Migrating to Huawei Cloud DNS for Domain Name Resolution
Scenarios
If you have registered a domain name that is being used on the Internet, you can change the current DNS service provider to Huawei Cloud DNS for domain name resolution.
Process
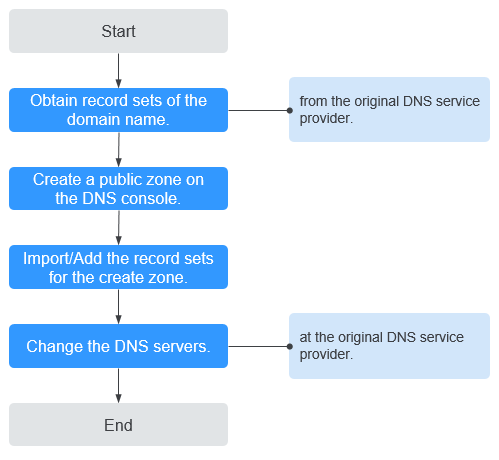
Figure 1 shows the process for changing the DNS service provider of a domain name to Huawei Cloud DNS.
Obtaining DNS Record Sets
Before you use Huawei Cloud DNS for domain name resolution, migrate all its record sets from the current DNS service provider. It is recommended that you export all record sets at a time if this function is supported by the current DNS service provider. For details about how to migrate the record sets, see the documentation of the DNS service provider.
Creating a Public Zone
On the Huawei Cloud DNS console, create a public zone for the domain name.
For details, see Creating a Public Zone.
Adding Record Sets
On the Huawei Cloud DNS console, add record sets to the created public zone. You can import all record sets obtained from the original DNS service provider.
For details, see Importing Record Sets.
For details, see How Do I Check Whether Record Sets Have Taken Effect?
Changing DNS Servers for the Domain Name
- Change the DNS servers for the domain name in the system of the original DNS service provider. For details, see the operation guide on the official website of the DNS service provider.
The following are Huawei Cloud DNS server addresses:
- ns1.huaweicloud-dns.com: DNS server for regions in the Chinese mainland
- ns1.huaweicloud-dns.cn: DNS server for regions in the Chinese mainland
- ns1.huaweicloud-dns.net: DNS server for countries or regions outside the Chinese mainland
- ns1.huaweicloud-dns.org: DNS server for countries or regions outside the Chinese mainland
For more information about the DNS servers, see What Are Huawei Cloud DNS Servers?
- Wait for the change to take effect.
Generally, the change to DNS servers is quickly updated to top-level DNS servers and rapidly takes effect on the Internet. However, some DNS service providers set the TTL value in the NS record set to 48 hours. In this scenario, if the NS record set is cached by a local DNS server, the change will take effect until 48 hours later.
Do not delete the original record sets until the change takes effect. Your services will continue to be served by the old DNS server before the new DNS server is being used.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot