Case: Setting cost_param and Optimizing Query Performance
Symptom 1
If bit0 of cost_param is set to 1 (set cost_param = 1), an improved mechanism is used for estimating the selection rate of non-equi-joins. This method is more accurate for estimating the selection rate of joins between two identical tables. The following example describes the optimization scenario when bit0 of cost_param is set to 1. At present, if cost_param & 1 is set to a value other than 0, the path is not used. An optimized formula is selected for calculation.
Note: The selection rate indicates the percentage for which the number of rows meeting the join conditions account of the JOIN results when the JOIN relationship is established between two tables.
The table structure is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
CREATE TABLE LINEITEM ( L_ORDERKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , L_PARTKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , L_SUPPKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , L_LINENUMBER BIGINT NOT NULL , L_QUANTITY DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_EXTENDEDPRICE DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_DISCOUNT DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_TAX DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , L_RETURNFLAG CHAR(1) NOT NULL , L_LINESTATUS CHAR(1) NOT NULL , L_SHIPDATE DATE NOT NULL , L_COMMITDATE DATE NOT NULL , L_RECEIPTDATE DATE NOT NULL , L_SHIPINSTRUCT CHAR(25) NOT NULL , L_SHIPMODE CHAR(10) NOT NULL , L_COMMENT VARCHAR(44) NOT NULL ) with (orientation = column, COMPRESSION = MIDDLE) distribute by hash(L_ORDERKEY); CREATE TABLE ORDERS ( O_ORDERKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , O_CUSTKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , O_ORDERSTATUS CHAR(1) NOT NULL , O_TOTALPRICE DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , O_ORDERDATE DATE NOT NULL , O_ORDERPRIORITY CHAR(15) NOT NULL , O_CLERK CHAR(15) NOT NULL , O_SHIPPRIORITY BIGINT NOT NULL , O_COMMENT VARCHAR(79) NOT NULL )with (orientation = column, COMPRESSION = MIDDLE) distribute by hash(O_ORDERKEY); |
The query statements are as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
explain verbose select count(*) as numwait from lineitem l1, orders where o_orderkey = l1.l_orderkey and o_orderstatus = 'F' and l1.l_receiptdate > l1.l_commitdate and not exists ( select * from lineitem l3 where l3.l_orderkey = l1.l_orderkey and l3.l_suppkey <> l1.l_suppkey and l3.l_receiptdate > l3.l_commitdate ) order by numwait desc; |
The following figure shows the execution plan. (When verbose is used, distinct is added for column selection which is controlled by cost off/on. The hash join rows show the estimated number of distinct values and the other rows do not.)
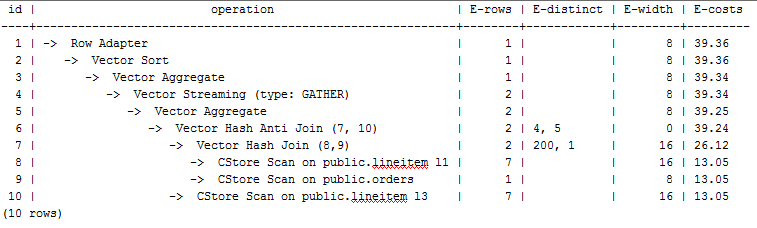
Optimization Analysis 1
These queries are from Anti Join connected in the lineitem table. When bit0 of cost_param is 0, the estimated number of Anti Join rows greatly differ from that of the actual number of rows so that the query performance deteriorates. You can estimate the number of Anti Join rows more accurately by setting bit0 of cost_param to 1 to improve the query performance. The optimized execution plan is as follows.
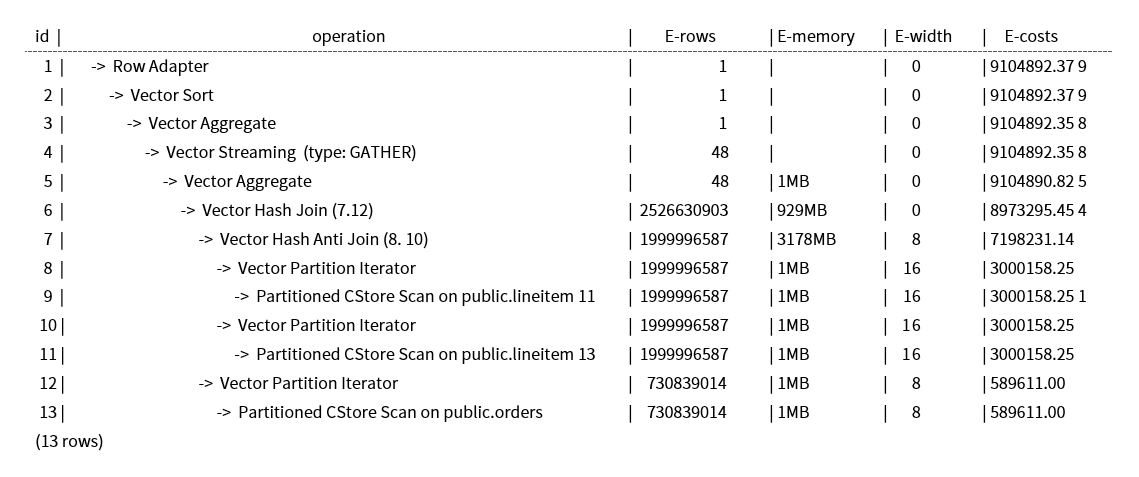
Symptom 2
When bit1 of cost_param is set to 1 (set cost_param=2), the selection rate is estimated based on multiple filter criteria. The lowest selection rate among all filter criteria, but not the product of the selection rates for two tables under a specific filter criterion, is used as the total selection rate. This method is more accurate when a close correlation exists between the columns to be filtered. The following example describes the optimization scenario when bit1 of cost_param is set to 1.
The table structure is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
CREATE TABLE NATION ( N_NATIONKEY INT NOT NULL , N_NAME CHAR(25) NOT NULL , N_REGIONKEY INT NOT NULL , N_COMMENT VARCHAR(152) ) distribute by replication; CREATE TABLE SUPPLIER ( S_SUPPKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , S_NAME CHAR(25) NOT NULL , S_ADDRESS VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL , S_NATIONKEY INT NOT NULL , S_PHONE CHAR(15) NOT NULL , S_ACCTBAL DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL , S_COMMENT VARCHAR(101) NOT NULL ) distribute by hash(S_SUPPKEY); CREATE TABLE PARTSUPP ( PS_PARTKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , PS_SUPPKEY BIGINT NOT NULL , PS_AVAILQTY BIGINT NOT NULL , PS_SUPPLYCOST DECIMAL(15,2)NOT NULL , PS_COMMENT VARCHAR(199) NOT NULL )distribute by hash(PS_PARTKEY); |
The query statements are as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
set cost_param=2; explain verbose select nation, sum(amount) as sum_profit from ( select n_name as nation, l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) - ps_supplycost * l_quantity as amount from supplier, lineitem, partsupp, nation where s_suppkey = l_suppkey and ps_suppkey = l_suppkey and ps_partkey = l_partkey and s_nationkey = n_nationkey ) as profit group by nation order by nation; |
When bit1 of cost_param is set to 0, the execution plan is shown as follows:
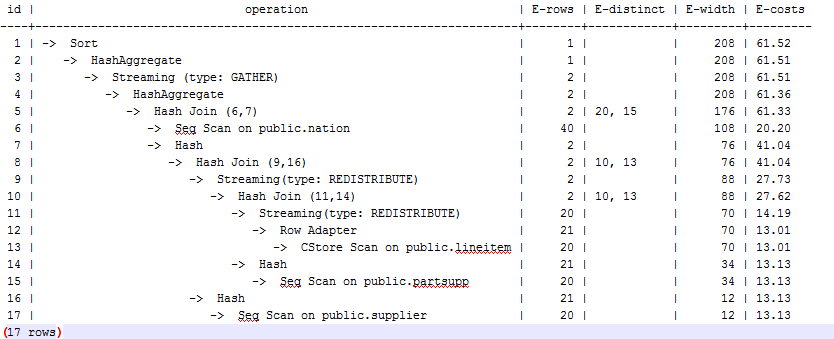
Optimization Analysis 2
In the preceding queries, the hash join criteria of the supplier, lineitem, and partsupp tables are setting lineitem.l_suppkey to supplier.s_suppkey and lineitem.l_partkey to partsupp.ps_partkey. Two filter criteria exist in the hash join conditions. lineitem.l_suppkey in the first filter criteria and lineitem.l_partkey in the second filter criteria are two columns with strong relationship of the lineitem table. In this situation, when you estimate the rate of the hash join conditions, if bit1 of cost_param is 0, the selection rate is estimated based on multiple filter criteria, and the product of the selection rates for two tables under a specific filter criterion is used as the total selection rate, which is inaccurate. If bit1 of cost_param is set to 1, the lowest selection rate among all filter criteria is used as the total selection rate. This method is more accurate and the query performance is better. The plan after optimization is shown as follows.
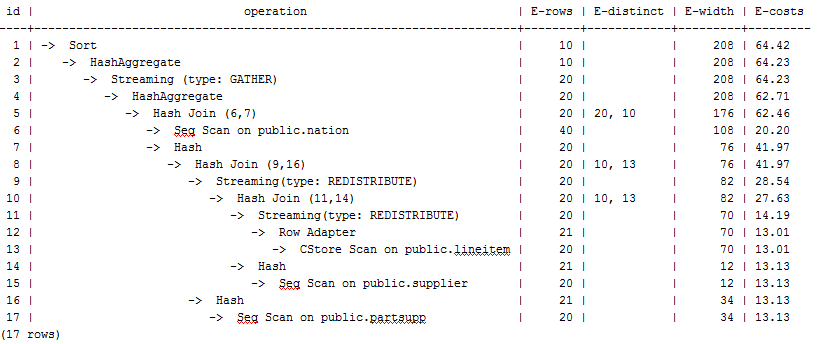
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot








