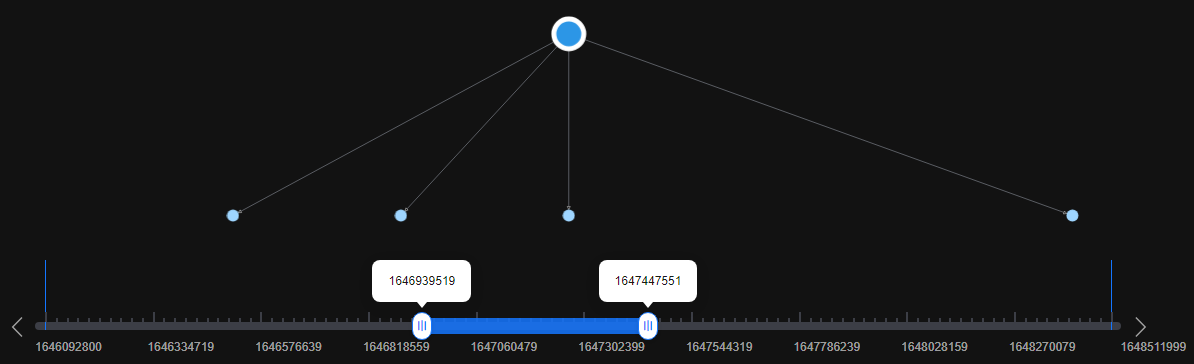
 on the right of Temporal BFS. The running result is displayed on the canvas. In this algorithm, a single slider is used for playback. As shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, vertices in the dynamic graph increase over time.
on the right of Temporal BFS. The running result is displayed on the canvas. In this algorithm, a single slider is used for playback. As shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, vertices in the dynamic graph increase over time.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot