Creating an Indicator
Indicators are quantifiable measures used to assess the performance or achievement of business objectives. Common indicators include sales revenue, number of users, growth rate, conversion rate, satisfaction rate, etc. These indicators provide decision-makers with powerful data support by intuitively reflecting the operations status of the business. This section describes how to create an indicator.
Prerequisites
- A project has been created by referring to Creating a Project.
- A data source has been created by referring to Connecting to a Data Source.
- A dataset has been created by referring to Creating a Dataset.
Procedure
- Log in to the DataArts Insight console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console to select a region. Then, select an enterprise project in the upper right corner.
in the upper left corner of the management console to select a region. Then, select an enterprise project in the upper right corner. - On the top menu of the console, click Project. On the displayed My Projects page, click the name of the desired project.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Data Management > Indicator. On the displayed page, click Create Indicator.
Figure 1 Create Indicator
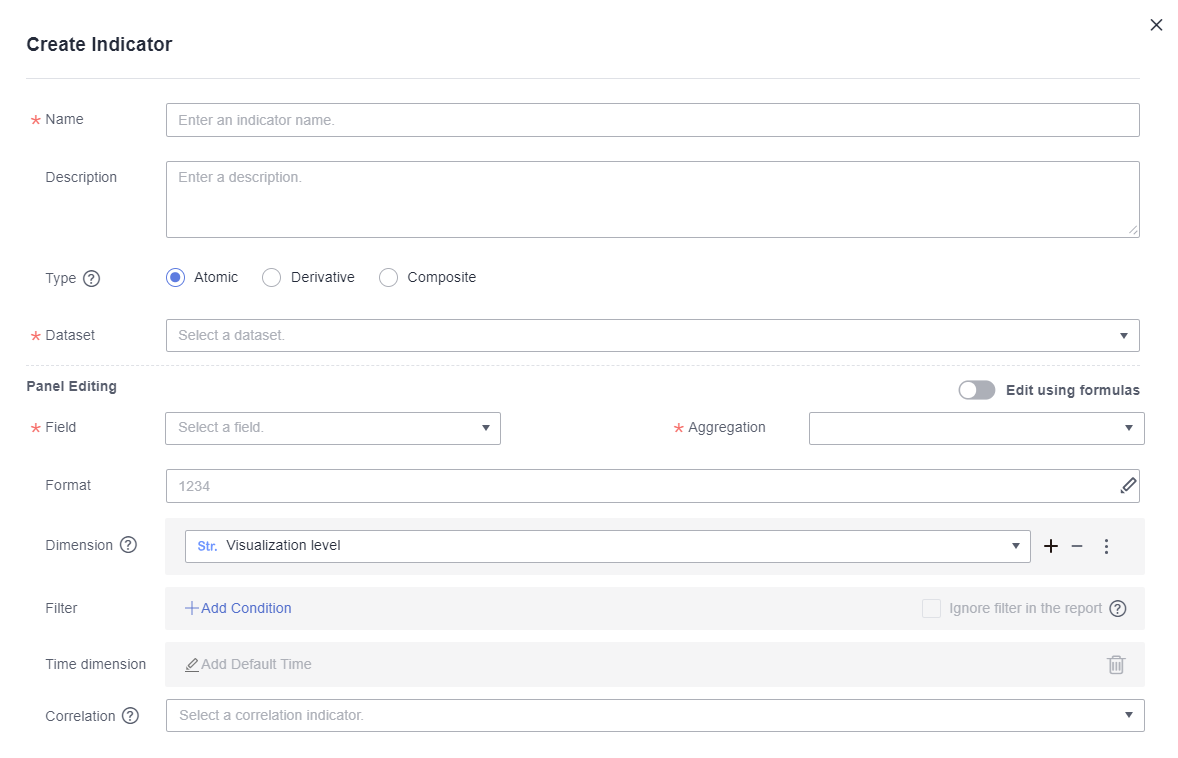
- Set the parameters based on Table 1 and click OK.
Table 1 Parameters for creating an indicator Parameter
Description
Name
Name of the indicator, which is user-defined. Enter a maximum of 512 characters. The following special characters are not supported: <>#=|+@
Description
Description of the indicator.
Type
Atomic indicators are quantitative measures of a product or business performance, such as sales revenue.
Derivative indicators are extensions of a single indicator commonly used to expand indicators over time, such as the sales revenue compared to the previous month.
Composite indicators are based on multiple indicators and defined by input expressions, such as profit = sales revenue – cost.
Dataset
Dataset you want to associate with the indicator.
Field
Dimensions and metrics.
Aggregation
The options include Sum, Average, Count, Distinct count, Maximum, Minimum, Population standard deviation, Sample standard deviation, Population variance, and Sample variance.
Derivative
The options include YoY and PoP growth rate, YoY and PoP growth, Period-to-date, Moving calculation, Cumulative calculation, Ranking, Difference, Difference percentage, and Total percentage.
Format
The options include No format, Numeric, Currency, Object quantifier, Length, Weight, Energy, Capacity, Time, and Percentage.
Dimension
You can select the dimensions from which indicator values are analyzed.
NOTE:If Dimension is set to Visualization level, all dimensions are associated by default.
Filter
It is used to add filter rules.- Click Add Condition.
- Select the filter field, filter type, fixed value filtering condition, and value.
- Filter Field: Filter the dataset fields for which rules need to be set. You can select only one dimension or metric field. To configure rules for other fields, add more conditions.
- Filter Type: Select Condition, Enumeration, or Expression filtering.
- Fixed value filtering condition: The options include Equal to, Not equal to, and more.
- Fixed Value: Enter the value of the filtering condition. For enumeration filtering, select a field value from the drop-down list box.
To set rules for other fields, click Add Condition.
If there are multiple condition rules, set the relationship between the rules.- AND: You can view the field values that meet both rules A and B.
- OR: You can view the field values that meet either rule A or B.
- To add a rule that is parallel to rule A and rule B, click Add Relationship to create a new rule group, rule C. Rule group C is at the same level as rules A and B.
NOTE:
Ignore filter in the report: If there are filters with the same column in the report, selecting this option will ignore filters at the report level. If not selected, it will intersect with filters at the report level.
Time Dimension
The default time filter is a filter that is specifically used to configure the default time for an indicator. Users expect a default time to be automatically displayed when asking about a certain indicator. If this parameter is set, the corresponding dataset must contain a time dimension, otherwise it cannot be set.
NOTE:- Composite and derivative indicators will inherit the time dimension of the atomic indicators.
- The default time filter that is set will take effect in dashboards, large screens, and intelligent analysis Q&A.
- If the time dimension is set for multiple filters at the same time, the priorities of the filters are as follows in descending order: dashboard filter time condition, indicator filter time condition, indicator default time filter, and dataset default filter time condition.
- If a filter is set for the same field in both the dataset and the indicator, the indicator filter will override the dataset filter, meaning that the default filter for the indicator has a higher priority than the default filter for the dataset.
- If filters are set in the dashboard and the intelligent analysis Q&A, the default filter set in the indicator will not take effect.
Correlation
Indicators associated with the new indicator. Once selected from the drop-down menu, the intelligent analysis assistant will recommend related metrics to you during the Q&A session.
Table 2 Date functions Function
Usage
Description
CURRENT_DATE
CURRENT_DATE()
Returns the current date.
CURRENT_TIME
CURRENT_TIME()
Returns the current time.
NOW
NOW()
Return system's current date and time.
UNIX_TIMESTAMP
UNIX_TIMESTAMP()
Returns the current time as a UNIX timestamp.
FROM_UNIXTIME
FROM_UNIXTIME(d)
Converts the time in the UNIX timestamp format to the time in the common format.
MONTH
MONTH(d)
Returns the month value in the date d, ranging from 1 to 12.
DAYOFWEEK
DAYOFWEEK(d)
Calculates the day of the week corresponding to date d.
DAYOFYEAR
DAYOFYEAR(d)
Calculates the day of the year corresponding to date d.
DAYOFMONTH
DAYOFMONTH(d)
Calculates the day of the month corresponding to date d.
QUARTER
QUARTER(d)
Returns the season of date d as a value between 1 and 4.
HOUR
HOUR(t)
Returns the hour value in t.
MINUTE
MINUTE(t)
Returns the minute value in t.
SECOND
SECOND(t)
Returns the second value in t.
DATEDIFF
DATEDIFF(d1,d2)
Calculates the number of days between d1 and d2.
ADDDATE
ADDDATE(d,n)
Calculates the date that is n days after the start date d.
SUBDATE
SUBDATE(d,n)
The date n days before date d.
DATE_FORMAT
DATE_FORMAT(d,f)
Displays the date d as required by expression f.
TIME_FORMAT
TIME_FORMAT(t,f)
Displays the time t as required by expression f.
Table 3 Text functions Function
Usage
Description
CHAR_LENGTH
CHAR_LENGTH(s)
Returns the number of characters in string s.
LENGTH
LENGTH(s)
Returns the length of string s.
CONCAT
CONCAT(s1,s2,...)
Combines multiple strings such as s1 and s2 into one string.
CONCAT_WS
CONCAT_WS(x,s1,s2,...)
Uses the first parameter as the separator, which is associated with all following parameters.
UPPER
UPPER(s)
Converts letters in string s into uppercase letters.
LOWER
LOWER(s)
Converts letters in string s into lowercase letters.
LEFT
LEFT(s,n)
Returns the first n characters of string s.
RIGHT
RIGHT(s,n)
Returns the last n characters of string s.
LPAD
LPAD(s1,len,s2)
Uses string s2 to fill the beginning of s1 so that the string length reaches len.
RPAD
RPAD(s1,len,s2)
Uses string s2 to fill the end of s1 so that the string length reaches len.
LTRIM
LTRIM(s)
Deletes the space at the beginning of the string s.
RTRIM
RTRIM(s)
Deletes the space at the end of the string s.
TRIM
TRIM(s1 FROM s)
Removes the string s and the string s1 at the end.
REPEAT
REPEAT(s,n)
Repeats the string s for n times.
REPLACE
REPLACE(s,s1,s2)
Replaces the string s1 in the string s with the string s2.
SUBSTRING
SUBSTRING(s,n,len)
Obtains a string whose length is len from the nth position in the string s.
LOCATE
LOCATE(s1,s)
Obtains the start position of s1 from the string s.
INSTR
INSTR(s,s1)
Obtains the start position of s1 from the string s.
REVERSE
REVERSE(s)
Reverses the sequence of the string s.
MD5
MD5(str)
You can hash the string str to encrypt data that does not require decryption.
Table 4 Numeric functions Function
Usage
Description
ABS
ABS(x)
Returns the absolute value of x.
CEIL
CEIL(x)
Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to x.
FLOOR
FLOOR(x)
Returns the largest integer less than or equal to x.
RANDOM
RANDOM()
Returns a random number ranging from 0.0 to 1.0.
SIGN
SIGN(x)
Returns the sign of x, which is either -1, 0, or 1 depending on whether x is negative, zero, or positive.
PI
PI()
Returns pi.
TRUNC
TRUNC(x, y)
Returns the value of x rounded to y decimal places.
ROUND
ROUND(x)
Returns the value of x rounded to y decimal places, with any truncated part being rounded off.
POWER
POWER(x,y)
Returns the value of x raised to the power of y.
SQRT
SQRT(x)
Returns the square root of x.
EXP
EXP(x)
Returns the value of e raised to the power of x.
MOD
MOD(x,y)
Returns the remainder when x is divided by y.
LOG
LOG(x)
In the ORA- or TD-compatible mode, this operator means the logarithm with 10 as the base. In the MySQL-compatible mode, this operator means the natural logarithm.
RADIANS
RADIANS(x)
Converts the angle to a radian.
DEGREES
DEGREES(x)
Converts the radian to an angle.
SIN
SIN(x)
Calculates the sine value given in radians.
ASIN
ASIN(x)
Calculates the arc sine value given in radians.
COS
COS(x)
Calculates the cosine value given in radians.
ACOS
ACOS(x)
Calculates the arc cosine value given in radians.
TAN
TAN(x)
Calculates the tangent value given in radians.
ATAN
ATAN(x)
Calculates the arc tangent value given in radians.
COT
COT(x)
Calculates the cotangent value given in radians.
Table 5 Window functions Function
Usage
Description
RANK_WINDOWS
RANK() OVER (PARTITIONBY expr1 ORDER BY expr2)
The RANK function is used for generating non-consecutive sequence numbers for the values in each group. The same values have the same sequence number.
ROW_NUMBER_WINDOWS
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY expr1 ORDER BY expr2)
The ROW_NUMBER function is used for generating consecutive sequence numbers for the values in each group. The same values have different sequence numbers.
AGG_WINDOWS
agg_func(x) OVER(PARTITION BY expr1 ORDER BY expr2)
agg_fun(x) is an aggregate function, for example, sum(x) and arg(x).
Table 6 Aggregate functions Function
Usage
Description
AVG
AVG(x)
Returns the average value in the column x.
COUNT
COUNT(x)
Returns the number of non-null values in the column x.
MAX
MAX(x)
Returns the largest value of the column x.
MIN
MIN(x)
Returns the smallest value of the column x.
SUM
SUM(x)
Returns the sum of the values in column x.
VAR_POP
VAR_POP(x)
Returns the population variance in the column x.
VAR_SAMP
VAR_SAMP(x)
Returns the sample variance in the column x.
STDDEV_SAMP
STDDEV_SAMP(x)
Returns the standard deviation of samples in the column x.
STDDEV_POP
STDDEV_POP(x)
Returns the population standard deviation in the column x.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





