Managing OpenSearch Cluster Logs
CSS provides log query, log backup, and log ingestion, enabling you to easily manage and analyze logs to efficiently locate faults, optimize performance, and enhance system security.
- Log query: On the log management page of the CSS management console, you can query the latest log records by node, log type, and other criteria, so you can quickly locate or diagnose issues.
- Log backup: Cluster logs are periodically synchronized to OBS buckets. You can download them for in-depth analysis at any time. You can configure custom log backup policies by specifying backup schedules and storage locations. The system backs up all critical logs, including run logs, slow query logs, and deprecation logs. They provide comprehensive data for auditing and troubleshooting purposes.
- Log ingestion: Cluster logs are transmitted in real time to the current cluster or another cluster on the same network. (Certain version and network compatibility requirements must be met.) You can use OpenSearch Dashboards or other visualization tools for log search and analysis. You can also set index prefixes and retention periods to flexibly manage the log lifecycle. Logs can be transferred across clusters, facilitating centralized monitoring in a multi-cluster environment.
Impact on Billing
When log backup is enabled, the generated log backups are stored in OBS buckets, which will result in additional costs. For details, see Object Storage Service Billing.
Prerequisites
The OBS bucket used for storing log backups has been created. The OBS bucket must meet the following requirements:
- Storage Class: Standard.
- Region: the same as that of the cluster.
Log Search
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Choose Logs > Log Search. The Log Search page is displayed.
You can search records by log type, node, log level, or keyword. For a detailed description of each type of logs, see Log Introduction.
When a log file reaches 128 MB or when the time reaches 00:00 UTC, the system automatically compresses and archives it. Only unarchived logs appear on the log search page, while archived logs remain accessible through the log backup function.
Log Backup
Cluster logs can be backed up to OBS buckets, where you can download them for in-depth analysis at any time.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Choose Logs > Log Backup. The Log Backup page is displayed.
- Enable log backup.
- Back up logs. Two options are available: automatic or manual.
- Check the backed-up log files.
Logs are backed up incrementally. After the backup is successful, you can access the target OBS bucket to obtain the full log files by clicking Log Path.
Figure 3 OBS bucket address
Table 3 lists the log types, where clustername indicates the cluster name.
- If the log backup function is no longer needed, you can disable it.
On the Log Backup page, click Disable Backup. In the displayed dialog box, click OK. Disabling log backup does not automatically delete existing log backups. Instead, you need to manually delete them on the OBS console.
Log Ingestion
With log ingestion, you can store the real-time logs of a cluster in itself or a different cluster on the same network, facilitating log search and analytics using OpenSearch Dashboards.
Log ingestion is supported only when the OpenSearch cluster version is 1.3.6 or 2.19.0 and the image version is no earlier than x.x.x_24.2.0_x.x.x.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Choose Logs > Log Ingestion. The Log Ingestion page is displayed.

If the Log Ingestion tab is not displayed, the cluster does not support log ingestion.
- Enable log ingestion. If it is already enabled, skip this step.
- Click Enable Log Ingestion. In the displayed dialog box, configure necessary settings.
Table 4 Log ingestion settings Parameter
Description
Index Prefix Name
If you set a prefix for the log file indexes, the log index names will use the format index prefix name + log ingestion date. The unit of log ingestion is days.
An index prefix name is a string of 1 to 128 characters. It can contain only digits, lowercase letters, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
Retention Period
Set the log retention period. Ingested logs will be deleted upon expiration of this period.
Value range: 1 to 3650
Unit: days
Log Storage Cluster
Select a cluster to store ingested logs. Options include Current cluster and Other clusters.
- Current cluster: Store ingested logs in the current cluster.
- Other clusters: Store ingested logs in another cluster.
Select a cluster from the Cluster drop-down list to use as the log storage destination. Make sure this cluster is in the same VPC and have the same version as the current cluster.
When you select another cluster, click Check to verify network connectivity between the current cluster and the selected other cluster. Log ingestion can start only when "The current cluster is available" is displayed.
- Click OK to enable log ingestion.
The configuration information will be displayed on the Log Ingestion tab.
- Click Enable Log Ingestion. In the displayed dialog box, configure necessary settings.
- View ingested logs.
If the task status changes to Running, log ingestion has started.
Figure 4 Viewing ingested logs
- Click Dashboards to log in to the target cluster and check the logs.
- Click the cluster name at Log Storage Cluster to go to the cluster details page.
- If you no longer need the log ingestion function, you can disable it to reclaim storage resources.
On the Log Ingestion page, click Disable Log Ingestion. In the displayed dialog box, click OK. Disabling log ingestion does not automatically remove ingested log data. Rather, it will be deleted by the system upon expiration of their retention period. You can also manually delete it from the target cluster before the retention period expires.
Log Introduction
|
Log Type |
Description |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
Run logs |
Run logs, or main logs, record the cluster status and key information about write and query operations. For example, write logs record operations such as index creation, index mapping update, and write queue exhaustion; and query logs record query queue status and query exceptions. |
Check the status and write and query operations of each cluster node, including inter-node connectivity, full GC, index creation or deletion, and cluster-level query errors. |
|
Slow indexing logs |
Slow indexing logs record indexing operations (such as bulk, index, update, and delete) that took a long time to complete, helping you identify performance bottlenecks. |
In the case of slow write performance, you can query slow indexing logs to locate the cause. |
|
Slow query logs |
Slow query logs record search requests that took a long time to complete. They help you monitor and analyze time-consuming search requests, so you can identify performance bottlenecks, optimize SQL queries, and improve overall system performance. |
In the case of slow query performance, you can query slow query logs to locate the cause. |
|
Deprecation logs |
Deprecation logs record deprecation warnings. Deprecation warnings are written to this log when you use APIs, configurations, or functions that are marked for removal in future versions. |
Check for APIs or features that are about to expire in future versions. |
|
Access logs |
Access logs record cluster access requests, such as the request path and source address. You cannot check access logs on the console. To check them, you need to back them up to an OBS bucket or transfer them to a target cluster first. |
If there is a surge in service requests, you can analyze the request sources and paths by checking the access logs. |
- Run log description
Run logs record the cluster status and key information about write and query operations. For example, the log record below indicates that an index named test was created and afterwards the cluster status changed from YELLOW to GREEN.
Figure 5 Run log sample Log content:
Log content:- 1. Log generation time
- 2. Log level, which can be DEBUG, INFO, WARN, or ERROR
- 3. Log-generating module
- 4. Name of the log-generating node
- 5. Log content
- Slow indexing log description
Slow indexing logs record indexing operations that took a long time to complete. For example, the log record below shows an indexing request that lasted longer than the preset threshold. The log contains the index name, duration, and request content.
Figure 6 Slow indexing log sample
- Slow query log description
Slow query logs record search requests that took a long time to complete. For example, the log record below shows a search request that lasted longer than the preset threshold. The log contains the index name, duration, and request content.
Figure 7 Slow query log sample Log content:
Log content:- 1. Log generation time
- 2. Log level, which can be DEBUG, INFO, WARN, or ERROR
- 3. Log-generating module
- 4. Name of the log-generating node
- 5. Index name and shard ID
- 6. Log content. In this example, the log recorded the query duration, number of hits, and query request body.
- Deprecation log description
Deprecation logs record deprecation warnings. For example, the log record below indicates that GET /_cat/master has been deprecated and should be replaced with GET /_cat/cluster_manager.
Figure 8 Deprecation log sample Log content:
Log content:- 1. Log generation time
- 2. Log level, which can only be DEPRECATION.
- 3. Log-generating module
- 4. Name of the log-generating node
- 5. Log content
- Access log description
Access logs record cluster access requests and source addresses. For example, the log record below has recorded source information for the /_snapshot/my_backup/my_snapshot/_restore?pretty=true operation.
Figure 9 Access log sample Log content:
Log content:- 1. Log generation time
- 2. Name of the log-generating node
- 3. Name of the log-generating thread
- 4. Log level, which can be DEBUG, INFO, WARN, or ERROR
- 5. Log request method
- 6. Request path
- 7. Source and destination addresses of the request
FAQ: How Do I Change Log Levels?
Log4j2 is used as the log component in OpenSearch clusters. Multiple log levels (ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, and TRACE) are supported. The default log level is INFO. To facilitate troubleshooting and debugging, you can dynamically adjust the log levels.
- INFO is the default log level. The levels, in order of increasing detail, are: ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, and TRACE. When INFO is set, you will see logs for itself and all higher-severity levels (ERROR and WARN), while more verbose levels (DEBUG and TRACE) are excluded.
- You can change the log level of a specified module in real time via an OpenSearch API.
Example
- Log in to OpenSearch Dashboards and go to the command execution page. OpenSearch clusters support multiple access methods. This topic uses OpenSearch Dashboards as an example to describe the operation procedures.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and click Dashboards in the Operation column to log in to OpenSearch Dashboards.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Dev Tools.
The left part of the console is the command input box, and the triangle icon in its upper-right corner is the execution button. The right part shows the execution result.
- Run the following command to change the log level of the action module to DEBUG:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent": { "logger": { "org.opensearch.action": "DEBUG" } } } - Run the following command to restore the default log level INFO:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent": { "logger": { "org.opensearch.action": null } } }
FAQ: How Do I Enable Trace Logging?
To facilitate troubleshooting, debugging, and performance analysis, you may enable trace logging for the HTTP/Transport module and view detailed trace logs.
Enabling trace logging is a non-persistent configuration and will be disabled upon a cluster restart.
Operation Guide
- Log in to OpenSearch Dashboards and go to the command execution page. OpenSearch clusters support multiple access methods. This topic uses OpenSearch Dashboards as an example to describe the operation procedures.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and click Dashboards in the Operation column to log in to OpenSearch Dashboards.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Dev Tools.
The left part of the console is the command input box, and the triangle icon in its upper-right corner is the execution button. The right part shows the execution result.
- Run the following command to enable trace logging:
PUT _cluster/settings { "transient": { "logger.org.opensearch.transport.TransportService.tracer": "trace", "transport.tracer.include": "", "http.tracer.include": "", "logger.org.opensearch.http.HttpTracer": "trace" } } - Go to the log details page to view trace logs.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Choose Logs > Log Search. The Log Search page is displayed.
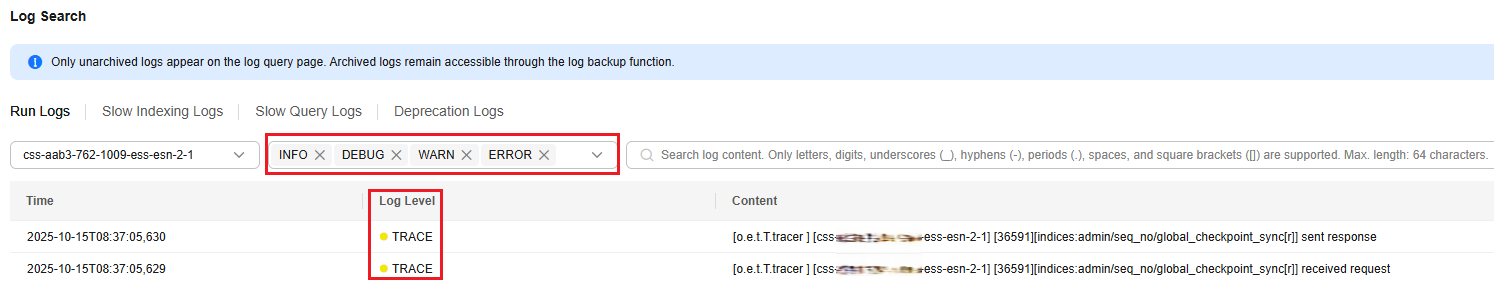
- Select all log levels (mandatory) and view trace logs.
Figure 10 Viewing trace logs
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot