Manually Changing a Xen ECS to a KVM ECS (Linux)
Scenarios
Before changing a Xen ECS that runs Linux to a KVM ECS, install and configure required drivers.
This section describes how to manually install drivers on a Linux ECS, configure automatic disk attachment, and change Xen to KVM.
For instructions about how to use a script to automatically install drivers, see Automatically Changing a Xen ECS to a KVM ECS (Linux).

- Xen ECS flavors: S1, C1, C2, and M1.
- KVM ECS flavors: See the Virtualization column in ECS Specifications.
- To support both Xen and KVM, Linux ECSs require the xen-pv and virtio drivers. Before changing a Xen ECS to a KVM ECS, make sure that the Linux ECS has been configured, including driver installation and automatic disk attachment.
Constraints
- The ECS needs to be stopped during the specification modification, so you are advised to perform this operation during off-peak hours.
- To prevent data loss, the specifications of Linux ECSs that use LVM or RAID arrays cannot be modified.
- A Xen ECS with more than 24 VBD disks attached cannot be changed to a KVM ECS.
- A Xen ECS can be changed to a KVM ECS, but a KVM ECS cannot be changed to a Xen ECS.
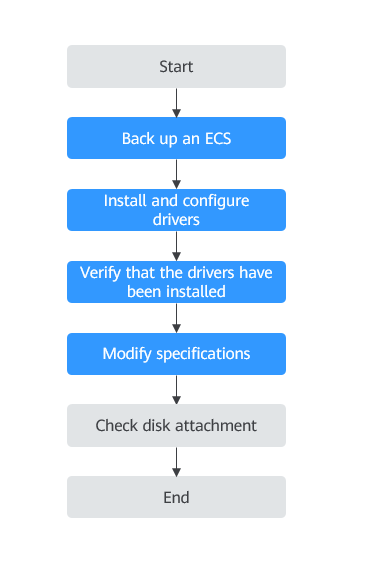
Procedure
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
5 |
Step 1: Back Up an ECS
If you modify the specifications of an ECS without installing the driver, the ECS may become unavailable and the data on the system disk may be lost. You are advised to back up the ECS first to prevent data loss.
- Check the ECS.
Before backing up the ECS, stop and then start the ECS to ensure that services can run properly after the ECS is started.
- Back up the ECS.
Backing up ECSs will generate storage costs. There are two types of EVS snapshots: standard snapshots and legacy snapshots. Legacy snapshots are in OBT and free of charge. Standard snapshots are billed. Select the one type as required.
- Method 1: Create a backup for the ECS.
For details, see ECS Backup Procedure.
- Method 2: Create a system disk snapshot and a data disk snapshot.
For details about how to create a snapshot, see Creating an EVS Snapshot in Elastic Volume Service User Guide.
- Method 1: Create a backup for the ECS.

Backups and snapshots created for the ECS are used to restore data. If the specifications fail to be modified, you can use the backups or snapshots to restore data.
- To use backups to restore data, see Restoring from a Cloud Server Backup.
- To use snapshots to roll back data, see Rolling Back Disk Data from a Snapshot.
After the specifications are modified, if services are running properly, delete the ECS backups or snapshots from the corresponding service console.
Step 2: Install and Configure Drivers
Perform the following operations to manually install drivers on an ECS.
- Log in to the ECS.
- Uninstall tools from the ECS.
For details, see Uninstalling PV Drivers.
- Change the GRUB disk ID to UUID.
For details, see Changing the Disk Identifier in the GRUB Configuration File to UUID.
- Change the fstab disk ID to UUID.
For details, see Changing the Disk Identifier in the fstab File to UUID.
- Install native Xen and KVM drivers.
For details, see Installing Native Xen and KVM Drivers.
Step 3: Verify that the Drivers Have Been Installed
Perform the following operations to check whether the drivers have been installed and the configuration files have been modified.

Before manually modifying specifications, make sure that the ECS has been configured correctly.
- Log in to the ECS.
- Run the following command to check whether the root partition is in UUID format:
- If yes, the disk ID in the GRUB configuration file has been changed to UUID.
- If no, the modification failed. In such a case, change the GRUB disk ID to UUID again by referring to Step 2: Install and Configure Drivers.
……menuentry 'Ubuntu Linux, with Linux 3.13.0-24-generic' --class ubuntu --class gnu-linux --class gnu --class os --unrestricted $menuentry_id_option 'gnulinux-3.13.0-24-generic-advanced-ec51d860-34bf-4374-ad46-a0c3e337fd34' { recordfail load_video gfxmode $linux_gfx_mode insmod gzio insmod part_msdos insmod ext2 if [ x$feature_platform_search_hint = xy ]; then search --no-floppy --fs-uuid --set=root ec51d860-34bf-4374-ad46-a0c3e337fd34 else search --no-floppy --fs-uuid --set=root ec51d860-34bf-4374-ad46-a0c3e337fd34 fi echo 'Loading Linux 3.13.0-24-generic ...' linux /boot/vmlinuz-3.13.0-24-generic root=UUID=ec51d860-34bf-4374-ad46-a0c3e337fd34 ro echo 'Loading initial ramdisk ...' initrd /boot/initrd.img-3.13.0-24-generic }
The path in which the GRUB configuration file is stored varies depending on the OS. For example, the path can be /boot/grub/menu.lst, /boot/grub/grub.cfg, /boot/grub2/grub.cfg, or /boot/grub/grub.conf.
- Run the following command to check whether the disk ID in the fstab configuration file is UUID:
- If yes, the disk ID has been changed to UUID.
- If no, the modification failed. In such a case, change the fstab disk ID to UUID again by referring to Step 2: Install and Configure Drivers.
[root@****** ~]# cat /etc/fstab UUID=4eb40294-4c6f-4384-bbb6-b8795bbb1130 / xfs defaults 0 0 UUID=2de37c6b-2648-43b4-a4f5-40162154e135 swap swap defaults 0 0
- Check whether the native Xen and KVM drivers have been installed.
- If the boot virtual file system is initramfs, run the following commands:
lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-`uname -r`.img | grep ` uname -r ` | grep xen
lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-`uname -r`.img | grep ` uname -r ` |grep virtio
- If the boot virtual file system is initrd, run the following commands:
lsinitrd /boot/initrd-`uname -r` | grep ` uname -r ` | grep xen
lsinitrd /boot/initrd-`uname -r` | grep ` uname -r ` | grep virtio
If the names of the native Xen and KVM drivers are displayed in the command output, the drivers have been installed.
[root@CTU10000xxxxx home]# lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-`uname -r`.img | grep ` uname -r`| grep xen -rwxr--r-- 1 root root 54888 Jul 16 17:53 lib/modules/2.6.32-573.8.1.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/block/xen-blkfront.ko -rwxr--r-- 1 root root 45664 Jul 16 17:53 lib/modules/2.6.32-573.8.1.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/net/xen-netfront.ko [root@CTU10000xxxxx home]# lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-`uname -r`.img | grep ` uname -r`| grep virtio -rwxr--r-- 1 root root 23448 Jul 16 17:53 lib/modules/2.6.32-573.8.1.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/block/virtio_blk.ko -rwxr--r-- 1 root root 50704 Jul 16 17:53 lib/modules/2.6.32-573.8.1.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/net/virtio_net.ko -rwxr--r-- 1 root root 28424 Jul 16 17:53 lib/modules/2.6.32-573.8.1.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/scsi/virtio_scsi.ko drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Jul 16 17:53 lib/modules/2.6.32-573.8.1.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/virtio -rwxr--r-- 1 root root 14544 Jul 16 17:53 lib/modules/2.6.32-573.8.1.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/virtio/virtio.ko -rwxr--r-- 1 root root 21040 Jul 16 17:53 lib/modules/2.6.32-573.8.1.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/virtio/virtio_pci.ko -rwxr--r-- 1 root root 18016 Jul 16 17:53 lib/modules/2.6.32-573.8.1.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/virtio/virtio_ring.ko
- If the boot virtual file system is initramfs, run the following commands:

Make sure that the ECS has been configured successfully, or the ECS may become unavailable after the specifications are modified.
Step 4: Modify Specifications
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - Click
 . Under Compute, click Elastic Cloud Server.
. Under Compute, click Elastic Cloud Server. - On the Elastic Cloud Server page, view the status of the target ECS.
If the ECS is not in Stopped state, choose More > Stop in the Operation column.
- Choose More > Modify Specifications in the Operation column.
The Modify ECS Specifications page is displayed.
- Select the new ECS type, vCPUs, and memory.
- (Optional) Set DeH.
If the ECS is created on a DeH, you can change the DeH where the ECS resides.
To do so, select the target DeH from the drop-down list. If no DeH is available in the drop-down list, it indicates that DeH resources are insufficient and cannot be used to create the ECS with new specifications.
- Select the checkbox to confirm that the configuration is complete.
- Click Next.
- Confirm the new specifications, read and agree to the agreement, and then click Submit Application.

- The cloud platform automatically creates a system disk snapshot for you. After the specifications are modified, manually delete the snapshot on the snapshot page if you have verified that services are running properly.
- If ECS specifications failed to be modified and the ECS becomes unavailable, reinstall the OS. This operation will clear the data on the system disk while the data on data disks is retained.
(Optional) Step 5: Check Disk Attachment
After a Xen ECS is changed to a KVM ECS, disk attachment may fail. Therefore, check disk attachment after specifications are modified. If disks are properly attached, the specifications are modified successfully.
- Linux ECS
For details, see Why Does the Disk Attachment of a Linux ECS Fail After I Modify the ECS Specifications?
Follow-up Procedure
If the ECS specifications have been modified but the OS cannot be started after a remote login, contact customer service or reinstall the ECS OS to resolve this issue. For details, see Reinstalling the OS.

Reinstalling the OS will clear the system disk data, but the data on data disks is not affected.
After the specifications are modified, manually delete the snapshot on the snapshot page if you have verified that services are running properly.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot